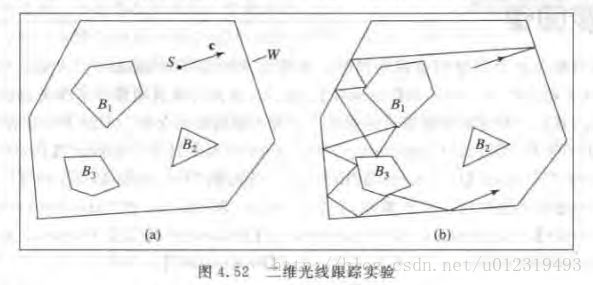
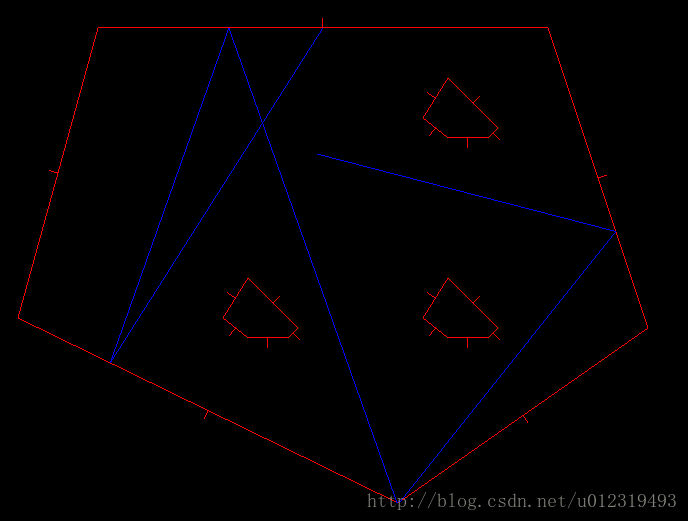
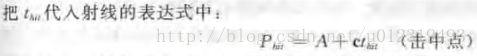OpenGL---二维光线追踪
代码、原理:计算机图形学(OpenGL)第三版 第4章
我在其中加上了注释
流程
需要用户从文件中读取多边形数据
1、由用户画出第一条射线,需调用函数raytrace2d_mouse,raytrace2d_motion。
2、函数raytrace2d_keyboard中,当按下空格键时,针对每个多边形调用函数timeToHitPoly,计算射线击中该多边形的时间,取最小的那个时间,根据该时间得到射线的可见部分,放入射线列表rays中。接着计算下一条射线,即反射射线:记录反射射线的起点,计算反射射线的方向向量。
3、函数raytrace2d_render绘制各个多边形,并绘制保存在rays中的射线。
timeToHitPoly:针对当前多边形的所有边,调用LipInterval,将射线与每条相交的时间保存在hitTimes中,并不断更新射线留在多边中的时间[t_in, t_out]。判断当前多边形是最外围的多边形,还是里边的小多边形,如果是前者,则击中多边形的时间hit_t = t_out;否则,hit_t = t_in。根据hit_t与hitTimes中的元素比较,得出多边形的哪条边被击中了。
LipInterval:根据射线与当前边的法向量的夹角,得到射线是射入多边形,还是射出多边形,并求出与当前边相交的时间t_hit。如果是射入多边形,t_in = max(t_in, t_hit);否则,t_out = min(t_out, t_hit)
—————————————-原理———————————–
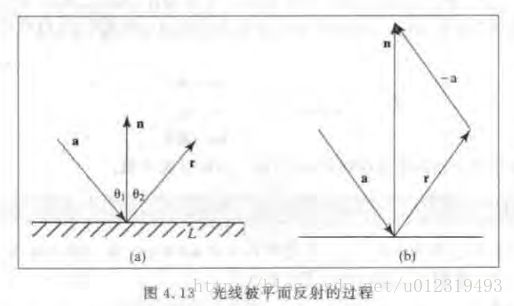
判断射线是射向物体,还是射出物体
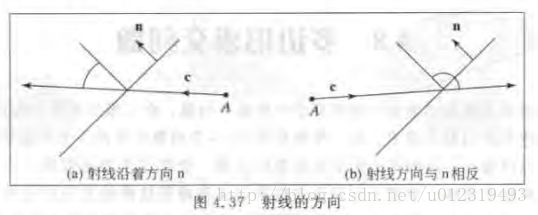

则对于多边形P:(n是直线的外法向量)

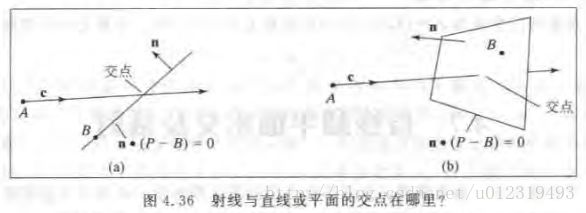
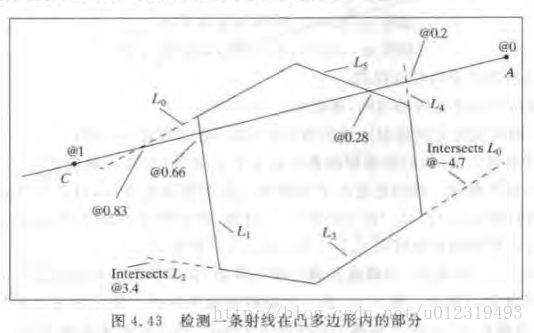
射线与凸多边形的交点以及裁剪问题
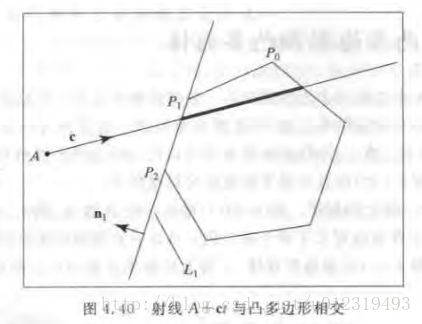
进入是的击中点:A + c * t_in
出去是的击中点:A + c * t_out
射线在多边形中的部分对应的t在区间[t_in, t_out]中。
裁剪算法如下:
将[t_in, t_out]看成候选区间。
1、 初始化候选区间[0, 无穷]
2、对每一条直线,计算击中时间t_hit,并判断这一击中是射入还是射出:
- 如果是射入,t_in = max(t_in, t_hit);
- 如果是射出,t_out = min(t_out, t_hit)
如果t_in大于t_out,说明射线与多边形完全不相交,结束检测。
3、检测完多边形的所有边后,如果候选区间非空,那么从A + c * t_in
到A + c * t_out是在多边形内的。
RayTrace2D.cpp
#include Line2.h
#ifndef _LINE2_H_
#define _LINE2_H_
#include "Vector2.h"
#include Line2.cpp
#include "Line2.h"
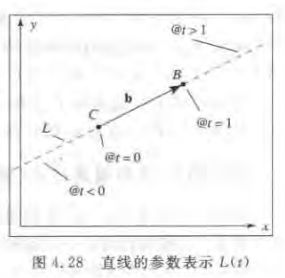
Line2::Line2( const Vector2 & a, const Vector2 & b, LineType t )
{
setVectors( a, b, t );
}
Line2::Line2( float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2 )
{
setVectors( Vector2( x1, y1 ),
Vector2( x2, y2 ),
LINE_SEGMENT );
}
void Line2::setVectors( const Vector2 & a, const Vector2 & b, LineType t )
{
switch( t )
{
case LINE_SEGMENT:
// init segment vars
A = a;
B = b;
isSeg = true;
// init param form
C = (a - b);
C.normalize();
S = a;
// init PN form
P = a;
N = C.perp();
break;
case LINE_PTNORM:
// init PV vars
P = a;
N = b;
N.normalize();
// init param form
S = a;
C = N.perp();
// segment form makse no sense here
isSeg = false;
break;
case LINE_PARAM:
// init param vars
S = a;
C = b;
C.normalize();
// init PV vars
P = a;
N = C.perp();
// segment form makse no sense here
isSeg = false;
break;
default: break;
}
}
bool Line2::getVectors( Vector2 & a, Vector2 & b, LineType t ) const
{
switch( t )
{
case LINE_SEGMENT:
if( isSeg )
{
a = A;
b = B;
}
else
{
// user asked for segment endpoints, and this is not a seg
return( false ); // = error
}
break;
case LINE_PTNORM:
a = P;
b = N;
break;
case LINE_PARAM:
a = S;
b = C;
break;
default:
return( false );
}
return( true );
}Vector2.h
#ifndef _Vector2_H
#define _Vector2_H
#include GlutWin.h
#ifndef _GLUTWIN_H_
#define _GLUTWIN_H_
#include GlutWin.cpp
#include "GlutWin.h"
GlutWin::GlutWin( int windowHeight, int windowWidth,
int windowPosX, int windowPosY,
unsigned int displayMode,
const char * windowTitle )
{
// initialize members
windowTitle = windowTitle;
windowHeight= windowHeight;
windowWidth = windowWidth;
windowPosX = windowPosX;
windowPosY = windowPosY;
displayMode = displayMode;
fullScreen = false;
// make some dummy command line for glut
char cmd_line[8];
char * argv[1];
argv[0] = cmd_line;
int argc = 1;
// initialize glut
glutInit( &argc, argv );
// initialize window
glutInitWindowSize( windowWidth, windowHeight );
glutInitWindowPosition( windowPosX, windowPosY );
glutInitDisplayMode( displayMode );
// create window
windowID = glutCreateWindow( windowTitle );
// set the view frustum
glMatrixMode( GL_PROJECTION );
glLoadIdentity();
gluOrtho2D( 0, windowWidth, 0, windowHeight );
glMatrixMode( GL_MODELVIEW );
// clear rendering surface
glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); // background is black
glViewport(0, 0, windowWidth, windowHeight);
}
ploys.txt
70 260
150 550
600 550
700 250
450 75
.
300 240
275 260
300 300
350 250
340 240
.
500 440
475 460
500 500
550 450
540 440
.
500 240
475 260
500 300
550 250
540 240
.
500 440
475 460
500 500
550 450
540 440
.