ICS lab1: Manipulating Bits
ICS lab1: Manipulating Bits
- lab说明文档
- lab1的要求
- 使用到的运算符号及其作用
- 开始写lab
- puzzle1
- puzzle2
- puzzle3
- puzzle4
- puzzle5
- puzzle6
- puzzle7
- puzzle8
- puzzle9
- puzzle10
- puzzle11
- puzzle12
- puzzle13
- puzzle14
- puzzle15
lab说明文档
lab1的要求
lab1分为15道独立的puzzle,每道puzzle限定使用的运算符号的个数,同时限定允许使用的运算符号,用这些运算符号完成指定的int运算。在完成一道题之后,可以使用 ./dlc 检查是否合乎标准,可以使用 ./btest 检查是否正确。
使用到的运算符号及其作用
~a : 对a按位取反
!a : 逻辑非a,a=0则为1,a!=0则为0
a&b :a和b按位进行与运算
a|b :a和b按位进行或运算
a^b :a和b按位异或运算
a+b :计算a+b,不考虑溢出情况
<< : 左移运算
>> :右移运算,在本lab里全部采用算数右移
开始写lab
首先注意到lab对于格式的要求:不能定义和使用函数;仅能进行限定个数的规定运算;不能使用逻辑运算符 if else while等;一切int的定义都必须在一切int运算之前(就是不能int x=…;x=…;之后再int y=…;)
puzzle1
/*
* bang - Compute !x without using !
* Examples: bang(3) = 0, bang(0) = 1
* Legal ops: ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 12
* Rating: 4
*/
题解:
int bang(int x) {
/* right shift 31 bits of (0-1)&(~0) is 0xffffffff,others is not */
int y = x + (~0);
y = (y & (~x)) >> 31;
return (~y + 1);
}
这道题就是考察了0和其他数的不同,用 (0-1)&(~0) 或 0&((~0)+1)都可以得出结果。
puzzle2
/*
* bitCount - returns count of number of 1's in word
* Examples: bitCount(5) = 2, bitCount(7) = 3
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 40
* Rating: 4
*/
题解:
int bitCount(int x) {
/* count 1s using 0x11111111 and add them using 0x0f0f */
int y1 = (0x11) + ((0x11) << 8);
int y = y1 + (y1 << 16);
int z = x & y;
int flag = 0xf + (0xf << 8);
z = z + ((x >> 1) & y);
z = z + ((x >> 2) & y);
z = z + ((x >> 3) & y);
z = z + (z >> 16);
z = (z & flag) + ((z >> 4) & flag);
z = z + (z >> 8);
z = z & 0xff;
return z;
}
这道题比较繁琐,因为规则要求和步数限制,所以必须选择更好的方法,PPT上也有这题的详解:

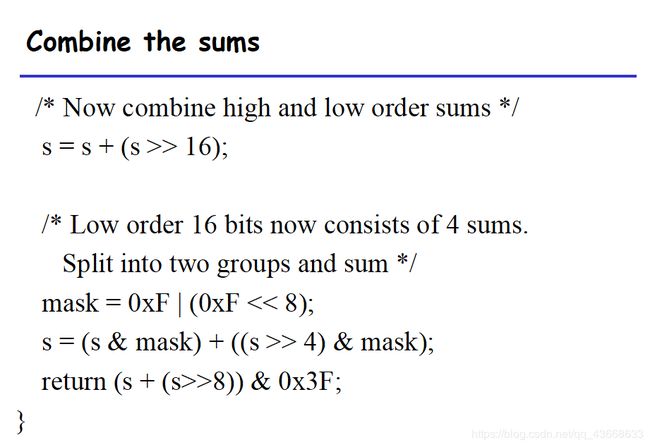
puzzle3
/*
* copyLSB - set all bits of result to least significant bit of x
* Example: copyLSB(5) = 0xFFFFFFFF, copyLSB(6) = 0x00000000
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 5
* Rating: 2
*/
题解:
int copyLSB(int x) {
/* change all bits by left shifting 31 bits then right shifting 31 bits */
int y = x << 31;
y = y >> 31;
return y;
}
因为默认为算数右移所以就先左移再右移就行了
puzzle4
/*
* divpwr2 - Compute x/(2^n), for 0 <= n <= 30
* Round toward zero
* Examples: divpwr2(15,1) = 7, divpwr2(-33,4) = -2
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 15
* Rating: 2
*/
题解:
int divpwr2(int x, int n) {
/* when one int is - ,then add 2^n -1. finally,right shift */
int flag1 = x >> 31;
int flag = flag1 & ((1<<n)+ ~0);
int y = (x +flag) >> n;
return y;
}
正的话好说,直接移就好了,负数的话需要先加上2^n-1因为要为-[log(-x)],用flag1来判断是不是负数,从而加或者不加
puzzle5
/*
* evenBits - return word with all even-numbered bits set to 1
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 8
* Rating: 2
*/
题解:
int evenBits(void) {
/* only need to left shift 0x55 */
int x = 85;
x = (x << 8) + 85;
x = (x << 8) + 85;
x = (x << 8) + 85;
return x;
}
左移0x55就好了
puzzle6
/*
* fitsBits - return 1 if x can be represented as an
* n-bit, two's complement integer.
* 1 <= n <= 32
* Examples: fitsBits(5,3) = 0, fitsBits(-4,3) = 1
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 15
* Rating: 2
*/
题解:
int fitsBits(int x, int n) {
int y = x >> (n + (~0));
int z1 = !y;
int z2 = !(y + 1);
return (z1 | z2);
}
不能表示的话x右移n-1位不等0(等0则能表示正数x)且不等-1(等-1则能表示负数x)
puzzle7
/*
* getByte - Extract byte n from word x
* Bytes numbered from 0 (LSB) to 3 (MSB)
* Examples: getByte(0x12345678,1) = 0x56
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 6
* Rating: 2
*/
题解:
int getByte(int x, int n) {
/* right shift 8n and &0xff */
int number = n << 3;
int y = x >> number;
y = y & 0xff;
return y;
}
左移再右移就好了
puzzle8
/*
* isGreater - if x > y then return 1, else return 0
* Example: isGreater(4,5) = 0, isGreater(5,4) = 1
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 24
* Rating: 3
*/
题解:
int isGreater(int x, int y) {
/* when x+,y-,then 1;when x-,y+,then 0;else x-y */
int flag1 = x + ( ~y ) + 1;
int tmp = flag1;
int flag0 = ((flag1 >> 31) + 1) &(!(!tmp));
int flag2 = ((x | (~y)) >> 31) + 1;
int flag3 = ((y | (~x)) >> 31) + 1;
int flag = flag0 | flag2;
flag = flag & (!flag3);
return flag;
}
分情况再汇总,正负为1,负正为0,否则相减,这时就不会溢出了。
puzzle9
/*
* isNonNegative - return 1 if x >= 0, return 0 otherwise
* Example: isNonNegative(-1) = 0. isNonNegative(0) = 1.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 6
* Rating: 3
*/
题解:
int isNonNegative(int x) {
/* just need judge the first bit of x */
return ((x >> 31) + 1);
}
右移不是0xffffffff而是0x00000000就好了
puzzle10
/*
* isNotEqual - return 0 if x == y, and 1 otherwise
* Examples: isNotEqual(5,5) = 0, isNotEqual(4,5) = 1
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 6
* Rating: 2
*/
题解:
int isNotEqual(int x, int y) {
/* judge if (x^y) equals 0 */
int z = x ^ y;
z = !z;
return !z;
}
异或取非非
puzzle11
/*
* isPower2 - returns 1 if x is a power of 2, and 0 otherwise
* Examples: isPower2(5) = 0, isPower2(8) = 1, isPower2(0) = 0
* Note that no negative number is a power of 2.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 60
* Rating: 4
*/
题解:
int isPower2(int x) {
/* if x is a power of 2,bitCount(x)equals 1;and x is not negative */
int y1 = (0x11) + ((0x11) << 8);
int y = y1 + (y1 << 16);
int z = x & y;
int flag = 0xf + (0xf << 8);
int a = ~0;
int b = 1;
z = z + ((x >> 1) & y);
z = z + ((x >> 2) & y);
z = z + ((x >> 3) & y);
z = z + (z >> 16);
z = (z & flag) + ((z >> 4) & flag);
z = z + (z >> 8);
z = z & 0xff;
a = !(z + a);
b = (x >> 31) + b;
return (a & b);
}
应用puzzle2,bitcount(x)为1且不是0x80000000就行了
puzzle12
/*
* leastBitPos - return a mask that marks the position of the
* least significant 1 bit. If x == 0, return 0
* Example: leastBitPos(96) = 0x20
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 6
* Rating: 4
*/
题解:
int leastBitPos(int x) {
/* the position of the least significant 1 bit is x&(-x) */
return (x & ((~x) + 1));
}
x&(-x)就行了,注意不能用负号
puzzle13
/*
* logicalShift - shift x to the right by n, using a logical shift
* Can assume that 1 <= n <= 31
* Examples: logicalShift(0x87654321,4) = 0x08765432
* Legal ops: ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 16
* Rating: 3
*/
题解:
int logicalShift(int x, int n) {
/* change the first n bits of the right shifting to 0 using right shifting of -1 */
int y = ~((1 << 31) >> (n + (~0)));
int z = (x >> n) & y;
return z;
}
用算数右移写逻辑右移
puzzle14
/*
* satAdd - adds two numbers but when positive overflow occurs, returns
* maximum possible value, and when negative overflow occurs,
* it returns minimum positive value.
* Examples: satAdd(0x40000000,0x40000000) = 0x7fffffff
* satAdd(0x80000000,0xffffffff) = 0x80000000
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
题解:
int satAdd(int x, int y) {
/* if x+,y+ or x-,y-,judge whether x+y overflow and then (num -x -y)+x+y or x+y */
int flag1 = ~((x >> 31) ^ (y >> 31));
int z = ~((x >> 31)^(1 << 31));
int num = z + (~x) + 1 + (~y) + 1;
int flag = (((x + y) >> 31) ^ (x >> 31)) & flag1;
int result = (num & flag) + x + y;
return result;
}
分情况讨论再用一种办法解决,这是个很有效的方法,如果overflow的话就(num-x-y)+x+y
puzzle15
/*
* tc2sm - Convert from two's complement to sign-magnitude
* where the MSB is the sign bit
* You can assume that x > TMin
* Example: tc2sm(-5) = 0x80000005.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 15
* Rating: 4
*/
题解:
int tc2sm(int x) {
/* a possitive number add 0(x>>31) and exclusive 0;a negative number add -1(x>>31) and exclusive 0xffffffff */
int n = x >> 31;
int y = x + n;
return ((y ^ n) + (n << 31));
}
注意好正负数的右移一个是0x00000000一个是0xffffffff就好了



