TensorFlow入门教程(7)读取数据集之TFRecord
#
#作者:韦访
#博客:https://blog.csdn.net/rookie_wei
#微信:1007895847
#添加微信的备注一下是CSDN的
#欢迎大家一起学习
#
1、概述
上一讲我们说了队列的有关知识并使用队列来读取了MNIST数据集,这一讲,我们来看看TensorFlow中很常见的TFRecord。
操作系统:Win10 64位
显卡:GTX 1080ti
Python:Python3.7
TensorFlow:1.15.0
2、TFRecord简介
通常,深度学习的数据集都是非常大的,如果数据集的图片或文本文件直接存放在磁盘中,比如上一讲中,我们将MNIST数据集保存成图片的形式,
这不仅会占用非常大的磁盘空间,而且,如果一个一个的读取这些文件会非常慢。TFRecord格式就是为了解决这个问题的,TFRecord格式使用”Protocol Buffer”二进制数据编码方案,读取时只需要一次性加载一个二进制文件即可,简单、快速,对于大型数据集的训练非常高效。
3、生成和读取TFRecord
先来看看TensorFlow如何生成和读取TFRecord。
生成
TFRecord可以写入的数据类型为3种,分别为Int64List、BytesList和FloatList,为了方便,将其封装成下面的函数,
# 整型
def int64_feature(val):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[val]))
# 字符串型
def bytes_feature(val):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[val]))
# 浮点型
def float_feature(val):
return tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=[val]))我们将要写入的数据写到Example模块中,代码如下,
# 将数据写入Example模块中
exp = tf.train.Example(
features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image/float': float_feature(0.123),
'image/int': int64_feature(28),
'image/bytes': bytes_feature(b'jpg')}))上面的代码中,我们分别将Int64List、BytesList和FloatList这3种数据类型写入到Example模块中,得到Example模块以后,再用TFRecord生成器写到文件中即可,生成器代码如下,
# TFRecord生成器
w = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(file)
w.write(exp.SerializeToString())
w.close()这样,我们就将数据写入到TFRecord格式中了。
读取
接下来看怎么读取TFRecord的数据,一般读取是需要结合我们上一讲的队列的知识,代码如下,
# TFRecord读取器
r = tf.TFRecordReader()
# 以队列的形式读取
queue = tf.train.string_input_producer([file])
key, value = r.read(queue)
# 这里features的命名和格式一定要跟写入的一样
pse = tf.parse_single_example(
value,
features={
'image/float': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32),
'image/int': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'image/bytes': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string)
}
)
f = pse['image/float']
i = pse['image/int']
b = pse['image/bytes']
with tf.Session() as sess:
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess)
fr, ir, br = sess.run([f, i, b])
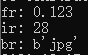
print("fr:", fr)
print("ir:", ir)
print("br:", br)生成和读取的完整代码如下,
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
import os
import shutil
# 整型
def int64_feature(val):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[val]))
# 字符串型
def bytes_feature(val):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[val]))
# 浮点型
def float_feature(val):
return tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=[val]))
# 生成TFRecord
def write(file):
# 将数据写入Example模块中
exp = tf.train.Example(
features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image/float': float_feature(0.123),
'image/int': int64_feature(28),
'image/bytes': bytes_feature(b'jpg')}))
# TFRecord生成器
w = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(file)
w.write(exp.SerializeToString())
w.close()
# 读取TFRecord
def reader(file):
# TFRecord读取器
r = tf.TFRecordReader()
# 以队列的形式读取
queue = tf.train.string_input_producer([file])
key, value = r.read(queue)
# 这里features的命名和格式一定要跟写入的一样
pse = tf.parse_single_example(
value,
features={
'image/float': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32),
'image/int': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'image/bytes': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string)
}
)
f = pse['image/float']
i = pse['image/int']
b = pse['image/bytes']
with tf.Session() as sess:
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess)
fr, ir, br = sess.run([f, i, b])
print("fr:", fr)
print("ir:", ir)
print("br:", br)
def main(argv=None):
dir = "MNIST_TFRECORD/tfrecord_writer"
if not os.path.exists(dir):
os.makedirs(dir)
file = os.path.join(dir, "test.tfrecords")
write(file)
reader(file)
if __name__ == '__main__':
tf.app.run()运行结果,
跟我们存入的数据一致。
3、将MNIST数据集以图片的形式保存
还是以MNIST数据集为例,跟上一讲一样,将数据保存成图片的形式,如下图所示,
4、将MNIST数据集制作成TFRecord格式
来看看如何将数据集制作成TFRecord格式,首先,还是老样子,遍历数据集的图片,将所有图片和其对应的标签保存到列表中,代码如下,
def load_files(dir):
print("Loading files...")
fileslist = []
labelslist = []
for path, dirs, files in os.walk(dir):
for file in files:
fileslist.append(os.path.join(path, file))
labelslist.append(int(os.path.basename(path)))
# 洗牌,打乱顺序
return shuffle(np.asarray(fileslist), np.asarray(labelslist))
# return np.asarray(fileslist), np.asarray(labelslist)接着,遍历列表,将图片数据和对应的标签写到TFRecord文件中,代码如下,
# 整型
def int64_feature(val):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[val]))
# 字符串型
def bytes_feature(val):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[val]))
# 浮点型
def float_feature(val):
return tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=[val]))
# 生成TFRecord
def write_tfrecord(file):
fileslist, labelslist = load_files("MNIST_TFRECORD/all_images")
# TFRecord生成器
w = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(file)
for i in tqdm(range(0, len(labelslist))):
images = Image.open(fileslist[i])
images = np.reshape(images, 28*28)
images = images.tobytes()
# 将数据写入Example模块中
exp = tf.train.Example(
features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'raw': bytes_feature(images),
'label': int64_feature(labelslist[i])}))
w.write(exp.SerializeToString())
w.close()调用write_tfrecord函数就可以生成TFRecord文件了,只需指定保存的文件路径即可,代码如下,
dir = "MNIST_TFRECORD/mnist_tfrecord"
if not os.path.exists(dir):
os.makedirs(dir)
file = os.path.join(dir, "mnist.tfrecords")
# 将数据集制作成TFRecord格式
write_tfrecord(file)5、读取TFRecord
制作完TFRecord后,肯定要用起来啊,来看读取的代码,我们批量读取,代码如下,
# 读取TFRecord
def get_batch(file, batchsize):
# TFRecord读取器
r = tf.TFRecordReader()
# 以队列的形式读取
queue = tf.train.string_input_producer([file])
key, value = r.read(queue)
# 这里features的命名和格式一定要跟写入的一样
pse = tf.parse_single_example(
value,
features={
'raw': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
'label': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64)
}
)
images = tf.decode_raw(pse['raw'], tf.uint8)
images = tf.reshape(images, [28 * 28])
images = tf.cast(images, tf.float32)
images /= 255
labels = tf.cast(pse['label'], tf.float32)
image_batch, label_batch = tf.train.batch([images, labels], batch_size=batchsize, capacity=20)
return image_batch, label_batch调用方式也很简单,只需要指定我们上面保存的文件以及batch size即可,代码如下,
# 批量获取数据
images_batch, labels_batch = get_batch(file, 50)
然后,在会话中,启动队列,代码如下,
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
# 从这里开始,队列才真正的开始工作
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)最后,run即可,
images, labels = sess.run([images_batch, labels_batch])6、使用CNN识别
和上一讲一样,我们获取到数据以后,将其送到CNN网络进行模型训练,也是比较简单的,直接上代码,核心代码如下,
def main(argv=None):
dir = "MNIST_TFRECORD/mnist_tfrecord"
if not os.path.exists(dir):
os.makedirs(dir)
file = os.path.join(dir, "mnist.tfrecords")
# 将数据集制作成TFRecord格式
write_tfrecord(file)
# 批量获取数据
images_batch, labels_batch = get_batch(file, 50)
# 创建x占位符,用于临时存放MNIST图片的数据,
# [None, 784]中的None表示不限长度,而784则是一张图片的大小(28×28=784)
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
# label 存的是实际图像的标签,即对应于每张输入图片实际的值
label = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
# 将图片从长度为784的向量重新还原为28×28的矩阵图片,
# 因为MNIST是黑白图片,所以深度为1,
# 第一个参数为-1,表示一维的长度不限定,这样就可以灵活设置每个batch的训练的个数了
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
# 搭建神经网络结构
acc, op, keep_prob, loss = net(x_image, label)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
# 从这里开始,队列才真正的开始工作
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
for i in range(20000):
images, labels = sess.run([images_batch, labels_batch])
# 将label转成one-hot形式
ls = []
for l in labels:
la = [i == int(l) for i in range(0, 10)]
ls.append(la)
ls = np.asarray(ls).astype(np.float)
# print('images', images)
# print('labels', ls)
# 将数据传入神经网络,开始训练
sess.run(op, feed_dict={x: images, label:ls, keep_prob: 0.5})
if i % 100 == 0:
train_accuracy = sess.run(acc, feed_dict={x: images, label:ls, keep_prob: 1.0})
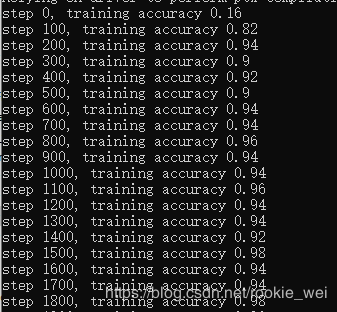
print("step %d, training accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy))运行结果,
先来看制作TFRecord,会有进度条显示制作进度,
接着就是训练过程了,如下图所示,
7、完整代码
完整代码链接如下,
https://mianbaoduo.com/o/bread/Ypaclpw=
下一讲,我们来看看读取数据集之Dataset的基本概念和知识。