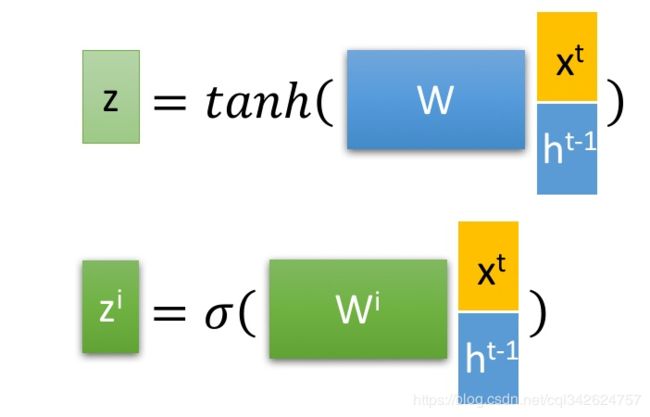RNN LSTM GRU介绍
文章目录
- RNN
- LSTM
- GRU
RNN
在实际应用中,我们会遇到很多序列形的数据
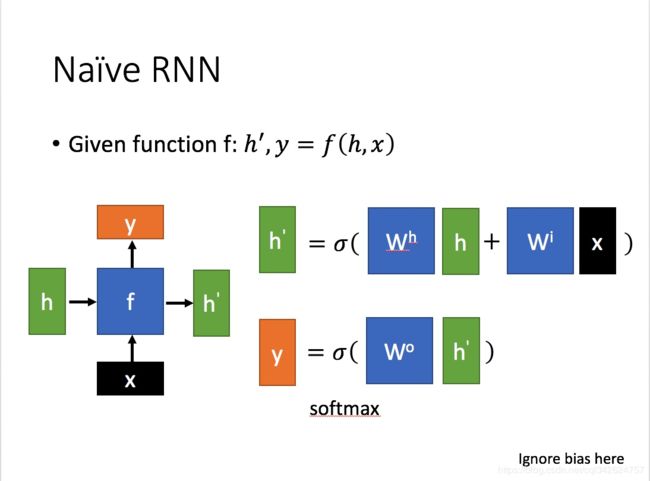
为了建模序列问题,RNN引入了隐状态h(hidden state)的概念,h可以对序列形的数据提取特征,接着再转换为输出。

每一步使用的参数U、W、b都是一样的,也就是说每个步骤的参数都是共享的,这是RNN的重要特点
class BasicRNNCell(RNNCell):
"""The most basic RNN cell.
Args:
num_units: int, The number of units in the RNN cell.
activation: Nonlinearity to use. Default: `tanh`.
reuse: (optional) Python boolean describing whether to reuse variables
in an existing scope. If not `True`, and the existing scope already has
the given variables, an error is raised.
"""
def __init__(self, num_units, activation=None, reuse=None):
super(BasicRNNCell, self).__init__(_reuse=reuse)
self._num_units = num_units
self._activation = activation or math_ops.tanh
self._linear = None
@property
def state_size(self):
return self._num_units
@property
def output_size(self):
return self._num_units
def call(self, inputs, state):
"""Most basic RNN: output = new_state = act(W * input + U * state + B)."""
if self._linear is None:
self._linear = _Linear([inputs, state], self._num_units, True)
output = self._activation(self._linear([inputs, state]))
return output, output
LSTM
长短期记忆(Long short-term memory, LSTM)是一种特殊的RNN,主要是为了解决长序列训练过程中的梯度消失和梯度爆炸问题。简单来说,就是相比普通的RNN,LSTM能够在更长的序列中有更好的表现。

相比RNN只有一个传递状态ht ,LSTM有两个传输状态,一个 Ct(cell state),和一个 Ht(hidden state)。(Tips:RNN中的 ht对于LSTM中的 ht)
其中对于传递下去的Ct改变得很慢,通常输出的Ct 是上一个状态传过来的 Ct-1 加上一些数值。
而 ht 则在不同节点下往往会有很大的区别。
三阶段:
-
忘记阶段: 具体来说是通过计算得到的zf(f表示forget)来作为忘记门控,来控制上一个状态的 [公式] 哪些需要留哪些需要忘。
-
选择记忆阶段: 这个阶段将这个阶段的输入有选择性地进行“记忆”。主要是会对输入Xt 进行选择记忆。哪些重要则着重记录下来,哪些不重要,则少记一些。当前的输入内容由前面计算得到的Z 表示。而选择的门控信号则是由 zi (i代表information)来进行控制
将上面两步得到的结果相加,即可得到传输给下一个状态的 ct 。也就是上图中的第一个公式。 -
输出阶段。
输出阶段。这个阶段将决定哪些将会被当成当前状态的输出。主要是通过 zo 来进行控制的。并且还对上一阶段得到的ct进行了放缩(通过一个tanh激活函数进行变化)。
引入了很多内容,导致参数变多,也使得训练难度加大了很多。因此很多时候我们往往会使用效果和LSTM相当但参数更少的GRU来构建大训练量的模型
def call(self, inputs, state):
"""Long short-term memory cell (LSTM).
Args:
inputs: `2-D` tensor with shape `[batch_size x input_size]`.
state: An `LSTMStateTuple` of state tensors, each shaped
`[batch_size x self.state_size]`, if `state_is_tuple` has been set to
`True`. Otherwise, a `Tensor` shaped
`[batch_size x 2 * self.state_size]`.
Returns:
A pair containing the new hidden state, and the new state (either a
`LSTMStateTuple` or a concatenated state, depending on
`state_is_tuple`).
"""
sigmoid = math_ops.sigmoid
# Parameters of gates are concatenated into one multiply for efficiency.
if self._state_is_tuple:
c, h = state
else:
c, h = array_ops.split(value=state, num_or_size_splits=2, axis=1)
if self._linear is None:
self._linear = _Linear([inputs, h], 4 * self._num_units, True)
# i = input_gate, j = new_input, f = forget_gate, o = output_gate
i, j, f, o = array_ops.split(
value=self._linear([inputs, h]), num_or_size_splits=4, axis=1)
new_c = (
c * sigmoid(f + self._forget_bias) + sigmoid(i) * self._activation(j))
new_h = self._activation(new_c) * sigmoid(o)
if self._state_is_tuple:
new_state = LSTMStateTuple(new_c, new_h)
else:
new_state = array_ops.concat([new_c, new_h], 1)
return new_h, new_state
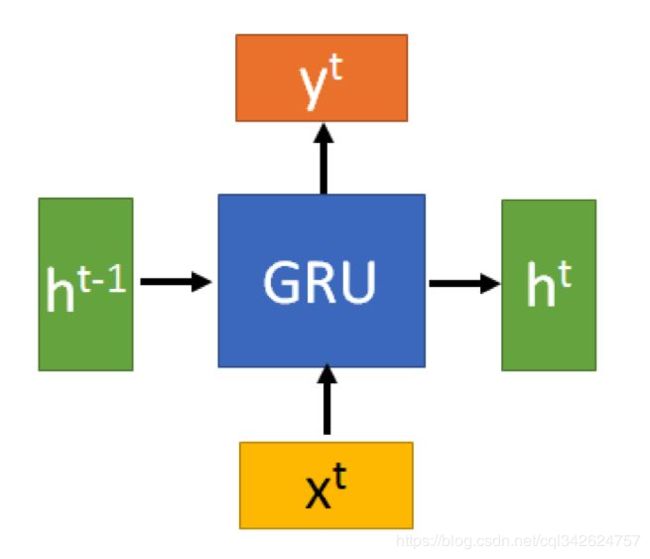
GRU
GRU更容易进行训练
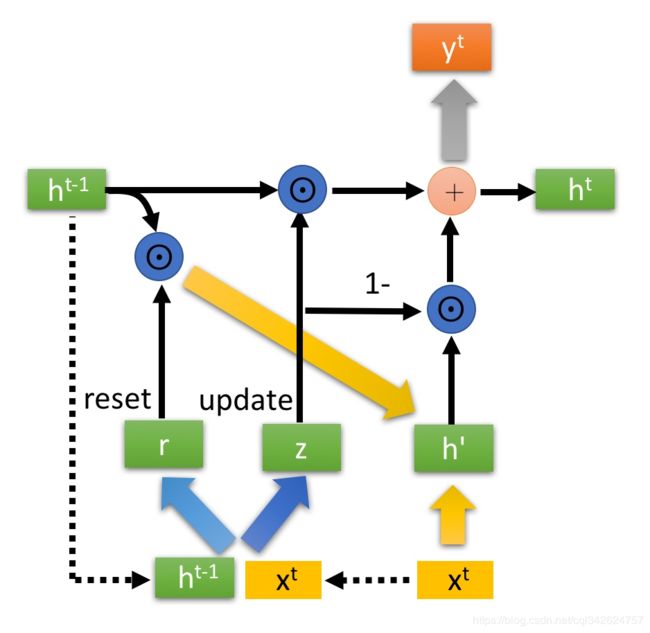
GRU的输入输出结构与普通的RNN是一样的。GRU只有两个门控
有一个当前的输入Xt ,和上一个节点传递下来的隐状态(hidden state) Ht,这个隐状态包含了之前节点的相关信息。
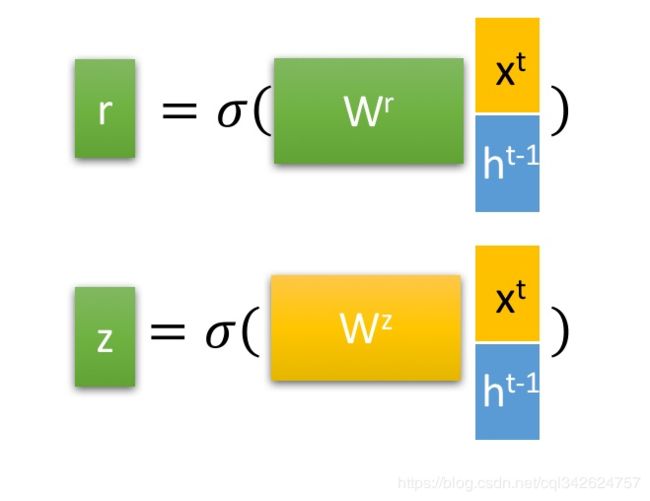
- 选择记忆阶段:
首先使用重置门控来得到“重置”之后的数据:h(t-1)’= h(t-1) r
再和Xt拼接后用tanh缩放得到当前输入 - 更新阶段:
ht = z 。h(t-1) + (1-z) . h’
z越大代表记忆下来的越多,z越小代表遗忘的越多
使用了同一个门控 [公式] 就同时可以进行遗忘和选择记忆(LSTM则要使用多个门控)
class GRUCell(RNNCell):
"""Gated Recurrent Unit cell (cf. http://arxiv.org/abs/1406.1078).
Args:
num_units: int, The number of units in the GRU cell.
activation: Nonlinearity to use. Default: `tanh`.
reuse: (optional) Python boolean describing whether to reuse variables
in an existing scope. If not `True`, and the existing scope already has
the given variables, an error is raised.
kernel_initializer: (optional) The initializer to use for the weight and
projection matrices.
bias_initializer: (optional) The initializer to use for the bias.
"""
def __init__(self,
num_units,
activation=None,
reuse=None,
kernel_initializer=None,
bias_initializer=None):
super(GRUCell, self).__init__(_reuse=reuse)
self._num_units = num_units
self._activation = activation or math_ops.tanh
self._kernel_initializer = kernel_initializer
self._bias_initializer = bias_initializer
self._gate_linear = None
self._candidate_linear = None
@property
def state_size(self):
return self._num_units
@property
def output_size(self):
return self._num_units
def call(self, inputs, state):
"""Gated recurrent unit (GRU) with nunits cells."""
if self._gate_linear is None:
bias_ones = self._bias_initializer
if self._bias_initializer is None:
bias_ones = init_ops.constant_initializer(1.0, dtype=inputs.dtype)
with vs.variable_scope("gates"): # Reset gate and update gate.
self._gate_linear = _Linear(
[inputs, state],
2 * self._num_units,
True,
bias_initializer=bias_ones,
kernel_initializer=self._kernel_initializer)
value = math_ops.sigmoid(self._gate_linear([inputs, state]))
r, u = array_ops.split(value=value, num_or_size_splits=2, axis=1)
r_state = r * state
if self._candidate_linear is None:
with vs.variable_scope("candidate"):
self._candidate_linear = _Linear(
[inputs, r_state],
self._num_units,
True,
bias_initializer=self._bias_initializer,
kernel_initializer=self._kernel_initializer)
c = self._activation(self._candidate_linear([inputs, r_state]))
new_h = u * state + (1 - u) * c
return new_h, new_h