目录
- 循环冗余校验码
- 简单例子
- 程序代码
- 运行结果
循环冗余校验码
了解CRC校验简单例子
实际的CRC校验码生成是采用二进制的模2算法(即减法不借位、加法不进位)计算出来的,这是一种异或操作。下面通过一些例子来进一步解释CRC的基本工作原理。假设:
(1)设约定的生成多项式为G(x)=x4+x+1,其二进制表示为10011,共5位,其中k=4。
(2)假设要发送数据序列的二进制为101011(即f(x)),共6位。
(3)在要发送的数据后面加4个0(生成f(x)*xk),二进制表示为1010110000,共10位。
(4)用生成多项式的二进制表示10011去除乘积1010110000,按模2算法求得余数比特序列为0100(注意余数一定是k位的)。
(5)将余数添加到要发送的数据后面,得到真正要发送的数据的比特流:1010110100,其中前6位为原始数据,后4位为CRC校验码。
(6)接收端在接收到带CRC校验码的数据后,如果数据在传输过程中没有出错,将一定能够被相同的生成多项式G(x)除尽,如果数据在传输中出现错误,生成多项式G(x)去除后得到的结果肯定不为0。
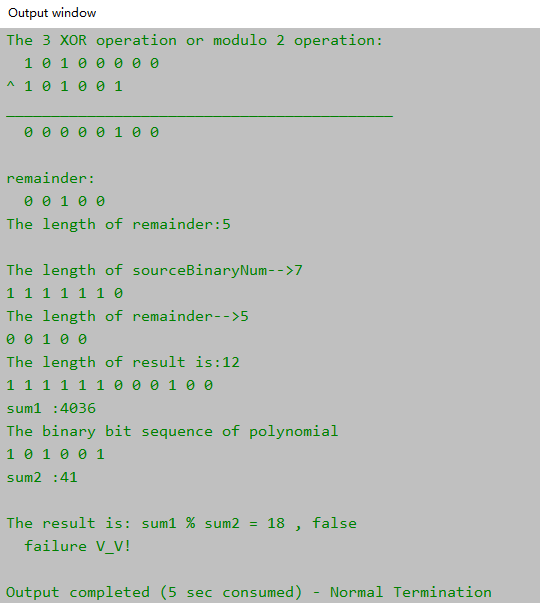
程序代码
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
*
* author: Zou WenXiang
* version: 1.0
* tool:Windows 10 Editplus5.2 JDK1.8.0
*/
public class CRCCheckTest {
private static int counts = 1; // Used to record the number of modulo 2 operations.
public static int[] checkBitArray = {1,0,1,0,0,1}; // Used to store the binary bit sequence of polynomials.
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get user input through the Scanner class.
// Create a Scanner object.
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
CRCCheckTest test = new CRCCheckTest();
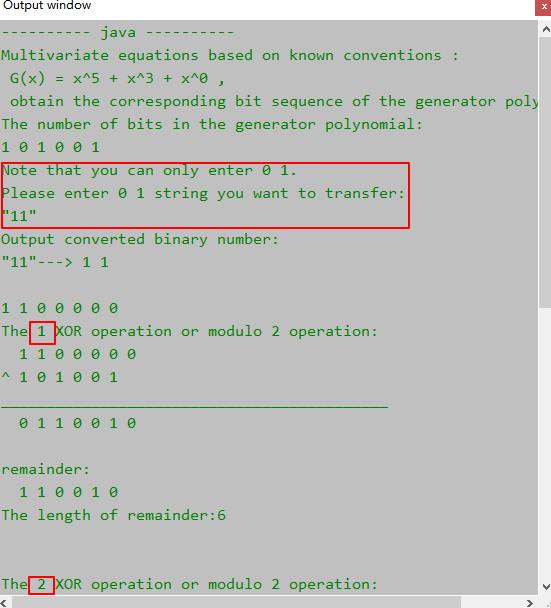
System.out.println("Multivariate equations based on known conventions : \n G(x) = x^5 + x^3 + x^0 , \n obtain the corresponding bit sequence of the generator polynomial.");
System.out.println("The number of bits in the generator polynomial:");
for(int item : checkBitArray){
System.out.printf("%d ", item);
}
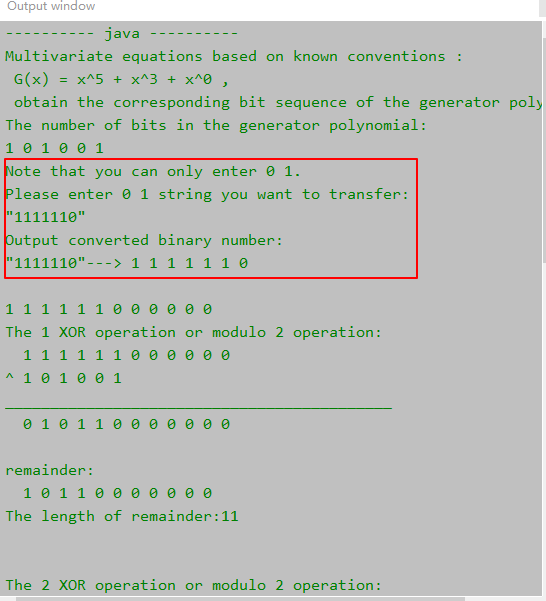
System.out.println("\nNote that you can only enter 0 1.\nPlease enter 0 1 string you want to transfer:");
// Receive 0 1 string from the keyboard.
String sourceData = scan.next();
System.out.println("\"" + sourceData + "\"");
scan.close();
int sceLen = sourceData.length();
int[] sourceBinaryNum = new int[sceLen]; // Used to store the binary data stream to be transferred.
System.out.println("Output converted binary number:");
System.out.printf("\"%s\"--->", sourceData);
sourceBinaryNum = test.getBinaryNumbers(sourceData);
System.out.println();
int[] comp = new int[sourceBinaryNum.length + checkBitArray.length - 1];
comp = test.compareTransBit(sourceBinaryNum, checkBitArray);
int[] tempArr = test.moduloSecordOperation(comp, checkBitArray);
System.out.println();
tempArr = test.removeInvalidZero(tempArr);
int remainderLen = tempArr.length;
int[] tmp = tempArr;
while(remainderLen >= checkBitArray.length){
tmp = test.moduloSecordOperation(tempArr, checkBitArray);
System.out.println();
tempArr = test.removeInvalidZero(tmp);
remainderLen = tempArr.length;
}
int[] result = new int[sourceBinaryNum.length + tempArr.length];
int index = 0;
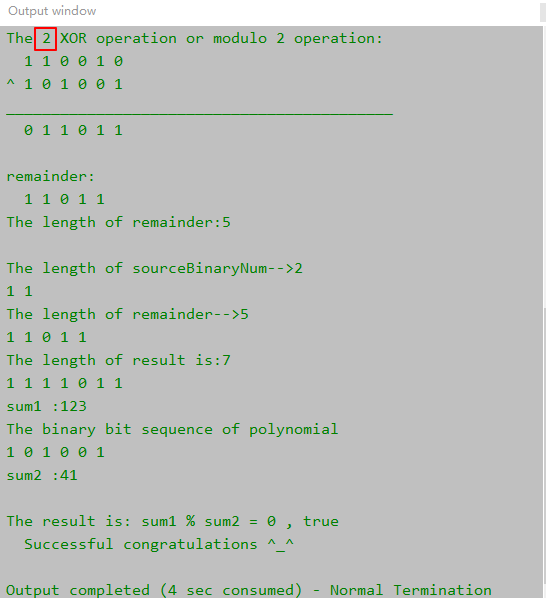
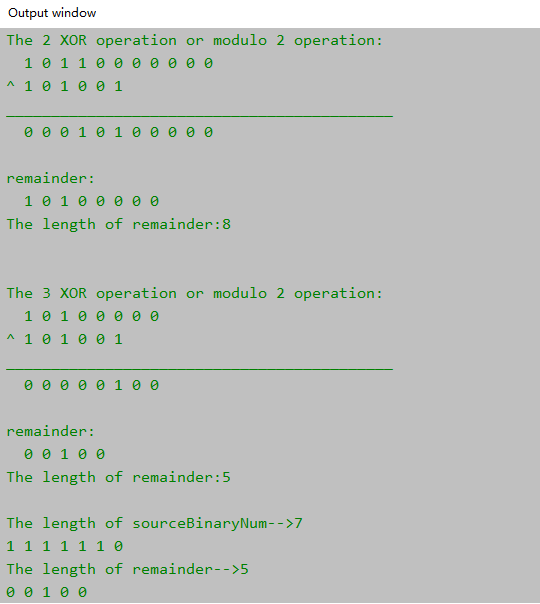
System.out.println("The length of sourceBinaryNum-->" + sourceBinaryNum.length);
for(int i = 0; i < sourceBinaryNum.length; i++){
result[index] = sourceBinaryNum[i];
System.out.printf("%d ", sourceBinaryNum[i]);
index++;
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The length of remainder-->" + tempArr.length);
for(int i = 0; i < tempArr.length; i++){
result[index] = tempArr[i];
System.out.printf("%d ", tempArr[i]);
index++;
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The length of result is:" + result.length);
for(int res = 0; res < result.length; res++){
System.out.printf("%d ", result[res]);
}
long sum1 = test.convertBinaryToDecimal(result);
System.out.println("\nsum1 :" + sum1);
System.out.println("The binary bit sequence of polynomial");
for(int k : checkBitArray){
System.out.printf("%d ", k);
}
long sum2 = test.convertBinaryToDecimal(checkBitArray);
System.out.println("\nsum2 :" + sum2);
System.out.println();
boolean bool = test.checkTransmission(sum1, sum2);
System.out.println("The result is: sum1 % sum2 = " + sum1 % sum2 + " , " + bool);
if(bool){
System.out.println(" Successful congratulations ^_^");
}else{
System.out.println(" failure V_V!");
}
}
// Convert 0 1 string to binary numbers.
public static int[] getBinaryNumbers(String s){
int sLen = s.length();
int[] binaryNum = new int[sLen];
for(int i = 0; i < sLen; i++){
binaryNum[i] = s.charAt(i) - '0';
}
// System.out.printf("\"%s\"--->\n", s);
System.out.printf(" ");
for(int j : binaryNum){
System.out.printf("%d ", j);
}
System.out.println();
return binaryNum;
}
// Compare the data to be transmitted with the length of the bit sequence generated by the polynomial.
public static int[] compareTransBit(int[] arr1, int[] arr2){
int i = arr2.length - 1;
int[] newArr = new int[arr1.length + i];
int k = 0;
for(int item = 0; item < arr1.length; item++){
newArr[k] = arr1[item];
k++;
}
while(i > 0){
newArr[k] = 0;
k++;
i--;
}
for(int item : newArr){
System.out.printf("%d ",item);
}
return newArr;
}
// Perform modulo 2 operation or XOR operation.
public static int[] moduloSecordOperation(int[] arr1, int[] arr2){
// int[] arrResult = new int[arr1.length]; // Used to store the remainder
System.out.printf("\nThe %d XOR operation or modulo 2 operation:\n", counts);
counts++;
System.out.printf(" ");
for(int index1 : arr1){
System.out.printf(" %d", index1);
}
System.out.print("\n^");
for(int index2 : arr2){
System.out.printf(" %d", index2);
}
for(int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++){
arr1[i] = arr1[i] ^ arr2[i];
}
// System.out.println("\nAfter modulo 2 operation arr1:");
System.out.printf("\n___________________________________________\n");
System.out.printf(" ");
for(int index1 : arr1){
System.out.printf(" %d", index1);
}
// return arrResult;
System.out.println();
return arr1;
}
// Remove invalid 0 front of a binary number.
public static int[] removeInvalidZero(int[] arr){
int sumZero = 0; // Used to count the number of 0.
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
// Read each consecutive 0 in front of the array and do statistics.
while(arr[i] == 0){
sumZero++;
i++;
if(checkBitArray.length -1 == arr.length - sumZero){
break;
}
}
int[] remainder = new int[arr.length - sumZero];
while(i < arr.length){
remainder[j] = arr[i];
j++;
i++;
}
System.out.println("remainder:");
System.out.print(" ");
for(int index : remainder){
System.out.printf(" %d",index);
}
System.out.println("\nThe length of remainder:" + remainder.length);
System.out.println();
return remainder;
}
// Convert binary numbers to decimal numbers.
public static long convertBinaryToDecimal(int[] arr){
long sum = 0L;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
int temp = i;
int mul = 1;
while(temp < arr.length - 1){
mul *= 2; // mul <<= 1;
temp++;
}
sum += arr[i] * mul;
}
return sum;
}
// Check if the transmission is correct by verification.
public static boolean checkTransmission(long sourceNum, long checkNum){
return sourceNum % checkNum == 0;
}
}