leetcode高频题笔记之递归
文章目录
- 括号生成
- 验证二叉搜索树
- 二叉树的最大高度
- 二叉树的最小深度
- 翻转二叉树
- 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- 二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
括号生成
public class Main {
List<String>res;
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
generator(0, 0, n, "");
return new res;
}
private void generator(int left, int right, int n, String s) {
if (left == n && right == n) {
res.add(s);
return;
}
//left随时可以加,只要不超过n
if (left < n)
generator(left + 1, right, n, s + "(");
//左括号》右括号才能加右括号
if (left > right)
generator(left, right + 1, n, s + ")");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Main().generateParenthesis(3);
}
}
验证二叉搜索树
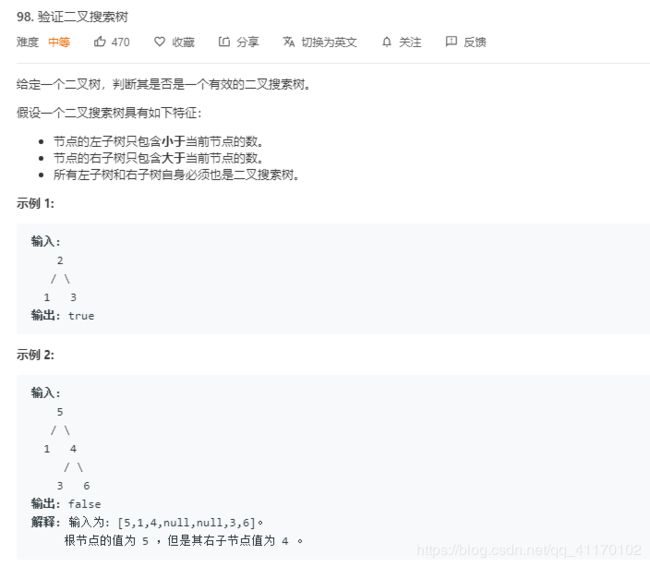
在这里需要记住一个知识点:二叉搜索树中序遍历结果就是有序的
思路1:将二叉搜索树中序遍历一次,然后将结果集逐个比对
思路2:每次保留上一个节点的值,如果当前节点的值<=上一个节点的值就直接返回false
解法1:
思路简单,效率较低
public class Main {
List<Integer> res;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
helper(root);
if (res.size() < 2) return true;
for (int i = 1; i < res.size(); i++) {
if (res.get(i) == res.get(i - 1)) return false;
}
return true;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
helper(root.left);
res.add(root.val);
helper(root.right);
}
}
解法2:(推荐)
public class Main {
//用例比较狗 用integer不够
long lastValue = Long.MIN_VALUE;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return helper(root);
}
private boolean helper(TreeNode root) {
//遍历到空了说明顺序无误往上层抛true
if (root == null) return true;
//如果左节点不满足,抛出false
if (!helper(root.left)) return false;
//如果当前节点值小于上一个节点的值,说明顺序不对,抛出false
if (root.val <= lastValue) return false;
//将上一个的值更新为当前值
lastValue = root.val;
//如果右节点不满足,抛出false
if (!helper(root.right)) return false;
//如果上述全部都不满足,说明遍历完有序,返回true
return true;
}
}
二叉树的最大高度

非常经典的递归题
最简子问题:找到左孩子和右孩子的高度的最大值再加1
public class Main {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
return root == null ? 0 : Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
二叉树的最小深度

仔细读题,千万不要大意!!!
虽然和二叉树的最大深度只相差一个字,但是坑多了不少
- 如果树的某一个子树为空,最小高度不为1,因为高度是按到叶子节点算的
- 如果[1,2]这个样例,2最为唯一叶子节点,最小高度应该是2而不是1
public class Main {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
if ((root.left == null) && (root.right != null))
return minDepth(root.right) + 1;
if ((root.left != null) && (root.right == null))
return minDepth(root.left) + 1;
return root == null ? 0 : Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + !;
}
}
翻转二叉树
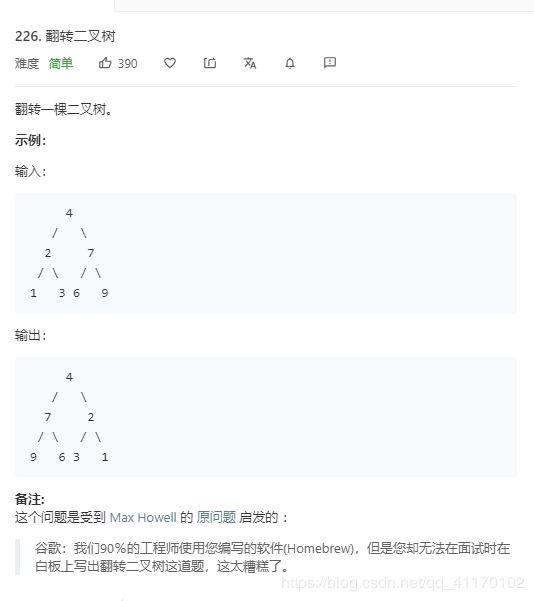
又一经典的递归实现案例
最简子问题:获取到左孩子和右孩子,然后赋值给右孩子和左孩子
public class Main {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return null;
TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left);
TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right);
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
}
}
二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- 如果两个节点都小于root,在左边
- 如果两个节点都大于root,在右边
- 如果一个大于root一个小于root或者有一个等于root,就是root
public class Main {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//保持p.val
if (p.val > q.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root, q, p);
}
//有一个等于root了
if (p.val == root.val || q.val == root.val) {
return root;
}
//两个都小于rot
if (q.val < root.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
//两个都大于root
} else if (p.val > root.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
//一大一小
} else {
return root;
}
}
}
二叉树的最近公共祖先
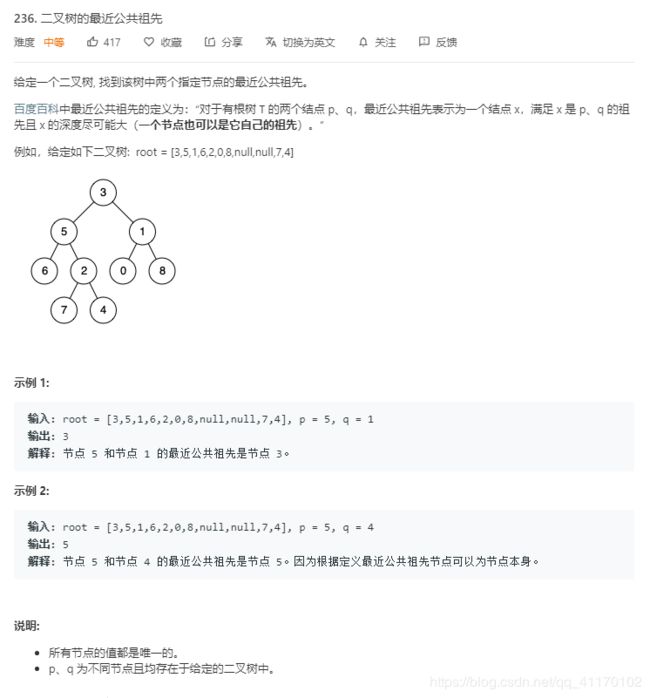
思路:
如果某个节点p,q的公共祖先,那么遍历这棵树和他的子树就一定能找到这两个节点
为了找到深度最深的,我们从根节点开始进行递归,逐层请求是否包含这两个节点,代码如下:
public class Main {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
//在左子树中没有找到,那一定在右子树中
if (left == null) {
return right;
}
//在右子树中没有找到,那一定在左子树中
if (right == null) {
return left;
}
//不在左子树,也不在右子树,那说明是根节点
return root;
}
}
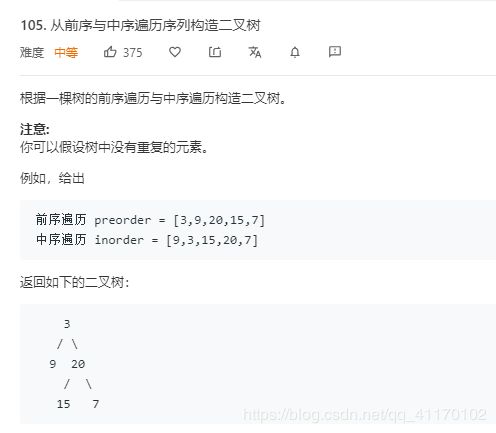
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
-
先序遍历的顺序是根节点,左子树,右子树。中序遍历的顺序是左子树,根节点,右子树。
-
所以我们只需要根据先序遍历得到根节点,然后在中序遍历中找到根节点的位置,它的左边就是左子树的节点,右边就是右子树的节点。
-
生成左子树和右子树就可以递归的进行了
对边界值和思路不太清楚的可以自己在草稿纸上模拟一下构建过程
preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
首先根据 preorder 找到根节点是 3
然后根据根节点将 inorder 分成左子树和右子树
左子树
inorder [9]
右子树
inorder [15,20,7]
把相应的前序遍历的数组也加进来
左子树
preorder[9]
inorder [9]
右子树
preorder[20 15 7]
inorder [15,20,7]
现在我们只需要构造左子树和右子树即可,成功把大问题化成了小问题
然后重复上边的步骤继续划分,直到 preorder 和 inorder 都为空,返回 null 即可
public class Main {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return builderTreeHelper(preorder, 0, preorder.length, inorder, 0, inorder.length);
}
private TreeNode builderTreeHelper(int[] preorder, int p_start, int p_end, int[] inorder, int i_start, int i_end) {
//先序为空,说明没有节点作为根节点了
if (p_start == p_end) return null;
//先序遍历获得的节点就是根结点
int root_val = preorder[p_start];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(root_val);
//从中序遍历中找到根节点的位置
int i_root_index = 0;
for (int i = i_start; i < i_end; i++) {
if (root_val == inorder[i]) {
i_root_index = i;
break;
}
}
int leftNum = i_root_index - i_start;//从中序遍历计算出左子树的节点个数,然后在前序遍历就可以划分
//递归构建左子树
root.left = builderTreeHelper(preorder, p_start + 1, p_start + leftNum + 1, inorder, i_start, i_root_index);
//递归构建右子树
root.right = builderTreeHelper(preorder, p_start + leftNum + 1, p_end, inorder, i_root_index + 1, i_end);
//构建完成,返回构建的根节点
return root;
}
}
为了简化每次递归都需要遍历一次中序遍历结果查找,将中序遍历结果存入map,查找就是0(1)了
public class Main {
Map<Integer, Integer> map;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return builderTreeHelper(preorder, 0, preorder.length, inorder, 0, inorder.length);
}
private TreeNode builderTreeHelper(int[] preorder, int p_start, int p_end, int[] inorder, int i_start, int i_end) {
//先序为空,说明没有节点作为根节点了
if (p_start == p_end) return null;
//先序遍历获得的节点就是根结点
int root_val = preorder[p_start];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(root_val);
//从中序遍历中找到根节点的位置
int i_root_index = map.get(root_val);
int leftNum = i_root_index - i_start;//从中序遍历计算出左子树的节点个数,然后在前序遍历就可以划分
//递归构建左子树
root.left = builderTreeHelper(preorder, p_start + 1, p_start + leftNum + 1, inorder, i_start, i_root_index);
//递归构建右子树
root.right = builderTreeHelper(preorder, p_start + leftNum + 1, p_end, inorder, i_root_index + 1, i_end);
//构建完成,返回构建的根节点
return root;
}
}
从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
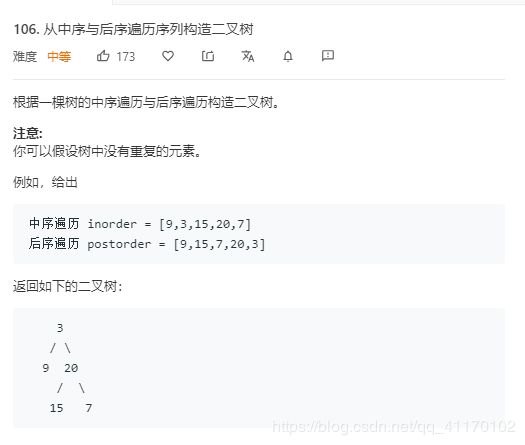
本题和105基本一致,前序遍历第一个节点是根节点,后序遍历最后一个节点是根节点
代码框架结构都是一致的,具体的边界值参数一定不要死记硬背,手写一个demo演算一下才能保证正确性
public class Main {
Map<Integer, Integer> map;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return builderTreeHelper(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder, 0, postorder.length);
}
private TreeNode builderTreeHelper(int[] inorder, int i_start, int i_end, int[] postorder, int p_start, int p_end) {
//后序为空,说明没有节点作为根节点了
if (p_start == p_end) return null;
//后序遍历的最后节点就是根结点
int root_val = postorder[p_end-1];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(root_val);
//从中序遍历中找到根节点的位置
int i_root_index = map.get(root_val);
int leftNum = i_root_index - i_start;//从中序遍历计算出左子树的节点个数,然后在后序遍历就可以划分
//递归构建左子树
root.left = builderTreeHelper(inorder, i_start, i_root_index, postorder, p_start, p_start+leftNum);
//递归构建右子树
root.right = builderTreeHelper(inorder, i_root_index+1, i_end, postorder, p_start+leftNum, p_end-1);
//构建完成,返回构建的根节点
return root;
}
}