Ubuntu之make:make命令行工具的简介、安装、使用方法之详细攻略
Ubuntu之make:make命令行工具的简介、安装、使用方法之详细攻略
目录
make命令行工具的简介
make命令行工具的安装
make命令行工具的使用方法
make命令行工具的简介
Ubuntu Make is a command line tool which allows you to download the latest version of popular developer tools on your installation, installing it alongside all of the required dependencies (which will only ask for root access if you don't have all the required dependencies installed already), enable multi-arch on your system if you are on a 64 bit machine, integrate it with the Unity launcher. Basically, one command to get your system ready to develop with!
Ubuntu Make是一个命令行工具,允许您在安装时下载最新版本的流行开发人员工具,并将其与所有必需的依赖项一起安装(如果尚未安装所有必需的依赖项,则只要求根访问),启用e如果您在64位机器上,系统上的multi-arch与Unity启动器集成。基本上,一个命令可以让您的系统准备好进行开发!
无论是在Linux还是在Unix环境中,make都是一个非常重要的编译命令。不管是自己进行项目开发还是安装应用软件,我们都经常要用到make或make install。利用make工具,我们可以将大型的开发项目分解成为多个更易于管理的模块,对于一个包括几百个源文件的应用程序,使用make和makefile工具就可以简洁明快地理顺各个源文件之间纷繁复杂的相互关系。而且如此多的源文件,如果每次都要键入gcc命令进行编译的话,那对程序员来说简直就是一场灾难。而make工具则可自动完成编译工作,并且可以只对程序员在上次编译后修改过的部分进行编译。因此,有效的利用make和makefile工具可以大大提高项目开发的效率。同时掌握make和makefile之后,您也不会再面对着Linux下的应用软件手足无措了。
ubuntu-makewiki
make命令行工具的安装
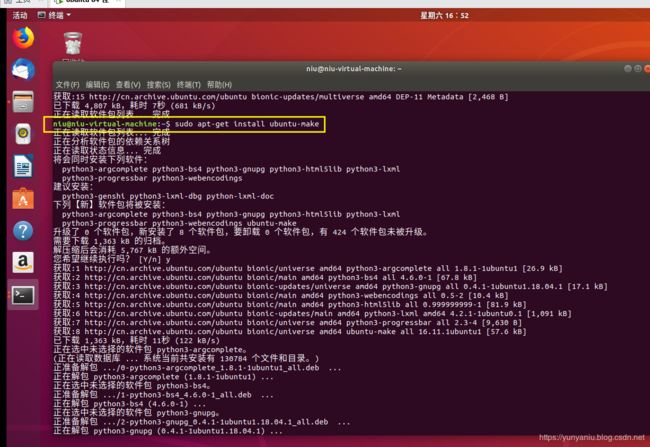
先更新找到ubuntu-make,再下载
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ubuntu-make
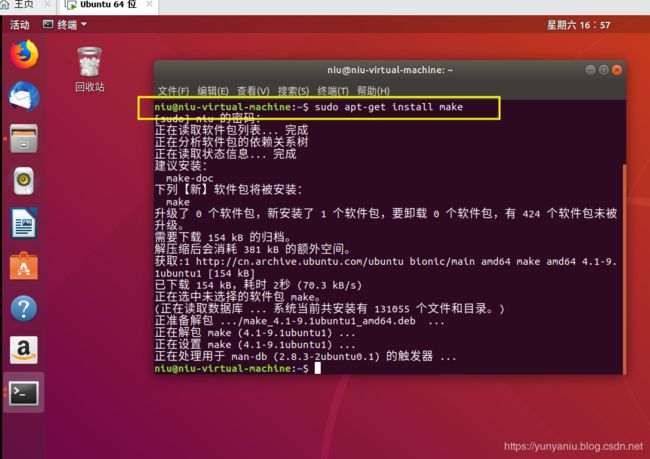
190727更新
sudo apt-get install make
make命令行工具的使用方法
1、Make命令参数的典型序列如下所示
make [-f makefile文件名][选项][宏定义][目标] #这里用[]括起来的表示是可选的。命令行选项由破折号“–”指明,后面跟选项
2、 一个简单的例子
为了编译整个工程,你可以简单的使用 make 或者在 make 命令后带上目标 all。
$ make
gcc -c -Wall test.c
gcc -c -Wall anotherTest.c
gcc -Wall test.o anotherTest.o -o test你能看到 make 命令第一次创建的依赖以及实际的目标。
如果你再次查看目录内容,里面多了一些 .o 文件和执行文件:
$ ls
anotherTest.c anotherTest.o Makefile test test.c test.h test.o现在,假设你对 test.c 文件做了一些修改,重新使用 make 编译工程:
$ make
gcc -c -Wall test.c
gcc -Wall test.o anotherTest.o -o test你可以看到只有 test.o 重新编译了,然而另一个 Test.o 没有重新编译。
现在清理所有的目标文件和可执行文件 test,你可以使用目标 clean:
$ make clean
rm -rf *.o test
$ ls
anotherTest.c Makefile test.c test.h你可以看到所有的 .o 文件和执行文件 test 都被删除了。
3. 通过 -B 选项让所有目标总是重新建立
到目前为止,你可能注意到 make 命令不会编译那些自从上次编译之后就没有更改的文件,但是,如果你想覆盖 make 这种默认的行为,你可以使用 -B 选项。下面是个例子:
$ make
make: Nothing to be done for `all'.
$ make -B
gcc -c -Wall test.c
gcc -c -Wall anotherTest.c
gcc -Wall test.o anotherTest.o -o test你可以看到尽管 make 命令不会编译任何文件,然而 make -B 会强制编译所有的目标文件以及最终的执行文件。
3. 使用 -d 选项打印调试信息
如果你想知道 make 执行时实际做了什么,使用 -d 选项。这是一个例子:
$ make -d | more
GNU Make 3.81
Copyright (C) 2006 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions.
There is NO warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
This program built for x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
Reading makefiles…
Reading makefile `Makefile'…
Updating makefiles….
Considering target file `Makefile'.
Looking for an implicit rule for `Makefile'.
Trying pattern rule with stem `Makefile'.
Trying implicit prerequisite `Makefile.o'.
Trying pattern rule with stem `Makefile'.
Trying implicit prerequisite `Makefile.c'.
Trying pattern rule with stem `Makefile'.
Trying implicit prerequisite `Makefile.cc'.
Trying pattern rule with stem `Makefile'.
Trying implicit prerequisite `Makefile.C'.
Trying pattern rule with stem `Makefile'.
Trying implicit prerequisite `Makefile.cpp'.
Trying pattern rule with stem `Makefile'.
--More--这是很长的输出,你也看到我使用了 more 命令来一页一页显示输出。
4. 使用 -C 选项改变目录
你可以为 make 命令提供不同的目录路径,在寻找 Makefile 之前会切换目录的。这是一个目录,假设你就在当前目录下:
$ ls
file file2 frnd frnd1.cpp log1.txt log3.txt log5.txt
file1 file name with spaces frnd1 frnd.cpp log2.txt log4.txt但是你想运行的 make 命令的 Makefile 文件保存在 ../make-dir/ 目录下,你可以这样做:
$ make -C ../make-dir/
make: Entering directory `/home/himanshu/practice/make-dir'
make: Nothing to be done for `all'.
make: Leaving directory `/home/himanshu/practice/make-dir你能看到 make 命令首先切到特定的目录下,在那执行,然后再切换回来。
5. 通过 -f 选项将其它文件看作 Makefile
如果你想将重命名 Makefile 文件,比如取名为 my_makefile 或者其它的名字,我们想让 make 将它也当成 Makefile,可以使用 -f 选项。
make -f my_makefile通过这种方法,make 命令会选择扫描 my_makefile 来代替 Makefile。
参考文章
详解linux下make命令的使用方法