双目测距理论及其python实现!
一、双目测距基本流程
stereo vision, 也叫双目立体视觉,它的研究可以帮助我们更好的理解人类的双眼是如何进行深度感知的。双目视觉在许多领域得到了应用,例如城市三维重建、3D模型构建(kinect fusion)、视角合成、3D跟踪、机器人导航(自动驾驶)、人类运动捕捉(Microsoft Kinect)等等。双目测距也属于双目立体视觉的一个应用领域,双目测距的基本原理主要是三角测量原理,即通过视差来判定物体的远近。为了对双目测距的内容有一个很好的认识大家可以先看一下这个博客,讲的挺的不错的:https://blog.csdn.net/piaoxuezhong/article/details/79016615。当然如果你想深入研究,建议去看《计算机视觉中的多视图几何》,这本书的优点是内容全面,每一个定理都给出了严格的数学证明,缺点就是内容太多了,而且难度非常高,读起来更像是在看一本数学书。
那么总结起来,双目测距的大致流程就是:
双目标定 --> 立体校正(含消除畸变) --> 立体匹配 --> 视差计算 --> 深度计算/3D坐标计算
下面分别阐述每一个步骤并使用opencv-python来实现。
linux下安装opencv-python:
pip install opencv-python二、双目标定
双目标定的目标是获得左右两个相机的内参、外参和畸变系数,其中内参包括左右相机的fx,fy,cx,cy,外参包括左相机相对于右相机的旋转矩阵和平移向量,畸变系数包括径向畸变系数(k1, k2,k3)和切向畸变系数(p1,p2)。关于双目相机的标定方法,请参考这篇博客:双目相机的标定过程详解!-----MATLAB
import cv2
import numpy
import stereoconfig
class stereoCameraCalibration():
pass三、畸变校正
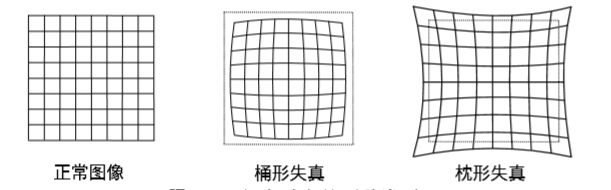
光线经过相机的光学系统往往不能按照理想的情况投射到传感器上,也就是会产生所谓的畸变。畸变有两种情况:一种是由透镜形状引起的畸变称之为径向畸变。在针孔模型中,一条直线投影到像素平面上 还是一条直线。可是,在实际拍摄的照片中,摄像机的透镜往往使得真实环境中的一条直 线在图片中变成了曲线¬。越靠近图像的边缘,这种现象越明显。由于实际加工制作的透镜 往往是中心对称的,这使得不规则的畸变通常径向对称。它们主要分为两大类,桶形畸变 和 枕形畸变(摘自《SLAM十四讲》)如图所示:
桶形畸变是由于图像放大率随着离光轴的距离增加而减小,而枕形畸变却恰好相反。 在这两种畸变中,穿过图像中心和光轴有交点的直线还能保持形状不变。
除了透镜的形状会引入径向畸变外,在相机的组装过程中由于不能使得透镜和成像面 严格平行也会引入切向畸变。如图所示:
那么消除畸变的方法就是:
1. 将三维空间点投影到归一化图像平面。设它的归一化坐标为 [x,y]T
2. 对归一化平面上的点进行径向畸变和切向畸变纠正。
3. 将纠正后的点通过内参数矩阵投影到像素平面,得到该点在图像上的正确位置
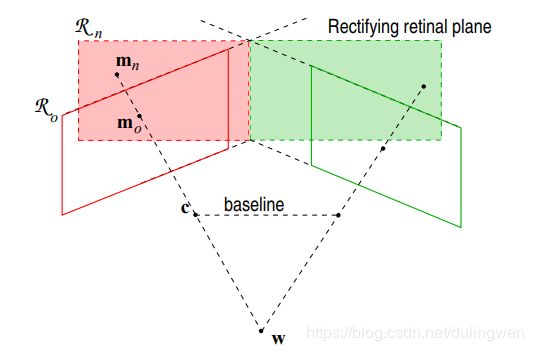
四、立体校正
立体校正的目的是将拍摄于同一场景的左右两个视图进行数学上的投影变换,使得两个成像平面平行于基线,且同一个点在左右两幅图中位于同一行,简称共面行对准。只有达到共面行对准以后才可以应用三角原理计算距离。
五、立体匹配与视差图计算
立体匹配的目的是为左图中的每一个像素点在右图中找到其对应点(世界中相同的物理点),这样就可以计算出视差: ![]() ,在视觉领域,视差disparity有时也被称为inverse depth,因此disparity和inverse depth指的是同一件东西。大部分立体匹配算法的计算过程可以分成以下几个阶段:匹配代价计算、代价聚合、视差优化、视差细化。立体匹配是立体视觉中一个很难的部分,主要困难在于:1.图像中可能存在重复纹理和弱纹理,这些区域很难匹配正确;2.由于左右相机的拍摄位置不同,图像中几乎必然存在遮挡区域,在遮挡区域,左图中有一些像素点在右图中并没有对应的点,反之亦然;3.左右相机所接收的光照情况不同;4.过度曝光区域难以匹配;5.倾斜表面、弯曲表面、非朗伯体表面;6.较高的图像噪声等。
,在视觉领域,视差disparity有时也被称为inverse depth,因此disparity和inverse depth指的是同一件东西。大部分立体匹配算法的计算过程可以分成以下几个阶段:匹配代价计算、代价聚合、视差优化、视差细化。立体匹配是立体视觉中一个很难的部分,主要困难在于:1.图像中可能存在重复纹理和弱纹理,这些区域很难匹配正确;2.由于左右相机的拍摄位置不同,图像中几乎必然存在遮挡区域,在遮挡区域,左图中有一些像素点在右图中并没有对应的点,反之亦然;3.左右相机所接收的光照情况不同;4.过度曝光区域难以匹配;5.倾斜表面、弯曲表面、非朗伯体表面;6.较高的图像噪声等。
常用的立体匹配方法基本上可以分为两类:局部方法,例如BM、SGM、ELAS、Patch Match等,非局部的,即全局方法,例如Dynamic Programming、Graph Cut、Belief Propagation等,局部方法计算量小,匹配质量相对较低,全局方法省略了代价聚合而采用了优化能量函数的方法,匹配质量较高,但是计算量也比较大。目前OpenCV中已经实现的方法有BM、binaryBM、SGBM、binarySGBM、BM(cuda)、Bellief Propogation(cuda)、Constant Space Bellief Propogation(cuda)这几种方法。比较好用的是SGBM算法,它的核心是基于SGM算法,但和SGM算法又有一些不同,比如匹配代价部分用的是BT代价(原图+梯度图)而不是HMI代价等等。有关SGM算法的原理解释,可以参考另一篇博客 : 双目立体匹配算法:SGM
此外还可以对视差图进行滤波后处理,比较常用的方法有Guided Filter、Fast Global Smooth Filter(一种快速WLS滤波方法)、Bilatera Filter、TDSR、RBS等,可以在一定程度上降低噪声,改善视差图的视觉效果,并能够进行稀疏视差插值,不过比较依赖于初始的匹配结果的好坏。
六、深度图计算
得到了视差图之后,就可以计算像素深度了,公式如下(推导略):
其中 f 为焦距长度(像素焦距),b为基线长度,d为视差。
七、双目测距的精度
双目测距的精度是很难进行理论分析的,需要根据实际情况去验证。一般来说,距离越远,误差越大,因此双目测距不适宜测量太远的目标。如果想要对与较远的目标能够得到较为可靠的深度,需要提高相机的基线距离,但是同时会导致左右视图的差异变大从而提高立体匹配的难度。
八、代码实现
最重要的就是代码了,不是么!
首先需要引入相应的包:
import cv2
import numpy as np然后:
# 预处理
def preprocess(img1, img2):
# 彩色图->灰度图
im1 = cv2.cvtColor(img1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
im2 = cv2.cvtColor(img2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 直方图均衡
im1 = cv2.equalizeHist(im1)
im2 = cv2.equalizeHist(im2)
return im1, im2
# 消除畸变
def undistortion(image, camera_matrix, dist_coeff):
undistortion_image = cv2.undistort(image, camera_matrix, dist_coeff)
return undistortion_image
# 获取畸变校正和立体校正的映射变换矩阵、重投影矩阵
# @param:config是一个类,存储着双目标定的参数:config = stereoconfig.stereoCamera()
def getRectifyTransform(height, width, config):
# 读取内参和外参
left_K = config.cam_matrix_left
right_K = config.cam_matrix_right
left_distortion = config.distortion_l
right_distortion = config.distortion_r
R = config.R
T = config.T
# 计算校正变换
height = int(height)
width = int(width)
R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, roi1, roi2 = cv2.stereoRectify(left_K, left_distortion, right_K, right_distortion, (width, height), R, T, alpha=0)
map1x, map1y = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(left_K, left_distortion, R1, P1, (width, height), cv2.CV_32FC1)
map2x, map2y = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(right_K, right_distortion, R2, P2, (width, height), cv2.CV_32FC1)
return map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y, Q
# 畸变校正和立体校正
def rectifyImage(image1, image2, map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y):
rectifyed_img1 = cv2.remap(image1, map1x, map1y, cv2.INTER_AREA)
rectifyed_img2 = cv2.remap(image2, map2x, map2y, cv2.INTER_AREA)
return rectifyed_img1, rectifyed_img2
# 立体校正检验----画线
def draw_line(image1, image2):
# 建立输出图像
height = max(image1.shape[0], image2.shape[0])
width = image1.shape[1] + image2.shape[1]
output = np.zeros((height, width, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
output[0:image1.shape[0], 0:image1.shape[1]] = image1
output[0:image2.shape[0], image1.shape[1]:] = image2
for k in range(15):
cv2.line(output, (0, 50 * (k + 1)), (2 * width, 50 * (k + 1)), (0, 255, 0), thickness=2, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA) # 直线间隔:100
return output
# 视差计算
def disparity_SGBM(left_image, right_image, down_scale=False):
# SGBM匹配参数设置
if left_image.ndim == 2:
img_channels = 1
else:
img_channels = 3
blockSize = 3
param = {'minDisparity': 0,
'numDisparities': 128,
'blockSize': blockSize,
'P1': 8 * img_channels * blockSize ** 2,
'P2': 32 * img_channels * blockSize ** 2,
'disp12MaxDiff': 1,
'preFilterCap': 63,
'uniquenessRatio': 15,
'speckleWindowSize': 100,
'speckleRange': 1,
'mode': cv2.STEREO_SGBM_MODE_SGBM_3WAY
}
# 构建SGBM对象
sgbm = cv2.StereoSGBM_create(**param)
# 计算视差图
size = (left_image.shape[1], left_image.shape[0])
if down_scale == False:
disparity_left = sgbm.compute(left_image, right_image)
disparity_right = sgbm.compute(right_image, left_image)
else:
left_image_down = cv2.pyrDown(left_image)
right_image_down = cv2.pyrDown(right_image)
factor = size[0] / left_image_down.shape[1]
disparity_left_half = sgbm.compute(left_image_down, right_image_down)
disparity_right_half = sgbm.compute(right_image_down, left_image_down)
disparity_left = cv2.resize(disparity_left_half, size, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
disparity_right = cv2.resize(disparity_right_half, size, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
disparity_left *= factor
disparity_right *= factor
return disparity_left, disparity_rightstereoconfig.py的代码:
import numpy as np
####################仅仅是一个示例###################################
# 双目相机参数
class stereoCamera1(object):
def __init__(self):
# 左相机内参
self.cam_matrix_left = np.array([[1499.64168081943, 0, 1097.61651199043],
[0., 1497.98941910377, 772.371510027325],
[0., 0., 1.]])
# 右相机内参
self.cam_matrix_right = np.array([[1494.85561041115, 0, 1067.32184876563],
[0., 1491.89013795616, 777.983913223449],
[0., 0., 1.]])
# 左右相机畸变系数:[k1, k2, p1, p2, k3]
self.distortion_l = np.array([[-0.110331619900584, 0.0789239541458329, -0.000417147132750895, 0.00171210128855920, -0.00959533143245654]])
self.distortion_r = np.array([[-0.106539730103100, 0.0793246026401067, -0.000288067586478778, -8.92638488356863e-06, -0.0161669384831612]])
# 旋转矩阵
self.R = np.array([[0.993995723217419, 0.0165647819554691, 0.108157802419652],
[-0.0157381345263306, 0.999840084288358, -0.00849217121126161],
[-0.108281177252152, 0.00673897982027135, 0.994097466450785]])
# 平移矩阵
self.T = np.array([[-423.716923177417], [2.56178287450396], [21.9734621041330]])
# 焦距
self.focal_length = 1602.46406 # 默认值,一般取立体校正后的重投影矩阵Q中的 Q[2,3]
# 基线距离
self.baseline = 423.716923177417 # 单位:mm, 为平移向量的第一个参数(取绝对值)九、构建点云
有了视差便可以计算深度,因此根据双目的视差图可以构建稠密点云,OpenCV中提供了reprojectImageTo3D()这个函数用于计算像素点的三维坐标,该函数会返回一个3通道的矩阵,分别存储X、Y、Z坐标(左摄像机坐标系下)。在python-pcl库中提供了用来显示点云的工具(python-pcl是PCL库的python接口,但是只提供了部分功能,且对点云的各种处理功能只限于PointXYZ格式的点云),python-pcl的下载地址:https://github.com/strawlab/python-pcl,下载好后按步骤安装好。windows平台下的安装可以参考这两个博客:1.Windows10下PCL1.8.1以及Python-pcl1.81环境配置的掉发之路 2.win10平台python-pcl环境搭建
下面是显示点云的代码:
# 将h×w×3数组转换为N×3的数组
def hw3ToN3(points):
height, width = points.shape[0:2]
points_1 = points[:, :, 0].reshape(height * width, 1)
points_2 = points[:, :, 1].reshape(height * width, 1)
points_3 = points[:, :, 2].reshape(height * width, 1)
points_ = np.hstack((points_1, points_2, points_3))
return points_
# 深度、颜色转换为点云
def DepthColor2Cloud(points_3d, colors):
rows, cols = points_3d.shape[0:2]
size = rows * cols
points_ = hw3ToN3(points_3d).astype(np.int16)
colors_ = hw3ToN3(colors).astype(np.int64)
# 颜色信息
blue = colors_[:, 0].reshape(size, 1)
green = colors_[:, 1].reshape(size, 1)
red = colors_[:, 2].reshape(size, 1)
rgb = np.left_shift(blue, 0) + np.left_shift(green, 8) + np.left_shift(red, 16)
# 将坐标+颜色叠加为点云数组
pointcloud = np.hstack((points_, rgb)).astype(np.float32)
# 删掉一些不合适的点
X = pointcloud[:, 0]
Y = pointcloud[:, 1]
Z = pointcloud[:, 2]
remove_idx1 = np.where(Z <= 0)
remove_idx2 = np.where(Z > 15000)
remove_idx3 = np.where(X > 10000)
remove_idx4 = np.where(X < -10000)
remove_idx5 = np.where(Y > 10000)
remove_idx6 = np.where(Y < -10000)
remove_idx = np.hstack((remove_idx1[0], remove_idx2[0], remove_idx3[0], remove_idx4[0], remove_idx5[0], remove_idx6[0]))
pointcloud_1 = np.delete(pointcloud, remove_idx, 0)
return pointcloud_1
# 点云显示
def view_cloud(pointcloud):
cloud = pcl.PointCloud_PointXYZRGBA()
cloud.from_array(pointcloud)
try:
visual = pcl.pcl_visualization.CloudViewing()
visual.ShowColorACloud(cloud)
v = True
while v:
v = not (visual.WasStopped())
except:
pass十、效果图
下面的数据使用的是MiddleBurry双目数据,可以不用做立体校正(因为已经校正过了):
利用SGBM算法得到视差图如下:
各位觉得不错的点个赞吧!
-------------------------------------------------------------------补充完整示例代码------------------------------------------------------------------------------
import cv2
import numpy as np
import time
import stereoconfig
import pcl
import pcl.pcl_visualization
# 预处理
def preprocess(img1, img2):
# 彩色图->灰度图
im1 = cv2.cvtColor(img1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
im2 = cv2.cvtColor(img2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 直方图均衡
im1 = cv2.equalizeHist(im1)
im2 = cv2.equalizeHist(im2)
return im1, im2
# 消除畸变
def undistortion(image, camera_matrix, dist_coeff):
undistortion_image = cv2.undistort(image, camera_matrix, dist_coeff)
return undistortion_image
# 获取畸变校正和立体校正的映射变换矩阵、重投影矩阵
# @param:config是一个类,存储着双目标定的参数:config = stereoconfig.stereoCamera()
def getRectifyTransform(height, width, config):
# 读取内参和外参
left_K = config.cam_matrix_left
right_K = config.cam_matrix_right
left_distortion = config.distortion_l
right_distortion = config.distortion_r
R = config.R
T = config.T
# 计算校正变换
R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, roi1, roi2 = cv2.stereoRectify(left_K, left_distortion, right_K, right_distortion, (width, height), R, T, alpha=0)
map1x, map1y = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(left_K, left_distortion, R1, P1, (width, height), cv2.CV_32FC1)
map2x, map2y = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(right_K, right_distortion, R2, P2, (width, height), cv2.CV_32FC1)
return map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y, Q
# 畸变校正和立体校正
def rectifyImage(image1, image2, map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y):
rectifyed_img1 = cv2.remap(image1, map1x, map1y, cv2.INTER_AREA)
rectifyed_img2 = cv2.remap(image2, map2x, map2y, cv2.INTER_AREA)
return rectifyed_img1, rectifyed_img2
# 立体校正检验----画线
def draw_line(image1, image2):
# 建立输出图像
height = max(image1.shape[0], image2.shape[0])
width = image1.shape[1] + image2.shape[1]
output = np.zeros((height, width, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
output[0:image1.shape[0], 0:image1.shape[1]] = image1
output[0:image2.shape[0], image1.shape[1]:] = image2
for k in range(15):
cv2.line(output, (0, 50 * (k + 1)), (2 * width, 50 * (k + 1)), (0, 255, 0), thickness=2, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA) # 直线间隔:100
return output
# 视差计算
def disparity_SGBM(left_image, right_image, down_scale=False):
# SGBM匹配参数设置
if left_image.ndim == 2:
img_channels = 1
else:
img_channels = 3
blockSize = 3
param = {'minDisparity': 0,
'numDisparities': 128,
'blockSize': blockSize,
'P1': 8 * img_channels * blockSize ** 2,
'P2': 32 * img_channels * blockSize ** 2,
'disp12MaxDiff': 1,
'preFilterCap': 63,
'uniquenessRatio': 15,
'speckleWindowSize': 100,
'speckleRange': 1,
'mode': cv2.STEREO_SGBM_MODE_SGBM_3WAY
}
# 构建SGBM对象
sgbm = cv2.StereoSGBM_create(**param)
# 计算视差图
size = (left_image.shape[1], left_image.shape[0])
if down_scale == False:
disparity_left = sgbm.compute(left_image, right_image)
disparity_right = sgbm.compute(right_image, left_image)
else:
left_image_down = cv2.pyrDown(left_image)
right_image_down = cv2.pyrDown(right_image)
factor = size[0] / left_image_down.shape[1]
disparity_left_half = sgbm.compute(left_image_down, right_image_down)
disparity_right_half = sgbm.compute(right_image_down, left_image_down)
disparity_left = cv2.resize(disparity_left_half, size, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
disparity_right = cv2.resize(disparity_right_half, size, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
disparity_left *= factor
disparity_right *= factor
return disparity_left, disparity_right
# 将h×w×3数组转换为N×3的数组
def hw3ToN3(points):
height, width = points.shape[0:2]
points_1 = points[:, :, 0].reshape(height * width, 1)
points_2 = points[:, :, 1].reshape(height * width, 1)
points_3 = points[:, :, 2].reshape(height * width, 1)
points_ = np.hstack((points_1, points_2, points_3))
return points_
# 深度、颜色转换为点云
def DepthColor2Cloud(points_3d, colors):
rows, cols = points_3d.shape[0:2]
size = rows * cols
points_ = hw3ToN3(points_3d).astype(np.int16)
colors_ = hw3ToN3(colors).astype(np.int64)
# 颜色信息
blue = colors_[:, 0].reshape(size, 1)
green = colors_[:, 1].reshape(size, 1)
red = colors_[:, 2].reshape(size, 1)
rgb = np.left_shift(blue, 0) + np.left_shift(green, 8) + np.left_shift(red, 16)
# 将坐标+颜色叠加为点云数组
pointcloud = np.hstack((points_, rgb)).astype(np.float32)
# 删掉一些不合适的点
X = pointcloud[:, 0]
Y = pointcloud[:, 1]
Z = pointcloud[:, 2]
remove_idx1 = np.where(Z <= 0)
remove_idx2 = np.where(Z > 15000)
remove_idx3 = np.where(X > 10000)
remove_idx4 = np.where(X < -10000)
remove_idx5 = np.where(Y > 10000)
remove_idx6 = np.where(Y < -10000)
remove_idx = np.hstack((remove_idx1[0], remove_idx2[0], remove_idx3[0], remove_idx4[0], remove_idx5[0], remove_idx6[0]))
pointcloud_1 = np.delete(pointcloud, remove_idx, 0)
return pointcloud_1
# 点云显示
def view_cloud(pointcloud):
cloud = pcl.PointCloud_PointXYZRGBA()
cloud.from_array(pointcloud)
try:
visual = pcl.pcl_visualization.CloudViewing()
visual.ShowColorACloud(cloud)
v = True
while v:
v = not (visual.WasStopped())
except:
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 读取MiddleBurry数据集的图片
iml = cv2.imread('/data/数据/MiddleBurry/Adirondack-perfect/im0.png') # 左图
imr = cv2.imread('/data/数据/MiddleBurry/Adirondack-perfect/im1.png') # 右图
height, width = iml.shape[0:2]
# 读取相机内参和外参
config = stereoconfig.stereoCamera()
# 立体校正
map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y, Q= getRectifyTransform(height, width, config) # 获取用于畸变校正和立体校正的映射矩阵以及用于计算像素空间坐标的重投影矩阵
iml_rectified, imr_rectified = rectifyImage(iml, imr, map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y)
# 绘制等间距平行线,检查立体校正的效果
line = draw_line(iml_rectified, imr_rectified)
cv2.imwrite('/data/检验.png', line)
# 立体匹配
iml_, imr_ = preprocess(iml, imr) # 预处理,不做也可以
disp, _ = disparity_SGBM(iml_, imr_) # 这里传入的是未经立体校正的图像,因为我们使用的middleburry图片已经是校正过的了
disp = np.divide(disp.astype(np.float32), 16.) # 除以16得到真实视差(因为SGBM算法得到的视差是×16的)
cv2.imwrite('/data/视差.png', disp)
# 计算像素点的3D坐标(左相机坐标系下)
points_3d = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(disp, Q) # 可以使用上文的stereo_config.py给出的参数
# 构建点云--Point_XYZRGBA格式
pointcloud = DepthColor2Cloud(points_3d, iml)
# 显示点云
view_cloud(pointcloud)
点云如图所示:
参考资料:
SGBM算法详解(一)
SGBM算法详解(二)
双目视觉之空间坐标计算
Stereo disparity quality problems
Disparity map post-filtering
OpenCV Stereo – Depth image generation and filtering
OpenCV+OpenGL 双目立体视觉三维重建