吴恩达作业7:梯度下降优化算法
先说说BatchGD用整个训练样本进行训练得出损失值,SGD是只用一个训练样本训练就得出损失值,GD导致训练慢,SGD导致收敛到最小值不平滑,故引入Mini-batch GD,选取部分样本进行训练得出损失值,
普通梯度下降算法如下:
""""
一般梯度下降算法
"""
def update_parameters_gd(parameters,grads,learning_rate):
L=len(parameters)//2
for i in range(L):
parameters['W'+str(i+1)]=parameters['W'+str(i+1)]-learning_rate*grads['dW'+str(i+1)]
parameters['b' + str(i + 1)] = parameters['b' + str(i + 1)] - learning_rate * grads['db' + str(i + 1)]
return parametersMomentum代码:
"""
Momentum初始化参数
"""
def initialize_Momentum_paremeters(parameters):
L=len(parameters)//2
v={}
for i in range(L):
v['dW'+str(i+1)]=np.zeros(parameters['W'+str(i+1)].shape)
v['db' + str(i + 1)] = np.zeros(parameters['b' + str(i + 1)].shape)
return v
"""
Momentum更新权重
"""
def upate_parameters_Momentum(parameters,grads,v,beta,learning_rate):
L=len(parameters)//2
for i in range(L):
v['dW' + str(i + 1)]=beta*v['dW'+str(i+1)]+(1-beta)*grads['dW'+str(i+1)]
v['db' + str(i + 1)] = beta * v['db' + str(i + 1)] + (1 - beta) * grads['db' + str(i + 1)]
parameters['W'+str(i+1)]=parameters['W'+str(i+1)]-learning_rate*v['dW' + str(i + 1)]
parameters['b' + str(i + 1)] = parameters['b' + str(i + 1)] - learning_rate * v['db' + str(i + 1)]
return parameters,vAdam代码:
"""
Adam初始化参数
"""
def initialize_Adam_parameters(parameters):
L=len(parameters)//2
v={}
s={}
for i in range(L):
v['dW' + str(i + 1)] = np.zeros(parameters['W'+str(i+1)].shape)
v['db' + str(i + 1)] = np.zeros(parameters['b' + str(i + 1)].shape)
s['dW' + str(i + 1)] = np.zeros(parameters['W' + str(i + 1)].shape)
s['db' + str(i + 1)] = np.zeros(parameters['b' + str(i + 1)].shape)
return v,s
"""
Adam更新权重
"""
def update_parameters_Adam(parameters,grads,v,s,t,beta1,beta2,learning_rate,epsilon):
L = len(parameters) // 2
v_correct={}
s_correct = {}
for i in range(L):
v['dW' + str(i + 1)] = beta1 * v['dW' + str(i + 1)] + (1 - beta1) * grads['dW' + str(i + 1)]
v['db' + str(i + 1)] = beta1 * v['db' + str(i + 1)] + (1 - beta1) * grads['db' + str(i + 1)]
v_correct['dW' + str(i + 1)]=v['dW' + str(i + 1)]/(1-beta1**t)
v_correct['db' + str(i + 1)] = v['db' + str(i + 1)] / (1 - beta1 ** t)
s['dW' + str(i + 1)] = beta2 * s['dW' + str(i + 1)] + (1 - beta2) * np.square(grads['dW' + str(i + 1)])
s['db' + str(i + 1)] = beta2 * s['db' + str(i + 1)] + (1 - beta2) * np.square(grads['db' + str(i + 1)])
s_correct['dW' + str(i + 1)] = s['dW' + str(i + 1)] / (1 - beta2 ** t)
s_correct['db' + str(i + 1)] = s['db' + str(i + 1)] / (1 - beta2 ** t)
parameters['W' + str(i + 1)] = parameters['W' + str(i + 1)] - \
learning_rate * (v_correct['dW' + str(i + 1)]/(np.sqrt(s['dW' + str(i + 1)])+epsilon))
parameters['b' + str(i + 1)] = parameters['b' + str(i + 1)] - \
learning_rate * (v_correct['db' + str(i + 1)]/(np.sqrt(s['db' + str(i + 1)])+epsilon))
return parameters, v,s数据集 放在opt_utils.py 代码如下:还包含激活函数 前向传播 后向传播等函数
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import h5py
import scipy.io
import sklearn
import sklearn.datasets
def sigmoid(x):
"""
Compute the sigmoid of x
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array of any size.
Return:
s -- sigmoid(x)
"""
s = 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
return s
def relu(x):
"""
Compute the relu of x
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array of any size.
Return:
s -- relu(x)
"""
s = np.maximum(0,x)
return s
def load_params_and_grads(seed=1):
np.random.seed(seed)
W1 = np.random.randn(2,3)
b1 = np.random.randn(2,1)
W2 = np.random.randn(3,3)
b2 = np.random.randn(3,1)
dW1 = np.random.randn(2,3)
db1 = np.random.randn(2,1)
dW2 = np.random.randn(3,3)
db2 = np.random.randn(3,1)
return W1, b1, W2, b2, dW1, db1, dW2, db2
def initialize_parameters(layer_dims):
"""
Arguments:
layer_dims -- python array (list) containing the dimensions of each layer in our network
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", ..., "WL", "bL":
W1 -- weight matrix of shape (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])
b1 -- bias vector of shape (layer_dims[l], 1)
Wl -- weight matrix of shape (layer_dims[l-1], layer_dims[l])
bl -- bias vector of shape (1, layer_dims[l])
Tips:
- For example: the layer_dims for the "Planar Data classification model" would have been [2,2,1].
This means W1's shape was (2,2), b1 was (1,2), W2 was (2,1) and b2 was (1,1). Now you have to generalize it!
- In the for loop, use parameters['W' + str(l)] to access Wl, where l is the iterative integer.
"""
np.random.seed(3)
parameters = {}
L = len(layer_dims) # number of layers in the network
for l in range(1, L):
parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])* np.sqrt(2 / layer_dims[l-1])
parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l], 1))
assert(parameters['W' + str(l)].shape == layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])
assert(parameters['W' + str(l)].shape == layer_dims[l], 1)
return parameters
def compute_cost(a3, Y):
"""
Implement the cost function
Arguments:
a3 -- post-activation, output of forward propagation
Y -- "true" labels vector, same shape as a3
Returns:
cost - value of the cost function
"""
m = Y.shape[1]
logprobs = np.multiply(-np.log(a3),Y) + np.multiply(-np.log(1 - a3), 1 - Y)
cost = 1./m * np.sum(logprobs)
return cost
def forward_propagation(X, parameters):
"""
Implements the forward propagation (and computes the loss) presented in Figure 2.
Arguments:
X -- input dataset, of shape (input size, number of examples)
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", "W2", "b2", "W3", "b3":
W1 -- weight matrix of shape ()
b1 -- bias vector of shape ()
W2 -- weight matrix of shape ()
b2 -- bias vector of shape ()
W3 -- weight matrix of shape ()
b3 -- bias vector of shape ()
Returns:
loss -- the loss function (vanilla logistic loss)
"""
# retrieve parameters
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
W3 = parameters["W3"]
b3 = parameters["b3"]
# LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID
z1 = np.dot(W1, X) + b1
a1 = relu(z1)
z2 = np.dot(W2, a1) + b2
a2 = relu(z2)
z3 = np.dot(W3, a2) + b3
a3 = sigmoid(z3)
cache = (z1, a1, W1, b1, z2, a2, W2, b2, z3, a3, W3, b3)
return a3, cache
def backward_propagation(X, Y, cache):
"""
Implement the backward propagation presented in figure 2.
Arguments:
X -- input dataset, of shape (input size, number of examples)
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if cat, 1 if non-cat)
cache -- cache output from forward_propagation()
Returns:
gradients -- A dictionary with the gradients with respect to each parameter, activation and pre-activation variables
"""
m = X.shape[1]
(z1, a1, W1, b1, z2, a2, W2, b2, z3, a3, W3, b3) = cache
dz3 = 1./m * (a3 - Y)
dW3 = np.dot(dz3, a2.T)
db3 = np.sum(dz3, axis=1, keepdims = True)
da2 = np.dot(W3.T, dz3)
dz2 = np.multiply(da2, np.int64(a2 > 0))
dW2 = np.dot(dz2, a1.T)
db2 = np.sum(dz2, axis=1, keepdims = True)
da1 = np.dot(W2.T, dz2)
dz1 = np.multiply(da1, np.int64(a1 > 0))
dW1 = np.dot(dz1, X.T)
db1 = np.sum(dz1, axis=1, keepdims = True)
gradients = {"dz3": dz3, "dW3": dW3, "db3": db3,
"da2": da2, "dz2": dz2, "dW2": dW2, "db2": db2,
"da1": da1, "dz1": dz1, "dW1": dW1, "db1": db1}
return gradients
def predict(X, y, parameters):
"""
This function is used to predict the results of a n-layer neural network.
Arguments:
X -- data set of examples you would like to label
parameters -- parameters of the trained model
Returns:
p -- predictions for the given dataset X
"""
m = X.shape[1]
p = np.zeros((1,m), dtype = np.int)
# Forward propagation
a3, caches = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
# convert probas to 0/1 predictions
for i in range(0, a3.shape[1]):
if a3[0,i] > 0.5:
p[0,i] = 1
else:
p[0,i] = 0
# print results
#print ("predictions: " + str(p[0,:]))
#print ("true labels: " + str(y[0,:]))
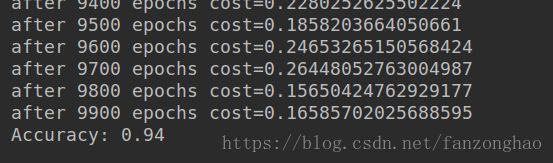
print("Accuracy: " + str(np.mean((p[0,:] == y[0,:]))))
return p
def load_2D_dataset():
data = scipy.io.loadmat('datasets/data.mat')
train_X = data['X'].T
train_Y = data['y'].T
test_X = data['Xval'].T
test_Y = data['yval'].T
plt.scatter(train_X[0, :], train_X[1, :], c=train_Y, s=40, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral);
return train_X, train_Y, test_X, test_Y
def plot_decision_boundary(model, X, y):
# Set min and max values and give it some padding
x_min, x_max = X[0, :].min() - 1, X[0, :].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[1, :].min() - 1, X[1, :].max() + 1
h = 0.01
# Generate a grid of points with distance h between them
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
# Predict the function value for the whole grid
Z = model(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
# Plot the contour and training examples
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
plt.ylabel('x2')
plt.xlabel('x1')
plt.scatter(X[0, :], X[1, :], c=y, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
plt.show()
def predict_dec(parameters, X):
"""
Used for plotting decision boundary.
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters
X -- input data of size (m, K)
Returns
predictions -- vector of predictions of our model (red: 0 / blue: 1)
"""
# Predict using forward propagation and a classification threshold of 0.5
a3, cache = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
predictions = (a3 > 0.5)
return predictions
def load_dataset():
np.random.seed(3)
#(300,2) (300,)
train_X, train_Y = sklearn.datasets.make_moons(n_samples=300, noise=.2) #300 #0.2
#print(train_X,train_Y)
# Visualize the data
#plt.scatter(train_X[:, 0], train_X[:, 1], c=train_Y, s=40, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral);
train_X = train_X.T
train_Y = train_Y.reshape((1, train_Y.shape[0]))
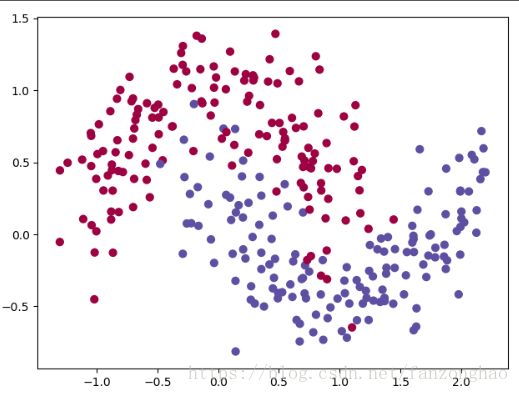
return train_X, train_Y打印数据集看看:
![]()
全部代码:
import numpy as np
import sklearn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sklearn
import sklearn.datasets
import scipy.io
import math
import opt_utils
import testCases1
""""
一般梯度下降算法
"""
def update_parameters_gd(parameters,grads,learning_rate):
L=len(parameters)//2
for i in range(L):
parameters['W'+str(i+1)]=parameters['W'+str(i+1)]-learning_rate*grads['dW'+str(i+1)]
parameters['b' + str(i + 1)] = parameters['b' + str(i + 1)] - learning_rate * grads['db' + str(i + 1)]
return parameters
""""
制作样本 mini-batch
"""
def random_mini_batches(X,Y,mini_batch_size):
m=X.shape[1]###3
mini_batchs=[]
permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))#[2,1,0]
shuffled_X = X[:,permutation]##X[:,[2,1,0]] 洗牌
shuffled_Y = Y[:, permutation] ##X[:,[2,1,0]]
num_mini_batch=math.floor(m/mini_batch_size)
for i in range(num_mini_batch):
mini_batch_X=shuffled_X[:,i*mini_batch_size:(i+1)*mini_batch_size]
mini_batch_Y=shuffled_Y[:,i*mini_batch_size:(i+1)*mini_batch_size]
mini_batch=(mini_batch_X,mini_batch_Y)
mini_batchs.append(mini_batch)
if m/mini_batch_size!=0:
mini_batch_X = shuffled_X[:, (i + 1) * mini_batch_size:]
mini_batch_Y = shuffled_Y[:, (i + 1) * mini_batch_size:]
mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
mini_batchs.append(mini_batch)
return mini_batchs
"""
Momentum初始化参数
"""
def initialize_Momentum_paremeters(parameters):
L=len(parameters)//2
v={}
for i in range(L):
v['dW'+str(i+1)]=np.zeros(parameters['W'+str(i+1)].shape)
v['db' + str(i + 1)] = np.zeros(parameters['b' + str(i + 1)].shape)
return v
"""
Momentum更新权重
"""
def upate_parameters_Momentum(parameters,grads,v,beta,learning_rate):
L=len(parameters)//2
for i in range(L):
v['dW' + str(i + 1)]=beta*v['dW'+str(i+1)]+(1-beta)*grads['dW'+str(i+1)]
v['db' + str(i + 1)] = beta * v['db' + str(i + 1)] + (1 - beta) * grads['db' + str(i + 1)]
parameters['W'+str(i+1)]=parameters['W'+str(i+1)]-learning_rate*v['dW' + str(i + 1)]
parameters['b' + str(i + 1)] = parameters['b' + str(i + 1)] - learning_rate * v['db' + str(i + 1)]
return parameters,v
"""
Adam初始化参数
"""
def initialize_Adam_parameters(parameters):
L=len(parameters)//2
v={}
s={}
for i in range(L):
v['dW' + str(i + 1)] = np.zeros(parameters['W'+str(i+1)].shape)
v['db' + str(i + 1)] = np.zeros(parameters['b' + str(i + 1)].shape)
s['dW' + str(i + 1)] = np.zeros(parameters['W' + str(i + 1)].shape)
s['db' + str(i + 1)] = np.zeros(parameters['b' + str(i + 1)].shape)
return v,s
"""
Adam更新权重
"""
def update_parameters_Adam(parameters,grads,v,s,t,beta1,beta2,learning_rate,epsilon):
L = len(parameters) // 2
v_correct={}
s_correct = {}
for i in range(L):
v['dW' + str(i + 1)] = beta1 * v['dW' + str(i + 1)] + (1 - beta1) * grads['dW' + str(i + 1)]
v['db' + str(i + 1)] = beta1 * v['db' + str(i + 1)] + (1 - beta1) * grads['db' + str(i + 1)]
v_correct['dW' + str(i + 1)]=v['dW' + str(i + 1)]/(1-beta1**t)
v_correct['db' + str(i + 1)] = v['db' + str(i + 1)] / (1 - beta1 ** t)
s['dW' + str(i + 1)] = beta2 * s['dW' + str(i + 1)] + (1 - beta2) * np.square(grads['dW' + str(i + 1)])
s['db' + str(i + 1)] = beta2 * s['db' + str(i + 1)] + (1 - beta2) * np.square(grads['db' + str(i + 1)])
s_correct['dW' + str(i + 1)] = s['dW' + str(i + 1)] / (1 - beta2 ** t)
s_correct['db' + str(i + 1)] = s['db' + str(i + 1)] / (1 - beta2 ** t)
parameters['W' + str(i + 1)] = parameters['W' + str(i + 1)] - \
learning_rate * (v_correct['dW' + str(i + 1)]/(np.sqrt(s['dW' + str(i + 1)])+epsilon))
parameters['b' + str(i + 1)] = parameters['b' + str(i + 1)] - \
learning_rate * (v_correct['db' + str(i + 1)]/(np.sqrt(s['db' + str(i + 1)])+epsilon))
return parameters, v,s
def model(X,Y,layer_dims,optimizer,learning_rate,mini_batch_size,beta,beta1,beta2,epsilon,num_pochs):
t=0
costs=[]
parameters=opt_utils.initialize_parameters(layer_dims)
if optimizer=='gd':
pass
elif optimizer=='Momentum':
v=initialize_Momentum_paremeters(parameters)
elif optimizer=='Adam':
v, s=initialize_Adam_parameters(parameters)
for i in range(num_pochs):
mini_batchs=random_mini_batches(X,Y,mini_batch_size) ###[([X],[Y]),([X2],[Y2])]
for minibatch in mini_batchs:
(minibatch_X,minibatch_Y)=minibatch
A3, cache=opt_utils.forward_propagation(minibatch_X,parameters)
cost=opt_utils.compute_cost(A3,minibatch_Y)
gradients=opt_utils.backward_propagation(minibatch_X, minibatch_Y, cache)
if optimizer=='gd':
parameters=update_parameters_gd(parameters,gradients,learning_rate)
elif optimizer=='Momentum':
parameters, v=upate_parameters_Momentum(parameters, gradients, v, beta, learning_rate)
elif optimizer=='Adam':
t=t+1
parameters, v, s=update_parameters_Adam(parameters, gradients, v, s, t, beta1, beta2, learning_rate, epsilon)
if i%1000==0:
costs.append(cost)
print('after {} epochs cost={}'.format(i,cost) )
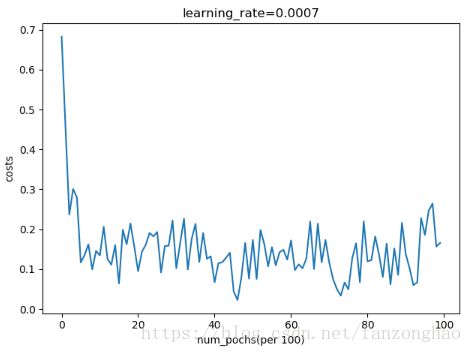
plt.plot(costs)
plt.xlabel('num_pochs(per 100)')
plt.ylabel('costs')
plt.title('learning_rate={}'.format(learning_rate))
plt.savefig('Adam.jpg')
plt.show()
return parameters
def test():
############test mini_batch
# X, Y, mini_batch_size=testCases1.random_mini_batches_test_case()
# mini_batchs=random_mini_batches(X, Y, mini_batch_size=64)
# print('first x shape={}'.format(mini_batchs[0][0].shape))
# print('second x shape={}'.format(mini_batchs[1][0].shape))
# print('third x shape={}'.format(mini_batchs[2][0].shape))
# print('first y shape={}'.format(mini_batchs[0][1].shape))
# print('second y shape={}'.format(mini_batchs[1][1].shape))
# print('third y shape={}'.format(mini_batchs[2][1].shape))
###############
#######test initialize_vecolity
# parameters=testCases1.initialize_velocity_test_case()
# v=initialize_velocity(parameters)
# print(v)
####################
#######test upate_parameters_Momentum
# parameters, grads, v=testCases1.update_parameters_with_momentum_test_case()
# parameters, v=upate_parameters_Momentum(parameters,grads,v,beta=0.9,learning_rate=0.01)
# print(parameters)
# print(v)
###############
########test upate_parameters_Adam
parameters, grads, v, s=testCases1.update_parameters_with_adam_test_case()
parameters, v, s=update_parameters_Adam(parameters,grads,v,s,t=2,beta1=0.9,beta2=0.999,learning_rate=0.01,epsilon=1e-8)
print(parameters,v,s)
def test_model():
train_X, train_Y=opt_utils.load_dataset()
layer_dims=[train_X.shape[0],5,2,1]
parameters=model(train_X,train_Y,layer_dims,optimizer='gd',learning_rate=0.0007,
mini_batch_size=64,beta=0.9,beta1=0.9,beta2=0.999,epsilon=1e-8,num_pochs=10000)
opt_utils.predict(train_X, train_Y, parameters)
if __name__=='__main__':
#test()
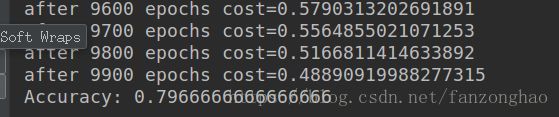
test_model()更改model()里的optimizer即可,普通梯度下降法结果:
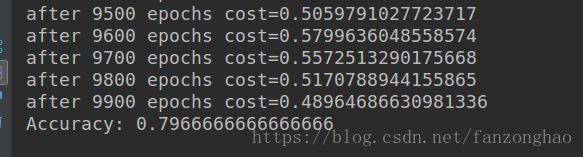
Momentum下降结果和上面结果差不多可能是学习率太小,数据集太简单导致的吧
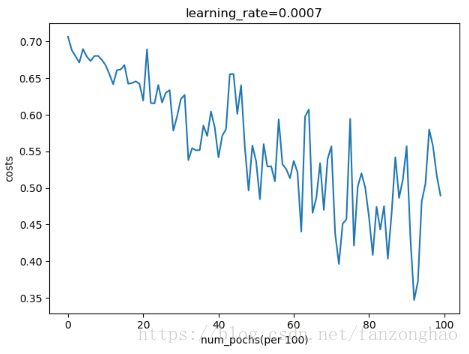
Adam下降结果,能够更快的收敛