MyBatis源码分析
篇章一:入口篇
我们学习Mybatis时知道其核心是SqlSessionFactory,它是mybatis的核心类,也是Mybatis运行的入口,spring集成mybatis时需要配置SqlSessionFactoryBean和扫描mapper的MapperScannerConfigurer,spring-mybatis集成主要的配置就这么点,从这理解也就不难理解mybatis入口问题了,但是
我们点进去看看SqlSessionFactoryBean.
public class SqlSessionFactoryBean implements FactoryBean, InitializingBean, ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (failFast && event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) {
// fail-fast -> check all statements are completed
this.sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getMappedStatementNames();
}
}
} 可以看到SqlSessionFactoryBean实现了三个接口:
1.ApplicationListener接口:里面只有一个onApplicationEvent方法,有什么用呢?看官方的注释,它是基于观察者模式创建的,当上下文ApplicationContext加载完实现了该接口的bean后,负责通知该bean,bean接收到通知后(onApplicationEvent方法),可以在方法内做自己的逻辑处理,简单点理解就是容器你好,我收到你加载我完毕的通知了,接下里就交给我吧,不用你操心了。
很显然这不是我们要找的方法入口,因为bean都加载完了,说明mybatis配置文件什么都处理完了,那我们再来看看InitializingBean接口
2.InitializingBean接口:接口为bean提供了初始化方法的方式,它只包括afterPropertiesSet方法,凡是继承该接口的类,在初始化bean的时候都会执行该方法(如果bean配置了init-method属性,afterPropertiesSet优先级高于init-method)。
由上可知,这就是我们要找的入口了,spring在初始化bean时,会先调用afterPropertiesSet()方法,从上面代码可知,它在里面调用了buildSqlSessionFactory()方法,哎,最上面我们是不是说了mybatis的核心是SqlSessionFactory,可想而知,这个构造SqlSessionFactory的方法buildSqlSessionFactory()是最核心的方法了。
入口篇完。
篇章二:配置篇
1.配置文件加载
Mybatis配置bean时注入了一个mapperLocations属性,指明项目xml mapper文件的路径,SqlSessionfactoryBean内定义了一个Resource数组接收mapperLocations的位置
public class SqlSessionFactoryBean implements FactoryBean, InitializingBean, ApplicationListener {
private Resource configLocation;
private Configuration configuration;
private Resource[] mapperLocations;
/**
* Set locations of MyBatis mapper files that are going to be merged into the {@code SqlSessionFactory}
* configuration at runtime.
*
* This is an alternative to specifying "<sqlmapper>" entries in an MyBatis config file.
* This property being based on Spring's resource abstraction also allows for specifying
* resource patterns here: e.g. "classpath*:sqlmap/*-mapper.xml".
*/
public void setMapperLocations(Resource[] mapperLocations) {
this.mapperLocations = mapperLocations;
}
} 2.读取配置文件
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
//省略了前面次要代码
if (!isEmpty(this.mapperLocations)) {
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
continue;
}
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
configuration, mapperLocation.toString(), configuration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
}
}
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified or no matching resources found");
}
}
}这段代码主要根据mapperLocation的文件流构造XMLMapperBuilder(解析xml文件的核心类),然后调用XMLMapperBuilder的parse()方法进行xml文件解析,点进去看看parse()方法体
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
public void parse() {
//判断资源文件是否被加载过
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));//解析mapper文件
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);//加载解析完毕放入Set容器中
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
}
public class Configuration{
protected final Set loadedResources = new HashSet();
public boolean isResourceLoaded(String resource) {
return loadedResources.contains(resource);
}
public void addLoadedResource(String resource) {
loadedResources.add(resource);
}
} 来看看ConfigurationElement()方法
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
//获取mapper文件命名空间
//即节点的namespace属性值
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));//解析
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));//解析节点
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));//解析节点
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));//解析CRUD节点
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
} 这里mybatis是将mapper.xml文件分为几个部分来单独解析的,主要关注解析
①
先上一波源码
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode, List additionalResultMappings) throws Exception {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("processing " + resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
//获取标签id属性的值,下面也是解析标签很多属性的值,就不一一注释了
String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("id",
resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
//需要映射的实体类(String)
String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("type",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("ofType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType"))));
String extend = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("extends");
Boolean autoMapping = resultMapNode.getBooleanAttribute("autoMapping");
Class typeClass = resolveClass(type);//根据全限定名加载类
Discriminator discriminator = null;
List resultMappings = new ArrayList();
resultMappings.addAll(additionalResultMappings);
List resultChildren = resultMapNode.getChildren();
//解析标签的子节点
for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren) {
if ("constructor".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else if ("discriminator".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else {
List flags = new ArrayList();
if ("id".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
}
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags));
}
}
ResultMapResolver resultMapResolver = new ResultMapResolver(builderAssistant, id, typeClass, extend, discriminator, resultMappings, autoMapping);
try {
return resultMapResolver.resolve();//该方法会调用MapperBuilderAssistant的addResultMap()方法,然后方法内部再调用 configuration.addResultMap(resultMap);将解析好的文件对象存到Configuration
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteResultMap(resultMapResolver);
throw e;
}
}
} 解析
package org.apache.ibatis.session;
public class Configuration {
protected final Map resultMaps = new StrictMap("Result Maps collection");
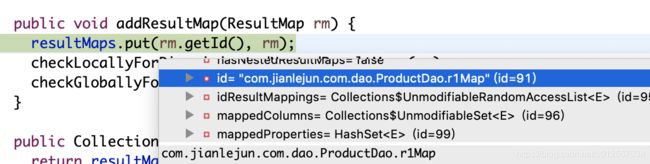
public void addResultMap(ResultMap rm) {
resultMaps.put(rm.getId(), rm);
checkLocallyForDiscriminatedNestedResultMaps(rm);
checkGloballyForDiscriminatedNestedResultMaps(rm);
}
}
StrictMap源码:
package org.apache.ibatis.session;
public class Configuration {
protected static class StrictMap extends HashMap {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4950446264854982944L;
private final String name;
public StrictMap(String name, int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.name = name;
}
public StrictMap(String name, int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
this.name = name;
}
public StrictMap(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public StrictMap(String name, Map m) {
super(m);
this.name = name;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public V put(String key, V value) {
if (containsKey(key)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(name + " already contains value for " + key);
}
if (key.contains(".")) {
final String shortKey = getShortName(key);
if (super.get(shortKey) == null) {
super.put(shortKey, value);
} else {
super.put(shortKey, (V) new Ambiguity(shortKey));
}
}
return super.put(key, value);
}
public V get(Object key) {
V value = super.get(key);
if (value == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(name + " does not contain value for " + key);
}
if (value instanceof Ambiguity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(((Ambiguity) value).getSubject() + " is ambiguous in " + name
+ " (try using the full name including the namespace, or rename one of the entries)");
}
return value;
}
private String getShortName(String key) {
final String[] keyParts = key.split("\\.");
return keyParts[keyParts.length - 1];
}
protected static class Ambiguity {
final private String subject;
public Ambiguity(String subject) {
this.subject = subject;
}
public String getSubject() {
return subject;
}
}
}
} 至此
②
继续来看看ConfigurationElement()方法内部调用的buildStatementFromContext()方法,主要负责解析
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private void buildStatementFromContext(List list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
} 里面创建了个XMLStatementBuilder来负责mapper文件
具体解析节点xml文件代码如下:
public class XMLStatementBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
Class resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
//解析前先解析引用的sql片段
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: and were parsed and removed)
#获得sql语句
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
} mybatis在做CURD解析前会调用XMLIncludeTransformer的applyIncludes()方法,将标签内
最终解析完后会调用MapperBuilderAssistant的addMappedStatement()方法,将
MapperBuilderAssistant类
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id,
SqlSource sqlSource,
StatementType statementType,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,
Integer fetchSize,
Integer timeout,
String parameterMap,
Class parameterType,
String resultMap,
Class resultType,
ResultSetType resultSetType,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
boolean resultOrdered,
KeyGenerator keyGenerator,
String keyProperty,
String keyColumn,
String databaseId,
LanguageDriver lang,
String resultSets) {
if (unresolvedCacheRef) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
}
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType)
.resource(resource)
.fetchSize(fetchSize)
.timeout(timeout)
.statementType(statementType)
.keyGenerator(keyGenerator)
.keyProperty(keyProperty)
.keyColumn(keyColumn)
.databaseId(databaseId)
.lang(lang)
.resultOrdered(resultOrdered)
.resultSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id))
.resultSetType(resultSetType)
.flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect))
.cache(currentCache);
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);//最终将解析好的节点信息放入configuration,如果存在相同id的节点则抛出异常
return statement;
}这里关键的是调用configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);跟resultMap节点一样,节点信息也是存入一个StrictMap中
,key为sql语句的id,value为构造好的MapperStatement对象,由于StrictMap是不允许存在相同key的,所以sql的id相同是回抛出一样
Configuration类
package org.apache.ibatis.session;
public class Configuration {
protected final Map keyGenerators = new StrictMap("Key Generators collection");
//存储解析好的节点信息
protected final Map mappedStatements = new StrictMap("Mapped Statements collection");
public boolean hasKeyGenerator(String id) {
return keyGenerators.containsKey(id);
}
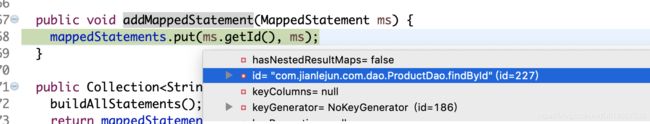
public void addMappedStatement(MappedStatement ms) {
mappedStatements.put(ms.getId(), ms);
}
} 由下图可以看到key为dao(mapper)全限定名+sql节点的id,value为MappedStatement对象
其他
至此
篇章三:应用篇
通过上面的章节,我们来思考些问题,mapper文件已经解析完了,那mybatis调用dao的方法时,如何通过dao的方法名找到对应的sql,并最终执行?执行后怎么映射到mapper文件配置的实体上?
先来看看我的service
@Service
@Transactional
public class ProductService {
@Autowired
private ProductDao dao;
public Product findById(Long id) {
return dao.findById(id);
}
public List findView(Long warehouseId) {
return dao.findView(warehouseId);
}
public List findView2(Long warehouseId) {
return dao.findView2(warehouseId);
}
public List findView3(Long warehouseId) {
return dao.findView3(warehouseId);
}
public List findView4(Long warehouseId) {
return dao.findView4(warehouseId);
}
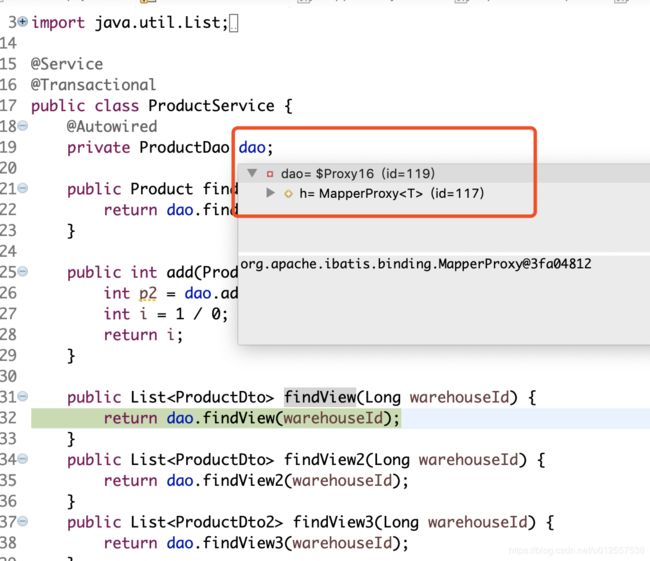
} 假设执行的是findView方法
由上图可以看到这这里注入的dao其实是一个MapperProxy代理,代理最终调用的都是invoke方法(不知道为什么的话请找找谷哥/度娘这对模范夫妻,请教他们是什么代理模式),点进去看看
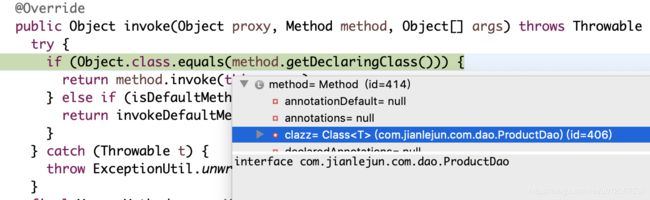
public class MapperProxy implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
} 这里先判断代理方法的声明类是否是Object,很显然我这里是ProductDao,不执行if语句块,会转到cachedMapperMethod(),从缓存中获取MapperMethod
接着执行MapperMethod的execute()
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
public class MapperMethod {
private final SqlCommand command;
private final MethodSignature method;
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
private Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
List result;
//方法参数转换成SQL执行所需要的参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
//最终调用的是SqlSessionTemplate模板类的selectList方法
result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param);
}
// issue #510 Collections & arrays support
if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {
if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
return convertToArray(result);
} else {
return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
}
}
return result;
}
} execute()方法内部根据带执行的SqlCommand类型匹配switch代码块,我这里的demo是SELECT语句,所以我们直接看 CASE SELECT语句块即可,里面会根据方法放回参数类型类型调用想对应的方法,这里返回的是List,即Many,往下看executeForMany()方法,首先将方法传递的参数转换成执行SQL需要的参数,然后最终会调用SqlSessionTemplate模板的的selectList方法
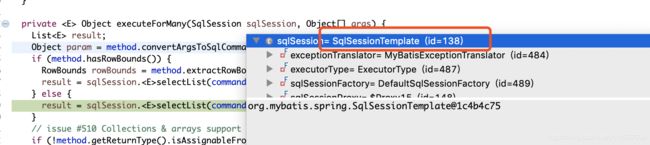
还没完呢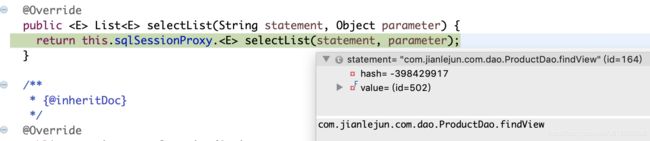 ,留意到传进selectList的参数并不是SQL语句,说明执行流程还没完,如上图可知这里传递的只是一个String类型的statement串,我们从篇章二的解析过程可以猜测,他最终肯定是要从Configuration对象中根据key来提取MapperStatement对象的?来继续追踪,看看是否验证我们的 猜想。打开SqlSessionTemplate类
,留意到传进selectList的参数并不是SQL语句,说明执行流程还没完,如上图可知这里传递的只是一个String类型的statement串,我们从篇章二的解析过程可以猜测,他最终肯定是要从Configuration对象中根据key来提取MapperStatement对象的?来继续追踪,看看是否验证我们的 猜想。打开SqlSessionTemplate类
public class SqlSessionTemplate implements SqlSession, DisposableBean {
private final SqlSession sqlSessionProxy;
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public List selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.sqlSessionProxy. selectList(statement, parameter);
}
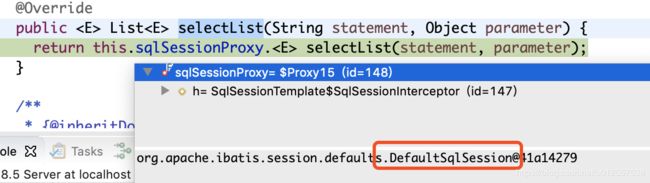
} 哎,这里只是调用了SqlSession接口的selectList,不慌,我们来看看这里注入的SqlSession实现类是哪个
哈哈,原来是DefaultSqlSession,继续追踪,要抱着不破楼兰誓不还的决心
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private final Configuration configuration;
private final Executor executor;
@Override
public List selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
}
@Override
public List selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
} 来到这里,终于真相大白了!!!果不其然,最终是从Configuration中获取封装了
完结撒花?????????????????
喜欢请轻轻点击下方小拇指