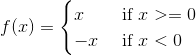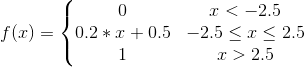ncnn源码学习(七):常见操作算子(上)
1.绝对值操作:AbsVal
对应代码:
// 前向在位传播
int AbsVal::forward_inplace(Mat& bottom_top_blob, const Option& opt) const
{
// 输入的width,height和channels
int w = bottom_top_blob.w;
int h = bottom_top_blob.h;
int channels = bottom_top_blob.c;
int size = w * h;
// 并行计算
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int q=0; q2.取最大top-k操作:ArgMax
对输入进行排序,取前k个最大值,如果是top-1,返还最大值及对应序号,否则,只返还top-k对应序号:
// 前向传播
int ArgMax::forward(const Mat& bottom_blob, Mat& top_blob, const Option& opt) const
{
int size = bottom_blob.total();
// 默认(topk, 1)
// 如果是top-1,获取最大值及序号
// 否则,只获取序号
if (out_max_val)
top_blob.create(topk, 2, 4u, opt.blob_allocator);
else
top_blob.create(topk, 1, 4u, opt.blob_allocator);
if (top_blob.empty())
return -100;
// 输入的指针
const float* ptr = bottom_blob;
// partial sort topk with index
// optional value
std::vector< std::pair > vec;
vec.resize(size);
// 绑定对应索引
for (int i=0; i >());
float* outptr = top_blob;
if (out_max_val)
{
float* valptr = outptr + topk;
// 获取值及序号
for (int i=0; i 3.批归一化:BatchNorm
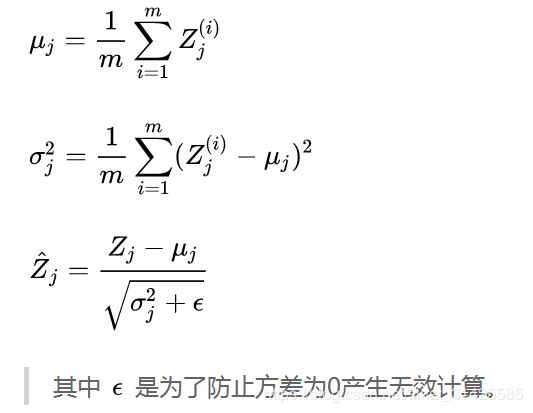
batch normalization的原因是为了缓解Internal Covariate Shift:在深层网络训练的过程中,由于网络中参数变化而引起内部结点数据分布发生变化的过程。
对每个特征进行独立的normalization,使得第l层每个特征的输入的分布都是0均值,方差为1,缓解了ICS,但是让每一层网络的输入数据分布都变得稳定,但却导致了数据表达能力的缺失。也就是我们通过变换操作改变了原有数据的信息表达(representation ability of the network),使得底层网络学习到的参数信息丢失。另一方面,通过让每一层的输入分布均值为0,方差为1,会使得输入在经过sigmoid或tanh激活函数时,容易陷入非线性激活函数的线性区域。(摘自参考资料[2])因此,BN引入两个可学习的参数,对规范化后的数据进行线性变换,恢复数据本身的表达能力:
这里跟NCNN代码就很好对应起来了:
// 载入模型
int BatchNorm::load_model(const ModelBin& mb)
{
// slope数据
slope_data = mb.load(channels, 1);
// 载入失败:返还-100
if (slope_data.empty())
return -100;
// mean数据
mean_data = mb.load(channels, 1);
// 载入数据失败,返还-100
if (mean_data.empty())
return -100;
// variance数据
var_data = mb.load(channels, 1);
// 载入数据失败,返还-100
if (var_data.empty())
return -100;
// bias数据
bias_data = mb.load(channels, 1);
// 载入数据失败,返还-100
if (bias_data.empty())
return -100;
// 创建矩阵
a_data.create(channels);
if (a_data.empty())
return -100;
// 创建矩阵
b_data.create(channels);
if (b_data.empty())
return -100;
for (int i=0; i4.偏置项:Bias
这个没啥,就是加上一个偏置常量,很简单:
// 在位前向传播
int Bias::forward_inplace(Mat& bottom_top_blob, const Option& opt) const
{
// 自下而上blob的size
int w = bottom_top_blob.w;
int h = bottom_top_blob.h;
int channels = bottom_top_blob.c;
int size = w * h;
// 前向操作就是一个加上bias的过程
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int q=0; q5.二项正态对数似然(binomial normal log likelihood):BNLL
![]()
对应代码为:
int BNLL::forward_inplace(Mat& bottom_top_blob, const Option& opt) const
{
int w = bottom_top_blob.w;
int h = bottom_top_blob.h;
int channels = bottom_top_blob.c;
int size = w * h;
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int q=0; q 0)
ptr[i] = ptr[i] + log(1.f + exp(-ptr[i]));
else
ptr[i] = log(1.f + exp(ptr[i]));
}
}
return 0;
} 6.类型转换:Cast
int Cast::forward(const Mat& bottom_blob, Mat& top_blob, const Option& opt) const
{
// 不需要进行类型转换
if (type_from == type_to)
{
top_blob = bottom_blob;
return 0;
}
int w = bottom_blob.w;
int h = bottom_blob.h;
int channels = bottom_blob.c;
int dims = bottom_blob.dims;
size_t elemsize = bottom_blob.elemsize;
int elempack = bottom_blob.elempack;
size_t out_elemsize = elemsize;
if (type_to == 1)
{
// float32
out_elemsize = 4 * elempack;
}
else if (type_to == 2)
{
// float16
out_elemsize = 2 * elempack;
}
else if (type_to == 3)
{
// int8
out_elemsize = elempack;
}
// 为输出分配内存
if (dims == 1)
{
top_blob.create(w, out_elemsize, elempack, opt.blob_allocator);
}
else if (dims == 2)
{
top_blob.create(w, h, out_elemsize, elempack, opt.blob_allocator);
}
else if (dims == 3)
{
top_blob.create(w, h, channels, out_elemsize, elempack, opt.blob_allocator);
}
if (top_blob.empty())
return -100;
int size = w * h * elempack;
// float32转float16
if (type_from == 1 && type_to == 2)
{
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int q=0; q7.截断:clip
int Clip::forward_inplace(Mat& bottom_top_blob, const Option& opt) const
{
int w = bottom_top_blob.w;
int h = bottom_top_blob.h;
int channels = bottom_top_blob.c;
int size = w * h;
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int q=0; q max)
ptr[i] = max;
}
}
return 0;
} 8.数据拼接:Concat
按照某个维度,对输入进行拼接,对应代码为:
// 前向传播:数据拼接
int Concat::forward(const std::vector& bottom_blobs, std::vector& top_blobs, const Option& opt) const
{
// 输入的blobs维度
int dims = bottom_blobs[0].dims;
// 每个blob的元素大小
size_t elemsize = bottom_blobs[0].elemsize;
// 如果是一维的
if (dims == 1) // axis == 0
{
// concat vector
// total length
int top_w = 0;
// 计算拼接后向量大小
for (size_t b=0; b 9. 目标检测输出:DetectionOutput
对目标检测模型输出层做非极大值抑制(NMS)等后处理,输出检测结果,NMS具体来说分为两个步骤,第一个步骤是按照置信度对检测到的boundingbox排序,ncnn采用的是快速排序法,代码如下:
template
static void qsort_descent_inplace(std::vector& datas, std::vector& scores, int left, int right)
{
int i = left;
int j = right;
float p = scores[(left + right) / 2];
while (i <= j)
{
while (scores[i] > p)
i++;
while (scores[j] < p)
j--;
if (i <= j)
{
// swap
std::swap(datas[i], datas[j]);
std::swap(scores[i], scores[j]);
i++;
j--;
}
}
if (left < j)
qsort_descent_inplace(datas, scores, left, j);
if (i < right)
qsort_descent_inplace(datas, scores, i, right);
}
排序完成后,根据框与框之间的交并比(IOU)对检测结果进行过滤:
static void nms_sorted_bboxes(const std::vector& bboxes, std::vector& picked, float nms_threshold)
{
picked.clear();
const int n = bboxes.size();
std::vector areas(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
const BBoxRect& r = bboxes[i];
float width = r.xmax - r.xmin;
float height = r.ymax - r.ymin;
areas[i] = width * height;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
const BBoxRect& a = bboxes[i];
int keep = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < (int)picked.size(); j++)
{
const BBoxRect& b = bboxes[picked[j]];
// intersection over union
float inter_area = intersection_area(a, b);
float union_area = areas[i] + areas[picked[j]] - inter_area;
// float IoU = inter_area / union_area
if (inter_area / union_area > nms_threshold)
keep = 0;
}
if (keep)
picked.push_back(i);
}
} 具体一点就是,ncnn在这里提供了对输出Mat的所有后处理过程:如解析输出位置、置信度、先验框对应blob,然后做NMS处理,得到最终输出结果
int DetectionOutput::forward(const std::vector& bottom_blobs, std::vector& top_blobs, const Option& opt) const
{
const Mat& location = bottom_blobs[0];
const Mat& confidence = bottom_blobs[1];
const Mat& priorbox = bottom_blobs[2];
bool mxnet_ssd_style = num_class == -233;
// mxnet-ssd _contrib_MultiBoxDetection
const int num_prior = mxnet_ssd_style ? priorbox.h : priorbox.w / 4;
int num_class_copy = mxnet_ssd_style ? confidence.h : num_class;
// apply location with priorbox
Mat bboxes;
bboxes.create(4, num_prior, 4u, opt.workspace_allocator);
if (bboxes.empty())
return -100;
const float* location_ptr = location;
const float* priorbox_ptr = priorbox.row(0);
const float* variance_ptr = mxnet_ssd_style ? 0 : priorbox.row(1);
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int i = 0; i < num_prior; i++)
{
const float* loc = location_ptr + i * 4;
const float* pb = priorbox_ptr + i * 4;
const float* var = variance_ptr ? variance_ptr + i * 4 : variances;
float* bbox = bboxes.row(i);
// CENTER_SIZE
float pb_w = pb[2] - pb[0];
float pb_h = pb[3] - pb[1];
float pb_cx = (pb[0] + pb[2]) * 0.5f;
float pb_cy = (pb[1] + pb[3]) * 0.5f;
float bbox_cx = var[0] * loc[0] * pb_w + pb_cx;
float bbox_cy = var[1] * loc[1] * pb_h + pb_cy;
float bbox_w = exp(var[2] * loc[2]) * pb_w;
float bbox_h = exp(var[3] * loc[3]) * pb_h;
bbox[0] = bbox_cx - bbox_w * 0.5f;
bbox[1] = bbox_cy - bbox_h * 0.5f;
bbox[2] = bbox_cx + bbox_w * 0.5f;
bbox[3] = bbox_cy + bbox_h * 0.5f;
}
// sort and nms for each class
std::vector< std::vector > all_class_bbox_rects;
std::vector< std::vector > all_class_bbox_scores;
all_class_bbox_rects.resize(num_class_copy);
all_class_bbox_scores.resize(num_class_copy);
// start from 1 to ignore background class
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int i = 1; i < num_class_copy; i++)
{
// filter by confidence_threshold
std::vector class_bbox_rects;
std::vector class_bbox_scores;
for (int j = 0; j < num_prior; j++)
{
// prob data layout
// caffe-ssd = num_class x num_prior
// mxnet-ssd = num_prior x num_class
float score = mxnet_ssd_style ? confidence[i * num_prior + j] : confidence[j * num_class_copy + i];
if (score > confidence_threshold)
{
const float* bbox = bboxes.row(j);
BBoxRect c = { bbox[0], bbox[1], bbox[2], bbox[3], i };
class_bbox_rects.push_back(c);
class_bbox_scores.push_back(score);
}
}
// sort inplace
qsort_descent_inplace(class_bbox_rects, class_bbox_scores);
// keep nms_top_k
if (nms_top_k < (int)class_bbox_rects.size())
{
class_bbox_rects.resize(nms_top_k);
class_bbox_scores.resize(nms_top_k);
}
// apply nms
std::vector picked;
nms_sorted_bboxes(class_bbox_rects, picked, nms_threshold);
// select
for (int j = 0; j < (int)picked.size(); j++)
{
int z = picked[j];
all_class_bbox_rects[i].push_back(class_bbox_rects[z]);
all_class_bbox_scores[i].push_back(class_bbox_scores[z]);
}
}
// gather all class
std::vector bbox_rects;
std::vector bbox_scores;
for (int i = 1; i < num_class_copy; i++)
{
const std::vector& class_bbox_rects = all_class_bbox_rects[i];
const std::vector& class_bbox_scores = all_class_bbox_scores[i];
bbox_rects.insert(bbox_rects.end(), class_bbox_rects.begin(), class_bbox_rects.end());
bbox_scores.insert(bbox_scores.end(), class_bbox_scores.begin(), class_bbox_scores.end());
}
// global sort inplace
qsort_descent_inplace(bbox_rects, bbox_scores);
// keep_top_k
if (keep_top_k < (int)bbox_rects.size())
{
bbox_rects.resize(keep_top_k);
bbox_scores.resize(keep_top_k);
}
// fill result
int num_detected = bbox_rects.size();
if (num_detected == 0)
return 0;
Mat& top_blob = top_blobs[0];
top_blob.create(6, num_detected, 4u, opt.blob_allocator);
if (top_blob.empty())
return -100;
for (int i = 0; i < num_detected; i++)
{
const BBoxRect& r = bbox_rects[i];
float score = bbox_scores[i];
float* outptr = top_blob.row(i);
outptr[0] = r.label;
outptr[1] = score;
outptr[2] = r.xmin;
outptr[3] = r.ymin;
outptr[4] = r.xmax;
outptr[5] = r.ymax;
}
return 0;
} 10.随机失活:Dropout
在训练阶段按照一定的概率P,随机地断开部分神经元之间连接,只让神经网络的部分神经元进行学习,在测试阶段,会对当前层神经元的权重乘以概率P,Dropout能够有效降低过拟合风险,Dropout原理请自行google,那么ncnn里面Dropout实现,实际上就是给权重乘以一个因子scale,具体代码如下:
int Dropout::forward_inplace(Mat& bottom_top_blob, const Option& opt) const
{
if (scale == 1.f)
{
return 0;
}
int w = bottom_top_blob.w;
int h = bottom_top_blob.h;
int channels = bottom_top_blob.c;
int size = w * h;
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int q=0; q11.ELU激活函数
计算公式为:
对应ncnn代码为:
int ELU::forward_inplace(Mat& bottom_top_blob, const Option& opt) const
{
int w = bottom_top_blob.w;
int h = bottom_top_blob.h;
int channels = bottom_top_blob.c;
int size = w * h;
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int q=0; q12.Exp操作
计算公式为:
对应ncnn源码为:
int Exp::forward_inplace(Mat& bottom_top_blob, const Option& opt) const
{
int w = bottom_top_blob.w;
int h = bottom_top_blob.h;
int channels = bottom_top_blob.c;
int size = w * h;
if (base == -1.f)
{
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int q=0; q13.ExpandDims:增加维度
具体操作就是对输入blob沿着某个axes增加长度为1的维度,与squeeze刚好相反,具体代码为:
// 增加维度
int ExpandDims::forward(const Mat& bottom_blob, Mat& top_blob, const Option& opt) const
{
int w = bottom_blob.w;
int h = bottom_blob.h;
int dims = bottom_blob.dims;
top_blob = bottom_blob;
// 输入为一维
if (dims == 1)
{
// 沿着width方向增加维度
if (expand_w)
{
// 沿着height方向增加维度
if (expand_h)
top_blob = bottom_blob.reshape(1, 1, w, opt.blob_allocator);
// 沿着channel方向增加维度
else if (expand_c)
top_blob = bottom_blob.reshape(1, w, 1, opt.blob_allocator);
// 只在width方向增加维度
else
top_blob = bottom_blob.reshape(1, w, opt.blob_allocator);
}
// 沿着height方向增加维度
else if (expand_h)
{
// 沿着channel方向增加维度
if (expand_c)
top_blob = bottom_blob.reshape(w, 1, 1, opt.blob_allocator);
// 只沿着height方向增加维度
else
top_blob = bottom_blob.reshape(w, 1, opt.blob_allocator);
}
}
// 输入维度为二
else if (dims == 2)
{
// 沿着width方向增加维度
if (expand_w)
top_blob = bottom_blob.reshape(1, w, h, opt.blob_allocator);
// 沿着height方向增加维度
else if (expand_h)
top_blob = bottom_blob.reshape(w, 1, h, opt.blob_allocator);
// 沿着channel方向增加维度
else if (expand_c)
top_blob = bottom_blob.reshape(w, h, 1, opt.blob_allocator);
}
if (top_blob.empty())
return -100;
return 0;
}14.Flatten操作
就是将输入blob按照channel展开,并拉伸成一个一维数组,具体代码为:
int Flatten::forward(const Mat& bottom_blob, Mat& top_blob, const Option& opt) const
{
int w = bottom_blob.w;
int h = bottom_blob.h;
int channels = bottom_blob.c;
size_t elemsize = bottom_blob.elemsize;
int size = w * h;
// 输出blob长度
top_blob.create(size * channels, elemsize, opt.blob_allocator);
if (top_blob.empty())
return -100;
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int q=0; q15.HardSigmoid操作
对应计算公式为:
对应ncnn代码为:
int HardSigmoid::forward_inplace(Mat& bottom_top_blob, const Option& opt) const
{
int w = bottom_top_blob.w;
int h = bottom_top_blob.h;
int channels = bottom_top_blob.c;
int size = w * h;
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(opt.num_threads)
for (int q=0; q upper)
ptr[i] = 1.f;
// 0.2*x + 0.5
else
ptr[i] = ptr[i] * alpha + beta;
}
}
return 0;
}
参考资料:
[1] https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn
[2] https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/34879333