转自 https://juejin.im/post/59083d7fda2f60005d14efdb
本文分析下Android的消息处理机制,主要是针对Handler、Looper、MessageQueue组成的异步消息处理模型,先主观想一下这个模型需要的材料:
- 消息队列:通过Handler发送的消息并是即刻执行的,因此需要一个队列来维护
- 工作线程:需要一个线程不断摘取消息,并执行回调,这种线程就是Looper线程
- 互斥机制,会有不同的线程向同一个消息队列插入消息,这个时候就需要同步机制进行保证
- 空消息队列时候的同步机制,生产者消费者模型
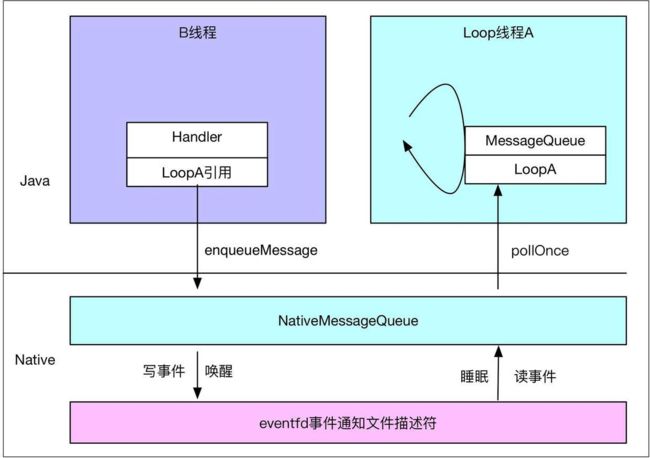
上面的三个部分可以简单的归结为如下图:
APP端UI线程都是Looper线程,每个Looper线程中维护一个消息队列,其他线程比如Binder线程或者自定义线程,都能通过Handler对象向Handler所依附消息队列线程发送消息,比如点击事件,都是通过InputManagerService处理后,通过binder通信,发送到App端Binder线程,再由Binder线程向UI线程发送送Message,其实就是通过Handler向UI的MessageQueue插入消息,与此同时,其他线程也能通过Handler向UI线程发送消息,显然这里就需要同步,以上就是Android消息处理模型的简单描述,之后跟踪源码,浅析一下具体的实现,以及里面的一些小手段,首先,从Handler的常见用法入手,分析其实现原理,
Handler的一种基本用法--消息Message的插入
<关键点1>
Handler hanlder=new Handler();
<关键点2>
hanlder.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//TODO
}
});
这里有两个点需要注意,先看关键点1,Handler对象的创建,直观来看可能感觉不到有什么注意的地方,但是如果你在普通线程创建Handler,就会遇到异常,因为普通线程是不能创建Handler对象的,必须是Looper线程才能创建,才有意义,可以看下其构造函数:
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}
从上面的代码可以看出,Looper.myLooper()必须非空,否则就会抛出 RuntimeException异常,Looper.myLooper()什么时候才会非空?
public static @Nullable Looper myLooper() {
return sThreadLocal.get();
}
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}
上面的两个函数牵扯到稍微拧巴的数据存储模型,不分析,只要记住只有调用过Looper.prepare的线程,才会生成一个线程单利的Looper对象,Looper.prepare只能调用一次,再次调用会抛出异常。其实prepare的作用就是新建一个Looper对象,而在new Looper对象的时候,会创建关键的消息队列对象:
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {
mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
}
之后,一个线程就有了MessageQueue,虽然还没有调用Loop.loop()将线程变成loop线程,但是new Handler已经没问题。接着看hanlder.post函数,它将会创建一个Message(如果需要),并将Message插入到MessageQueue,供loop线程摘取并执行。
public final boolean post(Runnable r)
{
return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), 0);
}
private static Message getPostMessage(Runnable r) {
Message m = Message.obtain();
m.callback = r;
return m;
}
// 静态方法,同步
public static Message obtain() {
synchronized (sPoolSync) {
if (sPool != null) {
Message m = sPool;
sPool = m.next;
m.next = null;
m.flags = 0; // clear in-use flag
sPoolSize--;
return m;
}
}
return new Message();
}
上面的Message新建流程,其实主要是涉及了一个Message线程池,默认线程池大小50,当然,不采用线程池,全部新建Message也是可以的,采用线程池主要是为了提高效率,避免重复创建对象,因为Handler与Message的时候实在是太频繁了,Message线程池消息池常用的方法有两个:obtain()和recycle(),前者是用于从线程池取出一个干净的Message,而后者是用于将使用完的Message清理干净,并放回线程池,当然以上方法都是需要同步的。之后,通过Looper对象将Message插入到MessageQueue,Handler发消息最终都会调用sendMessageAtTime函数
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
}
private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
msg.target = this;
if (mAsynchronous) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
}
mAsynchronous可以先不关心,我们使用的一般是mAsynchronous=false的,可以看到,Handler最后通过MessageQueue的enqueueMessage函数来进行插入,
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {
if (msg.target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Message must have a target.");
}
if (msg.isInUse()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(msg + " This message is already in use.");
}
// 需要同步
synchronized (this) {
msg.markInUse();
msg.when = when;
Message p = mMessages;
boolean needWake;
if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) {
msg.next = p;
mMessages = msg;
needWake = mBlocked;
} else {
needWake = mBlocked && p.target == null && msg.isAsynchronous();
Message prev;
for (;;) {
prev = p;
p = p.next;
if (p == null || when < p.when) {
break;
}
if (needWake && p.isAsynchronous()) {
needWake = false;
}}
msg.next = p; // invariant: p == prev.next
prev.next = msg;
}
if (needWake) {
nativeWake(mPtr);
} }
return true; }
很明显enqueueMessage需要同步,因为存在多个线程往一个Loop线程的MessageQueue中插入消息的场景。 这里其实是将Message根据延时插入到特定的地方,先看下关键点1,mMessages其实代表消息队列的头部,如果mMessages为空,说明还没有消息,如果当前插入的消息不需要延时,或者说延时比mMessages头消息的延时要小,那么当前要插入的消息就需要放在头部,至于是否需要唤醒队列,则需要根据当前的Loop线程的状态来判断,后面讲Loop线程的时候再回过头说;再来看下关键点2,这个时候需要将消息插入到队列中间,其实就是找到第一个Delay事件小于当前Message的非空Message,并插入到它的前面,往队列中插入消息时,如果Loop线程在睡眠,是不应该唤醒的,异步消息的处理会更加特殊一些,先不讨论。最后看关键点3,如果需要唤醒Loop线程,通过nativeWake唤醒,以上,普通消息的插入算结束了,接下来看一下消息的执行。
MessageQueue中Message消息的执行
在消息的发送部分已经消息模型的两个必要条件:消息队里+互斥机制,接下来看一下其他两个条件,Loop线程+消费者模型的同步机制。MessageQueue只有同Loop线程(死循环线程)配合起来才有意义,普通线程必须可以通过Looper的loop函数变成Loop线程,loop函数除了是个死循环,还包含了从MessageQueue摘取消息并执行的逻辑。看一下这个函数:
public static void loop() {
`
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
...
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
...
msg.recycleUnchecked();
}
}
先看下关键点1,它要确保当前线程已经调用过Looper.prepare函数,并且准备好了MessageQueue消息队列;再看关键点2,其实就是将线程化身成Looper线程,变成死循环,不断的读取执行消息;关键点3,就是从MessageQueue摘取消息的函数,如果当前消息队列上没有消息,Loop线程就会进入阻塞,直到其他线程插入消息,唤醒当前线程。如果消息读取成功,就走到关键点4,执行target对象的回调函数,执行完毕,进入关键点5,回收清理Message对象,放入Message缓存池。直接看关键点3,消息的摘取与阻塞:
Message next() {
int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iteration
int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
for (;;) {
nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);
synchronized (this) {
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
Message prevMsg = null;
Message msg = mMessages;
if (msg != null && msg.target == null) {
do {
prevMsg = msg;
msg = msg.next;
} while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous());
}
if (msg != null) {
if (now < msg.when) {
// Next message is not ready. Set a timeout to wake up when it is ready.
nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} else {
// Got a message.
mBlocked = false;
if (prevMsg != null) {
prevMsg.next = msg.next;
} else {
mMessages = msg.next;
}
msg.next = null;
msg.markInUse();
return msg;
}
} else {
nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;
}
if (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0
&& (mMessages == null || now < mMessages.when)) {
pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size();
}
if (pendingIdleHandlerCount <= 0) {
// No idle handlers to run. Loop and wait some more.
mBlocked = true;
continue;
}
if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) {
mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)];
}
mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers);
}
for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) {
final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i];
mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handler
boolean keep = false;
try {
keep = idler.queueIdle();
} catch (Throwable t) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "IdleHandler threw exception", t);
}
if (!keep) {
synchronized (this) {
mIdleHandlers.remove(idler);
}
}
}
pendingIdleHandlerCount = 0;
nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
}
}
先看下关键点1 nativePollOnce,这是个native函数,其主要作用是设置一个定时的睡眠,其参数timeoutMillis,不同的值意义不同
- timeoutMillis =0 :无需睡眠,直接返回
- timeoutMillis >0 :睡眠如果超过timeoutMillis,就返回
- timeoutMillis =-1:一直睡眠,知道其他线程唤醒它
next函数中,nextPollTimeoutMillis初始值=0 ,所以for循环第一次是一定不会阻塞的,如果能找到一个Delay倒计时结束的消息,就返回该消息,否则,执行第二次循环,睡眠等待,直到头部第一个消息Delay时间结束,所以next函数一定会返回一个Message对象。再看MessageQueue的nativePollOnce函数之前,先走通整个流程,接着看关键点2,这里其实是牵扯到一个互斥的问题,防止多个线程同时从消息队列取消息,关键点3主要是看看是否需要处理异步消息,关键点4,是常用的入口,看取到的消息是不是需要立即执行,需要立即执行的就返回当前消息,如果需要等待,计算出等待时间。最后,如果需要等待,还要查看,IdleHandler列表是否为空,不为空的话,需要处理IdleHandler列表,最后,重新计算一遍。
接着分析nativePollOnce函数,该函数可以看做睡眠阻塞的入口,该函数是一个native函数,牵扯到native层的Looper与MessageQueue,因为java层的MessageQueue只是一个简单的类,没有处理睡眠与唤醒的机制,首先看一下Java层MessageQueue构造函数,这里牵扯到后面的线程阻塞原理:
MessageQueue(boolean quitAllowed) {
mQuitAllowed = quitAllowed;
mPtr = nativeInit();
}
MessageQueue的nativeInit函数在Native层创建了NativeMessageQueue与Looper,不过对于Java层来说,Native层的NativeMessageQueue只用来处理线程的睡眠与唤醒,Java层发送的消息还是在Java层被处理:
static jlong android_os_MessageQueue_nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz) {
NativeMessageQueue* nativeMessageQueue = new NativeMessageQueue();
if (!nativeMessageQueue) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "Unable to allocate native queue");
return 0;
}
nativeMessageQueue->incStrong(env);
return reinterpret_cast(nativeMessageQueue);
}
NativeMessageQueue::NativeMessageQueue() :
mPollEnv(NULL), mPollObj(NULL), mExceptionObj(NULL) {
mLooper = Looper::getForThread();
if (mLooper == NULL) {
mLooper = new Looper(false);
Looper::setForThread(mLooper);
}
}
Looper::Looper(bool allowNonCallbacks) :
mAllowNonCallbacks(allowNonCallbacks), mSendingMessage(false),
mPolling(false), mEpollFd(-1), mEpollRebuildRequired(false),
mNextRequestSeq(0), mResponseIndex(0), mNextMessageUptime(LLONG_MAX) {
mWakeEventFd = eventfd(0, EFD_NONBLOCK | EFD_CLOEXEC);
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
rebuildEpollLocked();
}
void Looper::rebuildEpollLocked() {
if (mEpollFd >= 0) {
close(mEpollFd);
}
mEpollFd = epoll_create(EPOLL_SIZE_HINT);
struct epoll_event eventItem;
memset(& eventItem, 0, sizeof(epoll_event)); // zero out unused members of data field union
eventItem.events = EPOLLIN;
eventItem.data.fd = mWakeEventFd;
int result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mWakeEventFd, & eventItem);
for (size_t i = 0; i < mRequests.size(); i++) {
const Request& request = mRequests.valueAt(i);
struct epoll_event eventItem;
request.initEventItem(&eventItem);
int epollResult = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, request.fd, & eventItem);
if (epollResult < 0) {
ALOGE("Error adding epoll events for fd %d while rebuilding epoll set: %s",
request.fd, strerror(errno));
}
}
}
看一下关键点1,这里其实是采用了Linux的新API,这里用的是7.0的源码,eventfd函数会创建一个eventfd,这是一个计数器相关的fd,计数器不为零是有可读事件发生,read以后计数器清零,write递增计数器;返回的fd可以进行如下操作:read、write、select(poll、epoll)、close,现在我们知道了,Native层有也有一套MessageQueue与Looper,简单看一下Java层如何使用Native层对象的,接着走nativePollOnce
static void android_os_MessageQueue_nativePollOnce(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj,
jlong ptr, jint timeoutMillis) {
NativeMessageQueue* nativeMessageQueue = reinterpret_cast(ptr);
nativeMessageQueue->pollOnce(env, obj, timeoutMillis);
}
void NativeMessageQueue::pollOnce(JNIEnv* env, jobject pollObj, int timeoutMillis) {
mPollEnv = env;
mPollObj = pollObj;
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
mPollObj = NULL;
mPollEnv = NULL;
}
所以最终调用Looper::pollOnce,Java层有自己的消息队列,pollOnce也没有更新Java层对象,那么Native层的消息队里对于Java层有什么用呢,其实只有睡眠与唤醒的作用,比如2.3之前的版本,Native层的MessageQueue都不具备发送消息的能力。不过后来Native添加了发送消息的功能,但是日常开发我们用不到,不过如果native层如果有消息,一定会优先执行native层的消息
int Looper::pollOnce(int timeoutMillis, int* outFd, int* outEvents, void** outData) {
int result = 0;
...
result = pollInner(timeoutMillis);
}
}
pollInner 函数比较长,主要是通过利用epoll_wait监听上面的管道或者eventfd,等待超时或者其他线程的唤醒,不过多分析
int Looper::pollInner(int timeoutMillis) {
mPolling = true;
struct epoll_event eventItems[EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS];
int eventCount = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, eventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);
mPolling = false;
mLock.lock();
for (int i = 0; i < eventCount; i++) {
int fd = eventItems[i].data.fd;
uint32_t epollEvents = eventItems[i].events;
if (fd == mWakeEventFd) {
if (epollEvents & EPOLLIN) {
awoken();
} else { } }
else {
} }
以上牵扯到Linux中的epoll机制:epoll_create、epoll_ctl、epoll_wait、close等, 用一句话概括:线程阻塞监听多个fd句柄,其中一个fd有写入操作,当前线程就被唤醒。这里不用太过于纠结,只要理解,这是线程间通信的一种方式,为了处理多线程间生产者与消费者通信模型用的,看下7.0源码中native层实现的同步逻辑:
在更早的Android版本中,同步逻辑是利用管道通信实现的,不过思想是一致的,看一下4.3的代码
Looper::Looper(bool allowNonCallbacks) :
mAllowNonCallbacks(allowNonCallbacks), mSendingMessage(false),
mResponseIndex(0), mNextMessageUptime(LLONG_MAX) {
int wakeFds[2];
int result = pipe(wakeFds);
mWakeReadPipeFd = wakeFds[0];
mWakeWritePipeFd = wakeFds[1];
result = fcntl(mWakeReadPipeFd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
result = fcntl(mWakeWritePipeFd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
// Allocate the epoll instance and register the wake pipe.
mEpollFd = epoll_create(EPOLL_SIZE_HINT);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(mEpollFd < 0, "Could not create epoll instance. errno=%d", errno);
struct epoll_event eventItem;
memset(& eventItem, 0, sizeof(epoll_event)); // zero out unused members of data field union
eventItem.events = EPOLLIN;
eventItem.data.fd = mWakeReadPipeFd;
result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mWakeReadPipeFd, & eventItem);
}
小结
- loop线程睡眠的原理 :在MessageQueue中找到下一个需要执行的消息,没有消息的话,需要无限睡眠等待其他线程插入消息唤醒,如果有消息,计算出执行下一个消息需要等待的时间,阻塞等待,直到超时。
- Java层与Native层两份消息队列:Java层的主要是为了业务逻辑,native层,主要为了睡眠与唤醒
- 睡眠与唤醒的实现手段:早期版本通过管道,后来如6.0、7.0的版本,是通过eventfd来实现,思想一致。