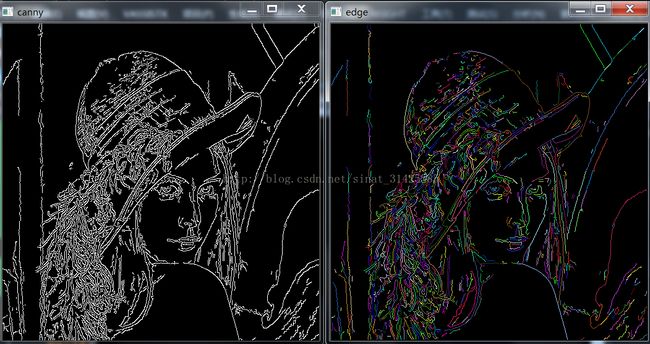
图像处理(五):八邻域边缘跟踪与区域生长算法
通常在进行边缘检测之后,需要通过边缘跟踪来将离散的边缘串接起来,常使用的方法为:边缘跟踪和区域生长两种方法。边缘跟踪又分为八邻域和四邻域两种,具体原理可以参考残影、的博客。
实现步骤:
1、灰度化并进行Canny边缘检测
2、按照预先设定的跟踪方向(顺时针)进行边缘跟踪
3、每次跟踪的终止条件为:8邻域都不存在轮廓
这里需要理解的点:
代码中为什么更新当前方向时,需要curr_d -= 2,原因如下:
一次八领域搜索是以当前点pt1为中心,顺时针(或逆时针)遍历八个邻近像素以后,定位到下一个像素点pt2,下一次遍历时,就以pt2为中心,再次遍历八个邻近像素,第二次遍历过程与第一次遍历过程存在重叠部分,这里 -2的目的就是为了避免与第一次遍历重复,减少无用功,至于为什么是2,你画个图自己推一推就知道了。
这里将残影博客中的图拿过来贴一下,帮助大家理解:
这里pt1为红色的3,第一次遍历时,找到7,因此,pt2为黑色的7。第一次遍历找到黑色点7意味着黑色的0-6位置不存在边缘像素,而黑色的0、6位置及pt1位置与红色的2、3、4位置是重叠的,这些位置不需要再次去遍历,而当前方向为红色7,将7-2=5,从5开始遍历,就可以避免再次遍历到红色2,3,4位置。
代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
// 8 neighbors
const Point directions[8] = { { 0, 1 }, {1,1}, { 1, 0 }, { 1, -1 }, { 0, -1 }, { -1, -1 }, { -1, 0 },{ -1, 1 } };
int main()
{
// 生成随机数
RNG rng(time(0));
Mat src = imread("1.jpg");
Mat gray;
cvtColor(src, gray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
Mat Edge;
// Canny边缘检测
Canny(gray, Edge, 50, 100);
vector edge_t;
vector> edges;
// 边缘跟踪
int i, j, counts = 0, curr_d = 0;
for (i = 1; i < Edge.rows - 1; i++)
for (j = 1; j < Edge.cols - 1; j++)
{
// 起始点及当前点
//Point s_pt = Point(i, j);
Point b_pt = Point(i, j);
Point c_pt = Point(i, j);
// 如果当前点为前景点
if (255 == Edge.at(c_pt.x, c_pt.y))
{
edge_t.clear();
bool tra_flag = false;
// 存入
edge_t.push_back(c_pt);
Edge.at(c_pt.x, c_pt.y) = 0; // 用过的点直接给设置为0
// 进行跟踪
while (!tra_flag)
{
// 循环八次
for (counts = 0; counts < 8; counts++)
{
// 防止索引出界
if (curr_d >= 8)
{
curr_d -= 8;
}
if (curr_d < 0)
{
curr_d += 8;
}
// 当前点坐标
// 跟踪的过程,应该是个连续的过程,需要不停的更新搜索的root点
c_pt = Point(b_pt.x + directions[curr_d].x, b_pt.y + directions[curr_d].y);
// 边界判断
if ((c_pt.x > 0) && (c_pt.x < Edge.cols - 1) &&
(c_pt.y > 0) && (c_pt.y < Edge.rows - 1))
{
// 如果存在边缘
if (255 == Edge.at(c_pt.x, c_pt.y))
{
curr_d -= 2; // 更新当前方向
edge_t.push_back(c_pt);
Edge.at(c_pt.x, c_pt.y) = 0;
// 更新b_pt:跟踪的root点
b_pt.x = c_pt.x;
b_pt.y = c_pt.y;
//cout << c_pt.x << " " << c_pt.y << endl;
break; // 跳出for循环
}
}
curr_d++;
} // end for
// 跟踪的终止条件:如果8邻域都不存在边缘
if (8 == counts )
{
// 清零
curr_d = 0;
tra_flag = true;
edges.push_back(edge_t);
break;
}
} // end if
} // end while
}
// 显示一下
Mat trace_edge = Mat::zeros(Edge.rows, Edge.cols, CV_8UC1);
Mat trace_edge_color;
cvtColor(trace_edge, trace_edge_color, CV_GRAY2BGR);
for (i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++)
{
Scalar color = Scalar(rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255));
//cout << edges[i].size() << endl;
// 过滤掉较小的边缘
if (edges[i].size() > 5)
{
for (j = 0; j < edges[i].size(); j++)
{
trace_edge_color.at(edges[i][j].x, edges[i][j].y)[0] = color[0];
trace_edge_color.at(edges[i][j].x, edges[i][j].y)[1] = color[1];
trace_edge_color.at(edges[i][j].x, edges[i][j].y)[2] = color[2];
}
}
}
imshow("edge", trace_edge_color);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
效果如下:
至于区域生长算法可以直接参考博文点击打开链接,代码写的很棒!
该勤快的时候不能懒,好吧,还是自己实现了一遍,代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
// 8邻域
const Point neighbors[8] = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 1, -1 },
{ 0, -1 }, { -1, -1 }, { -1, 0 }, {-1, 1} };
int main()
{
// 生成随机数
RNG rng(time(0));
Mat src = imread("1.jpg");
Mat gray;
cvtColor(src, gray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
Mat edges;
Canny(gray, edges, 30, 100);
vector seeds;
vector contour;
vector> contours;
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < edges.rows; i++)
for (j = 0; j < edges.cols; j++)
{
Point c_pt = Point(i, j);
//如果当前点为轮廓点
if (edges.at(c_pt.x, c_pt.y) == 255)
{
contour.clear();
// 当前点清零
edges.at(c_pt.x, c_pt.y) = 0;
// 存入种子点及轮廓
seeds.push_back(c_pt);
contour.push_back(c_pt);
// 区域生长
while (seeds.size() > 0)
{
// 遍历8邻域
for (k = 0; k < 8; k++)
{
// 更新当前点坐标
c_pt.x = seeds[0].x + neighbors[k].x;
c_pt.y = seeds[0].y + neighbors[k].y;
// 边界界定
if ((c_pt.x >= 0) && (c_pt.x <= edges.rows - 1) &&
(c_pt.y >= 0) && (c_pt.y <= edges.cols - 1))
{
if (edges.at(c_pt.x, c_pt.y) == 255)
{
// 当前点清零
edges.at(c_pt.x, c_pt.y) = 0;
// 存入种子点及轮廓
seeds.push_back(c_pt);
contour.push_back(c_pt);
}// end if
}
} // end for
// 删除第一个元素
seeds.erase(seeds.begin());
}// end while
contours.push_back(contour);
}// end if
}
// 显示一下
Mat trace_edge = Mat::zeros(edges.rows, edges.cols, CV_8UC1);
Mat trace_edge_color;
cvtColor(trace_edge, trace_edge_color, CV_GRAY2BGR);
for (i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++)
{
Scalar color = Scalar(rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255));
//cout << edges[i].size() << endl;
// 过滤掉较小的边缘
if (contours[i].size() > 5)
{
for (j = 0; j < contours[i].size(); j++)
{
trace_edge_color.at(contours[i][j].x, contours[i][j].y)[0] = color[0];
trace_edge_color.at(contours[i][j].x, contours[i][j].y)[1] = color[1];
trace_edge_color.at(contours[i][j].x, contours[i][j].y)[2] = color[2];
}
}
}
imshow("edge", trace_edge_color);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
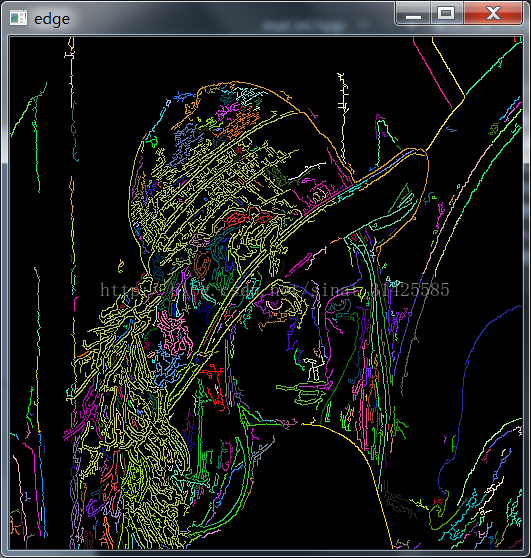
效果如下:
参考资料:
[1] https://blog.csdn.net/liumangmao1314/article/details/53844570