区块链多链架构设计原理
术语介绍
- Validator – 主链/子链共识系统的参与者。通过存50000BU到主链中就能成为一名验证者。
- Active validator set - 那些当前正在参与的验证者以及寻求产生以及证明区块,跨链路和其他共识对象的验证者。
- Committee - 从活跃验证者集合中(伪)随机抽样的子集。当一个委员会被集体提及时,如“该委员会证明X”,这种假定为“该委员会的某个子集包含足够的验证者,该协议承认其代表委员会”。
- Proposer - 创建一个区块的验证者
- Attester -在区块上签名的委员会中的一名验证者
- Main chain – 主链是分片系统的基础
- Shard chain - 进行交易和存储账户数据的链之一
- Observer client -监控分片并存储指定分片的全数据以及主链的全状态
- Stateless Client -提供state root
- Crosslink - 来自委员会的一组签名,证明一个块在子链中,(签名)可以包含在主中。Crosslink 是主链“了解”子链更新状态的主要手段。
- Slot - 长10秒的时间段,在此期间,一个提议人能够创建一个区块,一些证明人可以进行证明
- Dynasty transition - 验证节点集的变更
- Dynasty - 创世以来在特定链中发生代迁移的数量
- Cycle -一个多区块跨度,在此期间,所有验证人都只有一次机会进行证明(除非在验证人内部发生代迁移)
-
常量
- SHARD_COUNT - 代表分片数量的常数,目前设置为1024
- DEPOSIT_SIZE – 50000BU
- MAX_VALIDATOR_COUNT – 50000*217
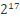
- GENESIS_TIME – 信标链的启动时间 (slot 0) 以秒为单位在Unix 周期中
- SLOT_DURATION – 10 seconds
- CYCLE_LENGTH - 64 slots
- MIN_DYNASTY_LENGTH - 1024 slots
- MIN_COMMITTEE_SIZE - 128
层次设计
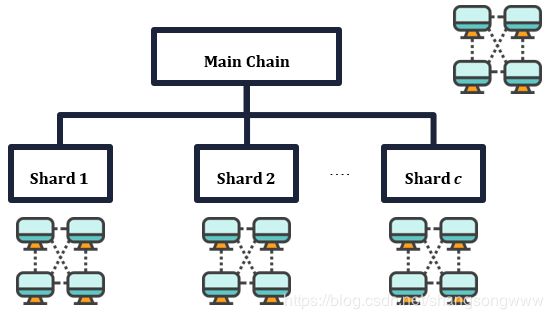
多链一共分为3层,链管理层SMC,通过一个合约SMC管理验证节点押金,验证节点随机抽样等;Date为具体的交易数据层,各个子链分别维护各个子链的全状态数据和主链的全状态;state层主要是交易的产生层,也可以说是智能合约的执行层。
基本的分片结构
假如一台计算机的处理能力为C笔交易,主链节点能观察C条子链,则整个系统能处理C*C笔交易。
多链系统中的大多数用户都会运行两部分程序。
(i) 一个在主链上的全节点(需要 O(c) 资源)或轻量节点(需要 O(log(c)) 资源)。
(ii) 一个通过 RPC 与主链交互的“子链客户端”(由于这个客户端同样运行在当前用户的计算机中,所以它被认为是可信的);它也可以作为任意子链的轻客户端、作为特定子链的全客户端(用户需要指定他们正在“监视”某个特定的子链),或者作为一个验证器节点。在这些情况下,一个子链客户端的存储和计算需求也将不会超过 O(c) (除非用户指定他们正在监视 每个 子链;区块浏览器和大型的交易所可能会这么做)。
3.3.3主链和子链的职责
主链的作用是生成随机数,保存验证节点相关信息,管理验证节点,追踪子链区块,子链的作用是处理交易,存储账户合约的状态。在本文中,术语 ShardBlock被用来与 Block(区块)相区别,因为: (i) 它们是不同的 RLP(Recursive Length Prefix)对象:交易是第 0 层的对象,ShardBlock是用来打包交易的第一层的对象,而 block 则是用来打包 ShardBlock(header)的第二层的对象; (ii) 在子链的情景中这更加清晰。通常,ShardBlock必须由ShardBlockHeader 和 TransactionList(交易列表)组成;
| Main Chain主链 |
Shard Chain子链 |
| 生成随机数 |
处理交易 |
| 保存验证节点相关信息,管理验证节点,追踪子链区块 |
存储账户/合约的状态 |
| Block |
ShardBlock |
| BlockHeader |
ShardBlockHeader |
| Block Proposer |
ShardBlock Proposer |
多链架构图
从架构图中我们可以看出具体的架构设计可以划分为4个层次,主链、子链、合约的执行处理、应用层。每个层次间的交互以及每个模块间的交互都采用BU通信协议(P2p、RPC、json、http)
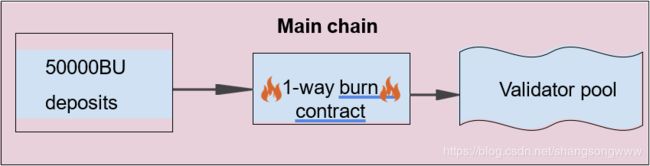
本协议中,有中央MainChain链用来存储并管理当前有效验证人集。在当前主链发送含有50000的交易才可成为初始验证人。交易发送完毕,到MainChain链处理该区块时,交易发送人进入验证人排序阶段并最终成为有效(活跃)验证人,直至自愿注销或因不当行为被强行注销。
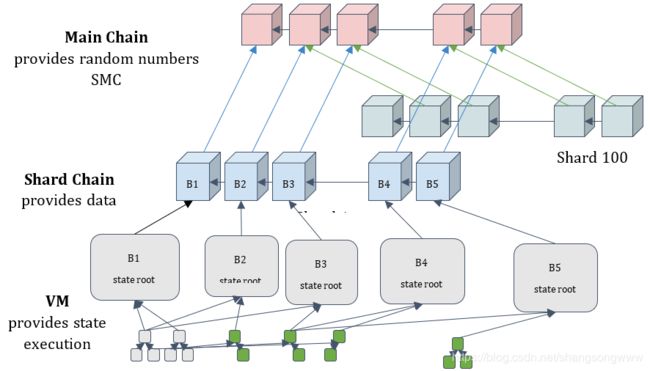
子链上的主要负载源是证明(attestations)。一个证明具有双重作用:
1. 证实主链中的某个父块
2. 证实子链中的区块哈希(足够数量的此类证明创造了“交联(crosslink)”,确认分片区块到主链中)。
每个子链(比方说,总共1024个子链)本身就是一条链,作存储交易和帐户用。交联一则用于将子链“确认”进主链,二则也是不同子链间能够彼此通讯的主要方式。或者,还可以想象个更简单的“最小子链算法”,其中交联就是提出数据块的哈希,这些数据块本身彼此互不链接。
主链变更
本子链协议可单独于现有MainChain主链实施。只需再主链中作出如下修改,其中第二个变更非技术必须。
在MainChain主链上增加合约;该合约支持存入DEPOSIT_SIZE的ETH;deposit函数以:
(i)pubkey(字节),
(ii)withdrawal_shard_id(int),
(iii)withdrawal_addr(地址),
(iv)randao_commitment(32字节),
(v)bls_proof_of_possession 为参数
从交入押金到成为一个验证的流程:
MainChain是整个orbit系统的“主链”。主要职责为:
存储并维护活跃、等待中以及退出的验证人集
处理交联(见上文)
处理自己链上的逐块共识
以下为进入每个信标链区块的字段:
fields = {
# Hash of the parent block
'parent_hash': 'hash32',
# Slot number (for the PoS mechanism)
'slot_number': 'int64',
# Randao commitment reveal
'randao_reveal': 'hash32',
# Attestations
'attestations': [AttestationRecord],
# Reference to bumo chain block
'bu_chain_ref': 'hash32',
# Hash of the active state
'active_state_root': 'hash32',
# Hash of the crystallized state
'crystallized_state_root': 'hash32',
}
主链状态分为活跃状态和结晶状态两种。
以下为活跃状态/ActiveState:
fields = {
# Attestations that have not yet been processed
'pending_attestations': [AttestationRecord],
# Most recent 2 * CYCLE_LENGTH block hashes, older to newer
'recent_block_hashes': ['hash32']
}
以下为结晶状态/CrystallizedState:
fields = {
# List of validators
'validators': [ValidatorRecord],
# Last CrystallizedState recalculation
'last_state_recalc': 'int64',
# What active validators are part of the attester set
# at what slot, and in what shard. Starts at slot
# last_state_recalc - CYCLE_LENGTH
'shard_and_committee_for_slots': [[ShardAndCommittee]],
# The last justified slot
'last_justified_slot': 'int64',
# Number of consecutive justified slots ending at this one
'justified_streak': 'int64',
# The last finalized slot
'last_finalized_slot': 'int64',
# The current dynasty
'current_dynasty': 'int64',
# Records about the most recent crosslink `for each shard
'crosslink_records': [CrosslinkRecord],
# Used to select the committees for each shard
'dynasty_seed': 'hash32',
# Start of the current dynasty
'dynasty_start': 'int64'
}
ShardAndCommittee对象的形式
fields = {
# The shard ID
'shard_id': 'int16',
# Validator indices
'committee': ['int24']
}
每个ValidatorRecord都是包含验证人信息的对象:
fields = {
# The validator's public key
'pubkey': 'int256',
# What shard the validator's balance will be sent to
# after withdrawal
'withdrawal_shard': 'int16',
# And what address
'withdrawal_address': 'address',
# The validator's current RANDAO MainChaincommitment
'randao_commitment': 'hash32',
# Current balance
'balance': 'int128',
# Dynasty where the validator is inducted
'start_dynasty': 'int64',
# Dynasty where the validator leaves
'end_dynasty': 'int64'
}
CrosslinkRecord包含待提交至区块链的上一个完整交联信息:
fields = {
# What dynasty the crosslink was submitted in
'dynasty': 'int64',
# What slot
'slot': 'int64',
# The block hash
'hash': 'hash32'
}
MainChain主链处理
处理MainChain链与处理bu1.0链在很多方面非常类似。客户端下载并处理区块,维护当前“规范链”,终止于当前的“头部”。但是,由于主链链与现有bu1.0链的关系,并且本身是一个多链的架构,所以(处理)也存在一定的差异。
由节点处理的MainChain链区块,必须满足三个条件:
parent_hash指向的父区块已被处理并认可
pow_chain_ref指向的bu1.0链区块已被处理并认可
节点的本地时钟时间大于或等于GENESIS_TIME + slot_number * SLOT_DURATION计算得出的最小时间戳
未满足这三个条件时,客户端应延迟处理区块,直至三个条件都满足。
客户端只在需要创建区块时检查其认为是规范链的链,并查找其时隙号;时隙到达时,按要求提议或证实区块。
以下为工作原理的例子:
MainChain状态迁移函数
现在定义下状态迁移函数。设置层面,状态迁移由两部分组成:
1. 结晶状态重算,仅在block.slot_number> = last_state_recalc + CYCLE_LENGTH时发生,且影响CrystallizedState和ActiveState
2. 每块处理,即每个区块都发生(结晶状态重算区块期间时,(每块处理)待结晶状态重算之后发生),且仅影响ActiveState
结晶状态重算通常关注验证人集的变更,包括调整余额、添加删除验证人以及处理交联和管理区块合理(block justification);每块处理通常关注验证聚合签名并保存ActiveState中区块内活动相关的临时记录。
辅助函数
先来定义一些辅助算法。首先,选择活跃验证人的函数:
def get_active_validator_indices(validators, dynasty):
o = []
for i in range(len(validators)):
if validators[i].start_dynasty <= dynasty < \
validators[i].end_dynasty:
o.append(i)
return o
然后是置乱该列表的函数:
def shuffle(lst, seed):
assert len(lst) <= 16777216
o = [x for x in lst]
source = seed
i = 0
while i < len(lst):
source = blake(source)
for pos in range(0, 30, 3):
m = int.from_bytes(source[pos:pos+3], 'big')
remaining = len(lst) - i
if remaining == 0:
break
rand_max = 16777216 - 16777216 % remaining
if m < rand_max:
replacement_pos = (m % remaining) + i
o[i], o[replacement_pos] = o[replacement_pos], o[i]
i += 1
return o
以下为将列表分成N份的函数:
def split(lst, N):
return [lst[len(lst)*i//N: len(lst)*(i+1)//N] for i in range(N)]
合并上述函数,就是辅助函数了:
def get_new_shuffling(seed, validators, dynasty, crosslinking_start_shard):
avs = get_active_validator_indices(validators, dynasty)
if len(avs) >= CYCLE_LENGTH * MIN_COMMITTEE_SIZE:
committees_per_slot = len(avs) // CYCLE_LENGTH // (MIN_COMMITTEE_SIZE * 2) + 1
slots_per_committee = 1
else:
committees_per_slot = 1
slots_per_committee = 1
while len(avs) * slots_per_committee < CYCLE_LENGTH * MIN_COMMITTEE_SIZE \
and slots_per_committee < CYCLE_LENGTH:
slots_per_committee *= 2
o = []
for i, slot_indices in enumerate(split(shuffle(avs, seed), CYCLE_LENGTH)):
shard_indices = split(slot_indices, committees_per_slot)
shard_id_start = crosslinking_start_shard + \
i * committees_per_slot // slots_per_committee
o.append([ShardAndCommittee(
shard_id = (shard_id_start + j) % SHARD_COUNT,
committee = indices
) for j, indices in enumerate(shard_indices)])
return o
用图片表示下原理: