Eigenface原理与python实现
1.问题描述
图像表示的难点在于它的高维度。二维的p×q的灰度图像就有一个维度为1×pq的特征,所以一张100×100的图像就有一个10000维的特征。这个数据对于任何计算来说都是庞大的,但是否所有维度的信息都是有用的?其实,我们只要找到存储着大量信息的部分就行。Principal Components Analysis (PCA) 由karl
等人提出,它将一组可能相关的变量变成较小的一组不相关的变量。它的思想是一个高维的数据通常由相关变量描述,因此仅有少部分维度具有大量有意义信息。PCA方法查找数据中方差最大的方向,也就是主成分。
2.计算公式
给定随机的向量 X = x 1 , x 2 , . . , x n X={x_1,x_2,..,x_n} X=x1,x2,..,xn,其中 x i ∈ R d x_i \in \R^d xi∈Rd。
- 计算均值
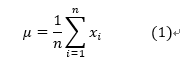
- 计算协方差矩阵S
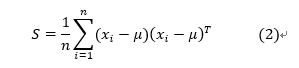
- 计算S的特征值和特征向量
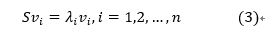
- 根据特征值对特征向量降序排序,选择前k个。向量x的k个主成分为:
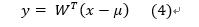
其中, W = ( v 1 , v 2 , . . , v k ) W=(v_1,v_2,..,v_k) W=(v1,v2,..,vk),利用PCA进行的重构为:
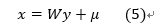
最后,利用eigenface进行人脸识别的过程如下:
a. 利用式(4),将所有的训练样本投影到PCA子空间。
b. 利用式(5),将所有的测试样本投到PCA子空间。
c. 在投影后的测试样本和投影后的训练样本中,找到最近邻。
但是依旧有一个问题需要解决。假设有400张图像,每张图像100×100。那么求得的协方差矩阵大小为10000×10000,大概0.8G。解这个协方差矩阵的特征值和特征向量是不可行的。但是如果将协方差矩阵换个角度思考,它也可以是 S = X T X S=X^TX S=XTX,那么协方差矩阵的大小就为400×400,这使得计算特征值和特征向量变得可行。
3.算法流程
①训练流程
a. 提取训练样本(100×100)的特征(10000×1)。
b. 根据式1,求得训练样本的平均脸
c. 训练样本的特征减去平均脸进行正则化
d. 计算协方差矩阵的特征值与特征向量,注意这里的协方差矩阵。
e. 根据特征值对特征向量进行排序,得到前k个特征向量
f. 利用式(4),将k个特征向量投影到PCA子空间。
g. 利用式(5),将每张图片表示成k个特征向量的线性组合。
② 测试流程
a. 提取测试样本特征
b. 减去平均脸对其正则化
c. 将该张量投影到特征脸空间
d. 获得权重矩阵
e. 计算测试样本与训练样本之间的距离
f. 根据阈值判断该测试样本的id
4. python实现
import os
import natsort
import cv2
import numpy as np
import PIL.Image as Image
import sys
imglist = os.listdir('data/face')
imglist = natsort.natsorted(imglist)
def asRowMatrix(X):
if len(X) == 0:
return np.array([])
mat = np.empty((0, X[0].size), dtype=X[0].dtype)
for row in X:
mat = np.vstack((mat, np.asarray(row).reshape(1,-1)))
return mat
def reconstruct(W, Y, mu=None):
if mu is None:
return np.dot(Y, W.T)
return np.dot(Y, W.T) + mu
def project(W, X, mu=None):
if mu is None:
return np.dot(X,W)
return np.dot(X - mu, W)
def pca(X, y, num_components=0):
[n, d] = X.shape
if (num_components <= 0) or (num_components > n):
num_components = n
mu = X.mean(axis=0)
X = X - mu
if n > d:
C = np.dot(X.T, X)
[eigenvalues, eigenvectors] = np.linalg.eigh(C)
else:
C = np.dot(X, X.T)
[eigenvalues, eigenvectors] = np.linalg.eigh(C)
eigenvectors = np.dot(X.T, eigenvectors)
for i in xrange(n):
eigenvectors[:, i] = eigenvectors[:, i] / np.linalg.norm(eigenvectors[:, i])
idx = np.argsort(-eigenvalues)
eigenvalues = eigenvalues[idx]
eigenvectors = eigenvectors[:, idx]
eigenvalues = eigenvalues[0:num_components].copy()
eigenvectors = eigenvectors[:, 0:num_components].copy()
return [eigenvalues, eigenvectors, mu]
def lda(X, y, num_components=0):
y = np.asarray(y)
[n, d] = X.shape
c = np.unique(y)
if (num_components <= 0) or (num_components > (len(c) - 1)):
num_components = (len(c) - 1)
meanTotal = X.mean(axis=0)
Sw = np.zeros((d, d), dtype=np.float32)
Sb = np.zeros((d, d), dtype=np.float32)
for i in c:
Xi = X[np.where(y == i)[0], :]
meanClass = Xi.mean(axis=0)
Sw = Sw + np.dot((Xi - meanClass).T, (Xi - meanClass))
Sb = Sb + n * np.dot((meanClass - meanTotal).T, (meanClass - meanTotal))
eigenvalues, eigenvectors = np.linalg.eig(np.linalg.inv(Sw) * Sb)
idx = np.argsort(-eigenvalues.real)
eigenvalues, eigenvectors = eigenvalues[idx], eigenvectors[:, idx]
eigenvalues = np.array(eigenvalues[0:num_components].real, dtype=np.float32, copy=True)
eigenvectors = np.array(eigenvectors[0:, 0:num_components].real, dtype=np.float32, copy=True)
return [eigenvalues, eigenvectors]
def fisherfaces(X, y, num_components=0):
y = np.asarray(y)
# print X.shape
[n, d] = X.shape
c = len(np.unique(y))
[eigenvalues_pca, eigenvectors_pca, mu_pca] = pca(X, y, (n - c))
[eigenvalues_lda, eigenvectors_lda] = lda(project(eigenvectors_pca, X, mu_pca), y, num_components)
eigenvectors = np.dot(eigenvectors_pca, eigenvectors_lda)
return [eigenvalues_lda, eigenvectors, mu_pca]
def read_images(path):
c = 0
X, y = [], []
for dirname, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(path):
for subdirname in dirnames:
subject_path = os.path.join(dirname, subdirname)
for filename in os.listdir(subject_path):
try:
im = Image.open(os.path.join(subject_path, filename))
im = im.convert("L")
X.append(np.asarray(im, dtype=np.uint8))
y.append(c)
except IOError:
print "I/O error({0}): {1}".format(errno, strerror)
except:
print "Unexpected error:", sys.exc_info()[0]
raise
c = c + 1
return [X, y]
def FisherfacesModel(X,y,train=True):
num_components = 0
[D, W, mu] = fisherfaces(asRowMatrix(X), y, num_components)
return W,mu
def dist_metric(p, q):
p = np.asarray(p).flatten()
q = np.asarray(q).flatten()
return np.sqrt(np.sum(np.power((p - q), 2)))
def predict(W,mu,projections,y,X):
minDist = np.finfo('float').max
# print minDist
minClass = -1
Q = project(W, X.reshape(1, -1), mu)
for i in xrange(len(projections)):
dist = dist_metric(projections[i], Q)
if dist < minDist:
minDist = dist
minClass = y[i]
return minClass
if __name__ == '__main__':
##########################
###train
[X, y] = read_images('face/train')
# print y
W,mu= FisherfacesModel(X, y)
projections = []
for xi in X:
projections.append(project(W, xi.reshape(1, -1), mu))
# projections = np.array(projections)
# print projections.shape
########################
##test
[Xtest, ytest] = read_images('face/test')
accurancy = 0
for i in range(len(Xtest)):
pred = predict(W,mu,projections,y,Xtest[i])
# print "expected =", ytest[i], "/", "predicted =", pred
if pred == ytest[i]:
accurancy += 1
print accurancy
print "accurancy:",accurancy*1.0/len(Xtest)