- Domain:包含主要的领域模型,比如User,UserRole,PermissionRecord等
- Helpers:包含一些帮助类,比如xml,email
- Mapping:数据映射
- Services:服务部分的接口和实现
而网站部分重要的有一些可以复用的Attributes,AccountController等,比如UserLastActivityIpAttribute,会记录用户的Ip并更新最后访问时间。
下面介绍下2个我认为重要点的部分
Ninject依赖注入:
Nop中使用的是Autofac,并构建了一个强大的EnginContext管理所有的依赖注入项,在这个项目中我拿掉了这一部分,换成Ninject来完成IOC的工作。并不涉及这两个组件的优劣问题,而且我认为前者的功能更要强悍一些。Ninject是在NinjectWebCommon类中注册的.它在App_Start文件夹下。 如下:
kernel.Bind().To ();
Ninject更详细的介绍请看我的博客:Ninject在MVC5中的使用。在不能用构造函数的地方,可以用属性注入。
[Inject] public IWorkContext WorkContext { get; set; } [Inject] public IUserService UserService { get; set; }
而有的Service需要用到HttpContext,这对象没有接口,是无法注册的,但可以通过HttpContextWrapper获得。
public HttpContextBase HttpContext { get { return new HttpContextWrapper(System.Web.HttpContext.Current); } }
HttpContextBase 是一个抽象类,HttpContextWrapper是其派生成员。这两者都是.Net3.5之后才出现。
更多的解释大家可以看老赵的博客:为什么是HttpContextBase而不是IHttpContext
领域设计
这个部分网上讨论的比较多,Nop是采用的单个仓库接口IRepository
IRepository
public interface IRepositorywhere T:BaseEntity { /// /// Gets the by id. /// /// The id. /// `0. T GetById(object id); /// /// Inserts the specified entity. /// /// The entity. void Insert(T entity); /// /// Inserts the specified entities. /// /// The entities. void Insert(IEnumerable entities); /// /// Updates the specified entity. /// /// The entity. void Update(T entity); /// /// Deletes the specified entity. /// /// The entity. void Delete(T entity); /// /// Gets the table. /// /// The table. IQueryable Table { get; } /// /// Gets the tables no tracking. /// /// The tables no tracking. IQueryable TableNoTracking { get; } }
用EfRepository
public class EfRepository:IRepository where T:BaseEntity { #region Fields private readonly IDbContext _context ; private IDbSet _entities; #endregion public EfRepository(IDbContext context) { if (context == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("context"); } _context = context; } #region property protected virtual IDbSet Entities { get { if (_entities == null) { _entities = _context.Set (); } return _entities ?? (_entities = _context.Set ()); // _entities ?? _entities = db.Set (); } } ////// Gets a table /// public virtual IQueryable Table { get { return Entities; } } public IQueryable TableNoTracking { get { return Entities.AsNoTracking(); } } #endregion public virtual T GetById(object id) { return Entities.Find(id); } public void Insert(T entity) { try { if(entity==null) throw new ArgumentException("entity"); Entities.Add(entity); _context.SaveChanges(); } catch (DbEntityValidationException dbEx) { GetException(dbEx); } } /// /// Insert entities /// /// Entities public virtual void Insert(IEnumerable entities) { try { if (entities == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("entities"); foreach (var entity in entities) Entities.Add(entity); _context.SaveChanges(); } catch (DbEntityValidationException dbEx) { GetException(dbEx); } } /// /// Update entity /// /// Entity public virtual void Update(T entity) { try { if (entity == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("entity"); _context.SaveChanges(); } catch (DbEntityValidationException dbEx) { GetException(dbEx); } } /// /// Delete entity /// /// Entity public virtual void Delete(T entity) { try { if (entity == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("entity"); Entities.Remove(entity); _context.SaveChanges(); } catch (DbEntityValidationException dbEx) { GetException(dbEx); } } /// /// Delete entities /// /// Entities public virtual void Delete(IEnumerable entities) { try { if (entities == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("entities"); foreach (var entity in entities) Entities.Remove(entity); _context.SaveChanges(); } catch (DbEntityValidationException dbEx) { GetException(dbEx); } } private static void GetException(DbEntityValidationException dbEx) { var msg = string.Empty; foreach (var validationErrors in dbEx.EntityValidationErrors) foreach (var validationError in validationErrors.ValidationErrors) msg += Environment.NewLine + string.Format("Property: {0} Error: {1}", validationError.PropertyName, validationError.ErrorMessage); var fail = new Exception(msg, dbEx); //Debug.WriteLine(fail.Message, fail); throw fail; } }
而其中的IDbContext是自定义的数据接口
public interface IDbContext { IDbSetSet () where TEntity : BaseEntity; int SaveChanges(); /// /// 执行存储过程,并返回对象列表 /// /// The type of the T entity. /// The command text. /// The parameters. /// IList{``0}. IList ExecuteStoredProcedureList (string commandText, params object[] parameters) where TEntity : BaseEntity, new(); /// /// 查询Sql语句 /// /// /// /// /// IEnumerable SqlQuery (string sql, params object[] parameters); /// /// 执行sql 是否启用事务 /// /// /// /// /// /// int ExecuteSqlCommand(string sql, bool doNotEnsureTransaction = false, int? timeout = null, params object[] parameters); }
然后注入:
kernel.Bind().To ().InSingletonScope();
对于和模型相关的Service内部都是注入的IRepository
private readonly IRepository_useRepository; private readonly IRepository _userRoleRepository; private readonly ICacheManager _cacheManager ; public UserService(IRepository useRepository,IRepository userRoleRepository,ICacheManager cacheManager) { _useRepository = useRepository; _userRoleRepository = userRoleRepository; _cacheManager = cacheManager; }
这样相互之间就比较干净。只依赖接口。
而数据模型都会继承BaseEntity这个对象。
public class User : BaseEntity { //... }
数据映射相关的部分在Mapping中,比如UserMap
public class UserMap : PortalEntityTypeConfiguration{ public UserMap() { ToTable("Users"); HasKey(n => n.Id); Property(n => n.Username).HasMaxLength(100); Property(n => n.Email).HasMaxLength(500); Ignore(n => n.PasswordFormat); HasMany(c => c.UserRoles).WithMany().Map(m => m.ToTable("User_UserRole_Mapping")); } }
在PortalDb的OnModelCreating方法中加入。这样就会影响到数据库的设计。
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder) { modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(new UserMap());
}
Nop的做法高级一些。反射找出所有的PortalEntityTypeConfiguration。一次性加入。这里大家可以自己去试
var typesToRegister = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetTypes() .Where(type => !String.IsNullOrEmpty(type.Namespace)) .Where(type => type.BaseType != null && type.BaseType.IsGenericType && type.BaseType.GetGenericTypeDefinition() == typeof(PortalEntityTypeConfiguration<>)); foreach (var type in typesToRegister) { dynamic configurationInstance = Activator.CreateInstance(type); modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(configurationInstance); }
权限管理:
默认设定了三种角色,Administrators,Admins,Employeer,他们分别配置了不同的权限,权限指定是在StandardPermissionProvider这个类中完成的,表示一个角色拥有哪些权限,Administrators拥有所有权限
new DefaultPermissionRecord { UserRoleSystemName = SystemUserRoleNames.Admin, PermissionRecords = new [] { AccessAdminPanel, SearchOrder, ManageUsers, } },
而权限验证的时候,在响应的Action上面加上AdminAuthorize和权限名称即可。
[AdminAuthorize("ManageUsers")] public ActionResult Index() { }
而在其内部是通过PermissionService来验证的:
public virtual bool HasAdminAccess(AuthorizationContext filterContext) { bool result = PermissionService.Authorize(Permission); return result; }
后台只有给用户设置角色的页面,我没做新增角色并分配权限的页面。不过这个实现起来也很简单了。如果你是更换数据库,这个时候设计到权限的初始化。调用下面的方法即可:
_permissionService.InstallPermissions(new StandardPermissionProvider());
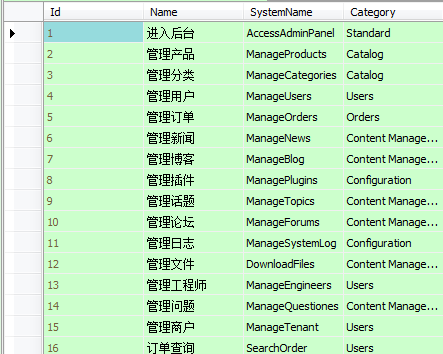
当然前提是你先注入这个_permissionService。更多的代码细节大家可以去看源码。安装完成之后会有以下默认权限
以上是关于工程的大体说明,欢迎大家拍砖。下面下载地址。数据文件需要附加。
1:github地址:https://github.com/stoneniqiu/Portal.MVC
2:百度云:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1juc5Mo20sTW0I5uJyaNBbw
数据库是Sql2008,附加不上,也可以自动生成。记得给自己添加用户。 默认用户名:stoneniqiu 密码 admin