线段树+扫描线(基本原理)
这一部分是线段树的一个难点了,这写天做了这么多的这方面的题,一直是稀里糊涂的搞不太明白,但是又得理解,看到了一个别人转载的讲解,贴在这里以便回顾(侵删)。
扫描线法:
假想有一条扫描线,从左往右(从右往左),或者从下往上(从上往下)扫描过整个多边形(或者说畸形。。多个矩形叠加后的那个图形)。如果是竖直方向上扫描,则是离散化横坐标,如果是水平方向上扫描,则是离散化纵坐标。下面的分析都是离散化横坐标的,并且从下往上扫描的。
扫描之前还需要做一个工作,就是保存好所有矩形的上下边,并且按照它们所处的高度进行排序,另外如果是上边我们给他一个值-1,下边给他一个值1,我们用一个结构体来保存所有的上下边
struct segment
{
double l,r,h; //l,r表示这条上下边的左右坐标,h是这条边所处的高度
int f; //所赋的值,1或-1
}
接着扫描线从下往上扫描,每遇到一条上下边就停下来,将这条线段投影到总区间上(总区间就是整个多边形横跨的长度),这个投影对应的其实是个插入和删除线段操作。还记得给他们赋的值1或-1吗,下边是1,扫描到下边的话相当于往总区间插入一条线段,上边-1,扫描到上边相当于在总区间删除一条线段(如果说插入删除比较抽象,那么就直白说,扫描到下边,投影到总区间,对应的那一段的值都要增1,扫描到上边对应的那一段的值都要减1,如果总区间某一段的值为0,说明其实没有线段覆盖到它,为正数则有,那会不会为负数呢?是不可能的,可以自己思考一下)。
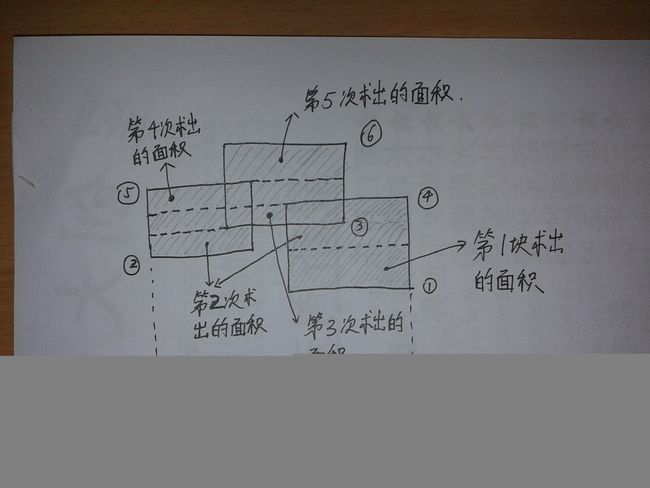
每扫描到一条上下边后并投影到总区间后,就判断总区间现在被覆盖的总长度,然后用下一条边的高度减去当前这条边的高度,乘上总区间被覆盖的长度,就能得到一块面积,并依此做下去,就能得到最后的面积
(这个过程其实一点都不难,只是看文字较难体会,建议纸上画图,一画即可明白,下面献上一图希望有帮助)
这里还有做的几道题。
二维线段树 (区间并) 查询被覆盖的面积 点击打开链接 简单题
模板!!!
代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX=210;
int N;
double x[MAX<<2];
struct Node
{
double l, r;
double h;
int flag;
}node[MAX<<2];
int cmp(Node a, Node b)
{
return a.h>1;
if(x[mid]>val)
r=mid-1;
else if(x[mid]>1;
build(rt<<1, left, mid);
build(rt<<1|1, mid+1, right);
}
void pushUp(int rt)
{
if(tree[rt].cnt)//非0,整段覆盖
tree[rt].len=x[tree[rt].r+1]-x[tree[rt].l];
else if(tree[rt].l==tree[rt].r)//叶子
tree[rt].len=0;
else//部分覆盖
tree[rt].len=tree[rt<<1].len+tree[rt<<1|1].len;
}
void update(int rt, int left, int right, int val)
{
if(left<=tree[rt].l && tree[rt].r<=right)//全部包含
{
tree[rt].cnt+=val;
pushUp(rt);
return ;
}
int mid=(tree[rt].l+tree[rt].r)>>1;
if(left<=mid)
update(rt<<1, left, right, val);
if(right>mid)
update(rt<<1|1, left, right, val);
pushUp(rt);//计算该区间被覆盖的总长度
}
int main()
{
int K=0;
int l, r;
double x1, x2, y1, y2;
while(~scanf("%d", &N), N)
{
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++)
{
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf", &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2);
x[++cnt]=x1;
node[cnt].l=x1;
node[cnt].r=x2;
node[cnt].h=y1;
node[cnt].flag=1;//下边
x[++cnt]=x2;
node[cnt].l=x1;
node[cnt].r=x2;
node[cnt].h=y2;
node[cnt].flag=-1;//上边
}
sort(x+1, x+cnt+1);//排序
sort(node+1, node+cnt+1, cmp);
/*
int M=1;
for(int i=1; i 二维线段树 (区间交) 查询两次的面积 点击打开链接 难题
代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX=2010;
int T, N, cnt;
double x[MAX<<2];
struct Node
{
double l, r;
double y;
double flag;
}node[MAX<<2];
int cmp(Node a ,Node b)
{
return a.y>1;
if(x[mid]val)
r=mid-1;
else
break;
}
return mid;
}
void build(int rt, int left, int right)
{
tree[rt].l=left;
tree[rt].r=right;
tree[rt].add=tree[rt].len1=tree[rt].len2=0;//全置0
if(left==right)//叶子
{
return ;
}
int mid=(left+right)>>1;
build(rt<<1, left, mid);
build(rt<<1|1, mid+1, right);
}
void pushUp(int rt)
{
if(tree[rt].add>=2)
{
tree[rt].len1=tree[rt].len2=x[tree[rt].r+1]-x[tree[rt].l];
}
else if(tree[rt].add==1)
{
tree[rt].len1=x[tree[rt].r+1]-x[tree[rt].l];
if(tree[rt].l==tree[rt].r)
tree[rt].len2=0;
else
tree[rt].len2=tree[rt<<1].len1+tree[rt<<1|1].len1;
}
else
{
if(tree[rt].l==tree[rt].r)
tree[rt].len1=tree[rt].len2=0;
else
{
tree[rt].len1=tree[rt<<1].len1+tree[rt<<1|1].len1;
tree[rt].len2=tree[rt<<1].len2+tree[rt<<1|1].len2;
}
}
}
void update(int rt, int left, int right, int val)
{
if(tree[rt].l==left && tree[rt].r==right)
{
tree[rt].add+=val;
pushUp(rt);
return ;
}
int mid=(tree[rt].l+tree[rt].r)>>1;
if(right<=mid)
update(rt<<1, left, right, val);
else if(left>mid)
update(rt<<1|1, left, right, val);
else
{
update(rt<<1, left, mid, val);
update(rt<<1|1, mid+1, right, val);
}
pushUp(rt);
}
int main()
{
double x1, x2, y1, y2;
int l, r;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
cnt=0;
memset(node, 0, sizeof(node));
memset(tree, 0, sizeof(tree));
cin>>N;
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++)
{
cin>>x1>>y1>>x2>>y2;
x[++cnt]=x1;
node[cnt].l=x1;
node[cnt].r=x2;
node[cnt].y=y1;
node[cnt].flag=1;//左边
x[++cnt]=x2;
node[cnt].l=x1;
node[cnt].r=x2;
node[cnt].y=y2;
node[cnt].flag=-1;//右边
}
//cout<<".......... cnt= "< 二维线段树 求固定面积矩形(W*H)内星星和的最大值 点击打开链接
代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX=20010;
typedef long long LL;
LL xis[MAX<<2];
struct Node
{
LL l, r;
LL h;
LL s;
bool operator <(const Node & a) const
{
if(h==a.h)
return s>1;
if(xis[mid]>val)
r=mid-1;
else if(xis[mid]>1;
build(rt<<1, left, mid);
build(rt<<1|1, mid+1, right);
}
void update(int L, int R, int c, int rt)
{
if(L<=tree[rt].l && tree[rt].r<=R)
{
tree[rt].cnt+=c;
tree[rt].sum+=c;
return ;
}
pushDown(rt);
int mid=(tree[rt].l+tree[rt].r)>>1;
if(L<=mid)
update(L, R, c, rt<<1);
if(mid>N>>W>>H && N && W && H)
{
int m=0;
LL ans=-1;
LL x, y, c;
int l, r;
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++)
{
cin>>x>>y>>c;
xis[++m]=x;
node[m].l=x;
node[m].r=x+W;
node[m].h=y;
node[m].s=c;
xis[++m]=x+W;
node[m].l=x;
node[m].r=x+W;
node[m].h=y+H;
node[m].s=-c;
}
build(1, 1, m);
sort(xis+1, xis+m+1);
sort(node+1, node+m+1);
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
l=findPos(1, m, node[i].l);
r=findPos(1, m, node[i].r)-1;
if(l<=r)
update(l, r, node[i].s, 1);
ans=max(ans, tree[1].sum);
}
cout<