记filebeat内存泄漏问题分析及调优
ELK 从发布5.0之后加入了beats套件之后,就改名叫做elastic stack了。beats是一组轻量级的软件,给我们提供了简便,快捷的方式来实时收集、丰富更多的数据用以支撑我们的分析。但由于beats都需要安装在ELK集群之外,在宿主机之上,其对宿主机的性能的影响往往成为了考量其是否能被使用的关键,而不是它到底提供了什么样的功能。因为业务的稳定运行才是核心KPI,而其他因运维而生的数据永远是更低的优先级。影响宿主机性能的方面可能有很多,比如CPU占用率,网络吞吐占用率,磁盘IO,内存等,这里我们详细讨论一下内存泄漏的问题
文章目录
- 问题场景和配置
- 监控文件过多
- 非常频繁的rotate日志
- 因为multiline导致内存占用过多
- 模拟场景
- 如何观察filebeat的内存
- 通过filebeat的日志
- filebeat文件解读
- filebeat日志解析
- 通过pprof
- 启动pprof监测
- 远程连接
- top 命令
- 查看堆栈调用图
- 查看源码
- 如何调优
filebeat是beats套件的核心组件之一(另一个核心是metricbeat),它一般和生成被采集文件(主要是日志)的程序安装在一个地方,根据官方的建议,是filebeat是不建议用来采集NFS(网络共享磁盘)上的数据的。当filebeat运行起来之后,必定会对cpu,内存,网络等资源产生一定的消耗,当这种消耗能够限定在一个可接受的范围时,我觉得没人会限制你在生产环境上使用filebeat。但如果出现一些非预期的情况,比如占用了大量的内存,那么运维团队肯定是优先保障核心业务的资源,把filebeat进程给杀了。很可惜的是,内存泄漏的问题,从filebeat的诞生到现在就一直没有完全解决过,无论是什么版本(最新的6.5版本暂时还没有观测到)在不同场景和配置下,均出现内存占用过多的问题。在这里,我主要描述一下我碰到的在filebeat 6.0上遇到的问题。
问题场景和配置
我们使用了一套统一的简单配置监控了很多的主机,正是这种无差异化的简单配置,造成了问题。这是不对的,这是不对的,这是不对的!!! 合理的方式是具体问题具体分析,针对不同的场景是做定制化的配置。
multiline,多行的配置,当日志文件不符合规范,大量的匹配pattern的时候,会造成内存泄漏max_procs,限制filebeat的进程数量,其实是内核数,建议手动设为1
filebeat.prospectors:
- type: log
enabled: true
paths:
- /qhapp/*/*.log
tail_files: true
multiline.pattern: '^[[:space:]]+|^Caused by:|^.+Exception:|^\d+\serror'
multiline.negate: false
multiline.match: after
fields:
app_id: bi_lass
service: "{{ hostvars[inventory_hostname]['service'] }}"
ip_address: "{{ hostvars[inventory_hostname]['ansible_host'] }}"
topic: qh_app_raw_log
filebeat.config.modules:
path: ${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml
reload.enabled: false
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3
#index.codec: best_compression
#_source.enabled: false
output.kafka:
enabled: true
hosts: [{{kafka_url}}]
topic: '%{[fields][topic]}'
max_procs: 1
注意,以上的配置中,仅仅对cpu的内核数进行了限制,而没有对内存的使用率进行特殊的限制。从配置层面来说,影响filebeat内存使用情况的指标主要有两个:
queue.mem.events消息队列的大小,默认值是4096,这个参数在6.0以前的版本是spool-size,通过命令行,在启动时进行配置max_message_bytes单条消息的大小, 默认值是10M
filebeat最大的可能占用的内存是max_message_bytes * queue.mem.events = 40G,考虑到这个queue是用于存储encode过的数据,raw数据也是要存储的,所以,在没有对内存进行限制的情况下,最大的内存占用情况是可以达到超过80G。
因此,建议是同时对filebeat的CPU和内存进行限制。
下面,我们看看,使用以上的配置在什么情况下会观测到内存泄漏
监控文件过多
对于实时大量产生内容的文件,比如日志,常用的做法往往是将日志文件进行rotate,根据策略的不同,每隔一段时间或者达到固定大小之后,将日志rotate。
这样,在文件目录下可能会产生大量的日志文件。
如果我们使用通配符的方式,去监控该目录,则filebeat会启动大量的harvester实例去采集文件。但是,请记住,我这里不是说这样一定会产生内存泄漏,只是在这里观测到了内存泄漏而已,不是说这是造成内存泄漏的原因。
当filebeat运行了几个月之后,占用了超过10个G的内存

非常频繁的rotate日志
另一个可能是,filebeat只配置监控了一个文件,比如test2.log,但由于test2.log不停的rotate出新的文件,虽然没有使用通配符采集该目录下的所有文件,但因为linux系统是使用inode number来唯一标示文件的,rotate出来的新文件并没有改变其inode number,因此,时间上filebeat还是同时开启了对多个文件的监控。
因为multiline导致内存占用过多
multiline.pattern: '^[[:space:]]+|^Caused by:|^.+Exception:|^\d+\serror,比如这个配置,认为空格或者制表符开头的line是上一行的附加内容,需要作为多行模式,存储到同一个event当中。当你监控的文件刚巧在文件的每一行带有一个空格时,会错误的匹配多行,造成filebeat解析过后,单条event的行数达到了上千行,大小达到了10M,并且在这过程中使用的是正则表达式,每一条event的处理都会极大的消耗内存。因为大多数的filebeat output是需应答的,buffer这些event必然会大量的消耗内存。
模拟场景
这里不多说,简单来一段python的代码:
[loggers]
keys=root
[handlers]
keys=NormalHandler
[formatters]
keys=formatter
[logger_root]
level=DEBUG
handlers=NormalHandler
[handler_NormalHandler]
class=logging.handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler
formatter=formatter
args=('./test2.log', 'S', 10, 200)
[formatter_formatter]
format=%(asctime)s %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s
以上,每隔10秒(‘S’, ‘M’ = 分钟,‘D’= 天)rotate一个文件,一共可以rotate 200个文件。
然后,随便找一段日志,不停的打,以下是330条/秒
import logging
from logging.config import fileConfig
import os
import time
CURRENT_FOLDER = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
fileConfig(CURRENT_FOLDER + '/logging.ini')
logger = logging.getLogger()
while True:
logger.debug("DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:35 com.sunyard.insurance.server.GetImage 43 - 资源请求:date=20181126&file_name=/imagedata/imv2/pool1/images/GXTB/2017/11/14/57/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_1/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_2.syd&file_encrypt=0&token=HUtGGG20GH4GAqq209R9tc9UGtAURR0b DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:40 com.sunyard.insurance.scheduler.job.DbEroorHandleJob 26 - [数据库操作异常处理JOB]处理异常文件,本机不运行,退出任务!")
logger.debug("DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:35 com.sunyard.insurance.server.GetImage 43 - 资源请求:date=20181126&file_name=/imagedata/imv2/pool1/images/GXTB/2017/11/14/57/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_1/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_2.syd&file_encrypt=0&token=HUtGGG20GH4GAqq209R9tc9UGtAURR0b DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:40 com.sunyard.insurance.scheduler.job.DbEroorHandleJob 26 - [数据库操作异常处理JOB]处理异常文件,本机不运行,退出任务!")
logger.debug("DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:35 com.sunyard.insurance.server.GetImage 43 - 资源请求:date=20181126&file_name=/imagedata/imv2/pool1/images/GXTB/2017/11/14/57/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_1/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_2.syd&file_encrypt=0&token=HUtGGG20GH4GAqq209R9tc9UGtAURR0b DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:40 com.sunyard.insurance.scheduler.job.DbEroorHandleJob 26 - [数据库操作异常处理JOB]处理异常文件,本机不运行,退出任务!")
logger.debug("DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:35 com.sunyard.insurance.server.GetImage 43 - 资源请求:date=20181126&file_name=/imagedata/imv2/pool1/images/GXTB/2017/11/14/57/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_1/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_2.syd&file_encrypt=0&token=HUtGGG20GH4GAqq209R9tc9UGtAURR0b DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:40 com.sunyard.insurance.scheduler.job.DbEroorHandleJob 26 - [数据库操作异常处理JOB]处理异常文件,本机不运行,退出任务!")
logger.debug("DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:35 com.sunyard.insurance.server.GetImage 43 - 资源请求:date=20181126&file_name=/imagedata/imv2/pool1/images/GXTB/2017/11/14/57/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_1/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_2.syd&file_encrypt=0&token=HUtGGG20GH4GAqq209R9tc9UGtAURR0b DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:40 com.sunyard.insurance.scheduler.job.DbEroorHandleJob 26 - [数据库操作异常处理JOB]处理异常文件,本机不运行,退出任务!")
logger.debug("DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:35 com.sunyard.insurance.server.GetImage 43 - 资源请求:date=20181126&file_name=/imagedata/imv2/pool1/images/GXTB/2017/11/14/57/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_1/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_2.syd&file_encrypt=0&token=HUtGGG20GH4GAqq209R9tc9UGtAURR0b DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:40 com.sunyard.insurance.scheduler.job.DbEroorHandleJob 26 - [数据库操作异常处理JOB]处理异常文件,本机不运行,退出任务!")
logger.debug("DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:35 com.sunyard.insurance.server.GetImage 43 - 资源请求:date=20181126&file_name=/imagedata/imv2/pool1/images/GXTB/2017/11/14/57/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_1/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_2.syd&file_encrypt=0&token=HUtGGG20GH4GAqq209R9tc9UGtAURR0b DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:40 com.sunyard.insurance.scheduler.job.DbEroorHandleJob 26 - [数据库操作异常处理JOB]处理异常文件,本机不运行,退出任务!")
logger.debug("DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:35 com.sunyard.insurance.server.GetImage 43 - 资源请求:date=20181126&file_name=/imagedata/imv2/pool1/images/GXTB/2017/11/14/57/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_1/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_2.syd&file_encrypt=0&token=HUtGGG20GH4GAqq209R9tc9UGtAURR0b DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:40 com.sunyard.insurance.scheduler.job.DbEroorHandleJob 26 - [数据库操作异常处理JOB]处理异常文件,本机不运行,退出任务!")
logger.debug("DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:35 com.sunyard.insurance.server.GetImage 43 - 资源请求:date=20181126&file_name=/imagedata/imv2/pool1/images/GXTB/2017/11/14/57/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_1/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_2.syd&file_encrypt=0&token=HUtGGG20GH4GAqq209R9tc9UGtAURR0b DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:40 com.sunyard.insurance.scheduler.job.DbEroorHandleJob 26 - [数据库操作异常处理JOB]处理异常文件,本机不运行,退出任务!")
logger.debug("DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:35 com.sunyard.insurance.server.GetImage 43 - 资源请求:date=20181126&file_name=/imagedata/imv2/pool1/images/GXTB/2017/11/14/57/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_1/06b6bcdd31763b70b20f56c689e51f5e_2.syd&file_encrypt=0&token=HUtGGG20GH4GAqq209R9tc9UGtAURR0b DEBUG 2018-11-26 09:31:40 com.sunyard.insurance.scheduler.job.DbEroorHandleJob 26 - [数据库操作异常处理JOB]处理异常文件,本机不运行,退出任务!!@#!@#!@#!@#!@#!@#!@#!@#!@#!@#!@#!#@!!!@##########################################################################################################################################################")
time.sleep(0.03)
如何观察filebeat的内存
在6.5版本之前,我们是无法通过xpack的monitoring功能来观察beats套件的性能的。因此,这里讨论的是没有monitoring时,我们如何去检测filebeat的性能。当然,简单的方法是通过top,ps等操作系统的命令进行查看,但这些都是实时的,无法做趋势的观察,并且都是进程级别的,无法看到filebeat内部的真是情况。因此,这里介绍如何通过filebeat的日志和pprof这个工具来观察内存的使用情况
通过filebeat的日志
filebeat文件解读
其实filebeat的日志,已经包含了很多参数用于实时观测filebeat的资源使用情况,以下是filebeat的一个日志片段(这里的日志片段是6.0版本的,6.5版本之后,整个日志格式变了,从kv格式变成了json对象格式,xpack可以直接通过日志进行filebeat的monitoring):
2018-11-02T17:40:01+08:00 INFO Non-zero metrics in the last 30s: beat.memstats.gc_next=623475680 beat.memstats.memory_alloc=391032232 beat.memstats.memory_total=155885103371024 filebeat.events.active=-402 filebeat.events.added=13279 filebeat.events.done=13681 filebeat.harvester.closed=1 filebeat.harvester.open_files=7 filebeat.harvester.running=7 filebeat.harvester.started=2 libbeat.config.module.running=0 libbeat.output.events.acked=13677 libbeat.output.events.batches=28 libbeat.output.events.total=13677 libbeat.outputs.kafka.bytes_read=12112 libbeat.outputs.kafka.bytes_write=1043381 libbeat.pipeline.clients=1 libbeat.pipeline.events.active=0 libbeat.pipeline.events.filtered=4 libbeat.pipeline.events.published=13275 libbeat.pipeline.events.total=13279 libbeat.pipeline.queue.acked=13677 registrar.states.cleanup=1 registrar.states.current=8 registrar.states.update=13681 registrar.writes=28
里面的参数主要分成三个部分:
beat.*,包含memstats.gc_next,memstats.memory_alloc,memstats.memory_total,这个是所有beat组件都有的指标,是filebeat继承来的,主要是内存相关的,我们这里特别关注memstats.memory_alloc,alloc的越多,占用内存越大filebeat.*,这部分是filebeat特有的指标,通过event相关的指标,我们知道吞吐,通过harvester,我们知道正在监控多少个文件,未消费event堆积的越多,havester创建的越多,消耗内存越大libbeat.*,也是beats组件通用的指标,包含outputs和pipeline等信息。这里要主要当outputs发生阻塞的时候,会直接影响queue里面event的消费,造成内存堆积registrar,filebeat将监控文件的状态放在registry文件里面,当监控文件非常多的时候,比如10万个,而且没有合理的设置close_inactive参数,这个文件能达到100M,载入内存后,直接占用内存
filebeat日志解析
当然,我们不可能直接去读这个日志,既然我们使用ELK,肯定是用ELK进行解读。因为是kv格式,很方便,用logstash的kv plugin:
filter {
kv {}
}
kv无法指定properties的type,所以,我们需要稍微指定了一下索引的模版:
PUT _template/template_1
{
"index_patterns": ["filebeat*"],
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1
},
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"_source": {
"enabled": false
},
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"longs_as_strings": {
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"path_match": "*beat.*",
"path_unmatch": "*.*name",
"mapping": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
上面的模版,将kv解析出的properties都mapping到long类型,但注意"path_match": "*beat.*"无法match到registrar的指标,读者可以自己写一个更完善的mapping。
这样,我们就可以通过kibana可视化组件,清楚的看到内存泄漏的过程
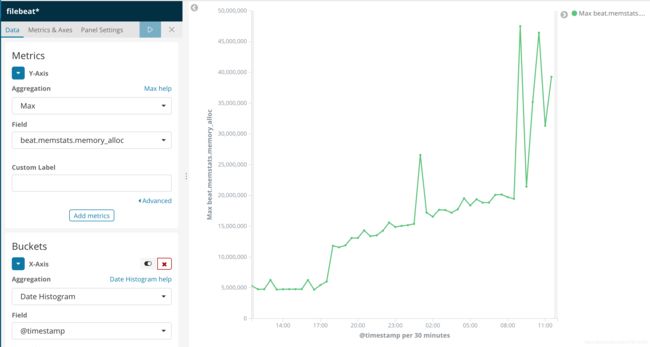
以及资源的使用情况:
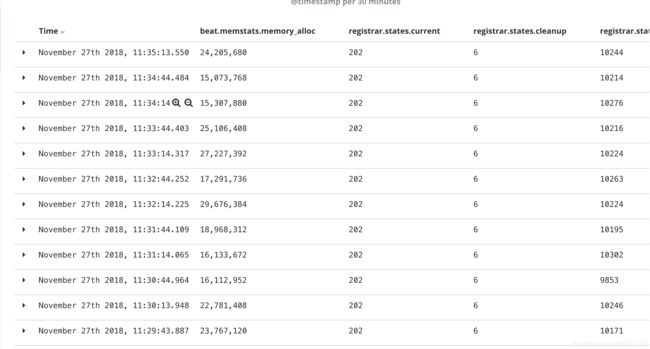
将信息可视化之后,我们可以明显的发现,内存的突变和ERR是同时发生的
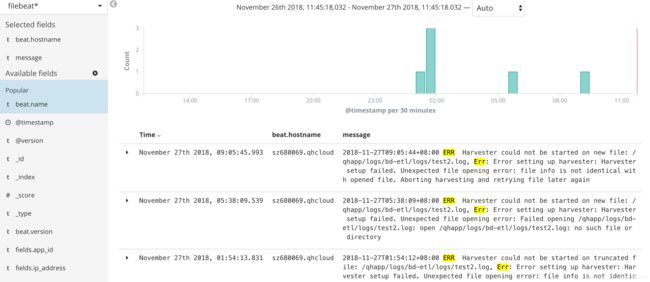
即以下error:
2018-11-27T09:05:44+08:00 ERR Harvester could not be started on new file: /qhapp/logs/bd-etl/logs/test2.log, Err: Error setting up harvester: Harvester setup failed. Unexpected file opening error: file info is not identical with opened file. Aborting harvesting and retrying file later again
会导致filebeat突然申请了额外的内存。具体请查看issue
通过pprof
众所周知,filebeat是用go语言实现的,而go语言本身的基础库里面就包含pprof这个功能极其强大的性能分析工具,只是这个工具是用于debug的,在正常模式下,filebeat是不会启动这个选贤的,并且很遗憾,在官方文档里面根本没有提及我们可以使用pprof来观测filebeat。我们接下来可以通过6.3上修复的一个内存泄漏的issue,来学习怎么使用pprof进行分析
启动pprof监测
首先,需要让filebeat在启动的时候运行pprof,具体的做法是在启动是加上参数-httpprof localhost:6060,即/usr/share/filebeat/bin/filebeat -c /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml -path.home /usr/share/filebeat -path.config /etc/filebeat -path.data /var/lib/filebeat -path.logs /var/log/filebeat -httpprof localhost:6060。这里只绑定了localhost,无法通过远程访问,如果想远程访问,应该使用0.0.0.0。
这时,你就可以通过curl http://localhost:6060/debug/pprof/heap > profile.txt等命令,获取filebeat的实时堆栈信息了。
远程连接
当然,你也可以通过在你的本地电脑上安装go,然后通过go tool远程连接pprof。
因为我们是需要研究内存的问题,所以以下连接访问的是/heap子路径
go tool pprof http://10.60.x.x:6060/debug/pprof/heap
top 命令
连接之后,你可以通过top命令,查看消耗内存最多的几个实例:
33159.58kB of 33159.58kB total ( 100%)
Dropped 308 nodes (cum <= 165.80kB)
Showing top 10 nodes out of 51 (cum >= 512.04kB)
flat flat% sum% cum cum%
19975.92kB 60.24% 60.24% 19975.92kB 60.24% runtime.malg
7680.66kB 23.16% 83.40% 7680.66kB 23.16% github.com/elastic/beats/filebeat/channel.SubOutlet
2048.19kB 6.18% 89.58% 2048.19kB 6.18% github.com/elastic/beats/filebeat/prospector/log.NewHarvester
1357.91kB 4.10% 93.68% 1357.91kB 4.10% runtime.allgadd
1024.08kB 3.09% 96.76% 1024.08kB 3.09% runtime.acquireSudog
544.67kB 1.64% 98.41% 544.67kB 1.64% github.com/elastic/beats/libbeat/publisher/queue/memqueue.NewBroker
528.17kB 1.59% 100% 528.17kB 1.59% regexp.(*bitState).reset
0 0% 100% 528.17kB 1.59% github.com/elastic/beats/filebeat/beater.(*Filebeat).Run
0 0% 100% 512.04kB 1.54% github.com/elastic/beats/filebeat/channel.CloseOnSignal.func1
0 0% 100% 512.04kB 1.54% github.com/elastic/beats/filebeat/channel.SubOutlet.func1
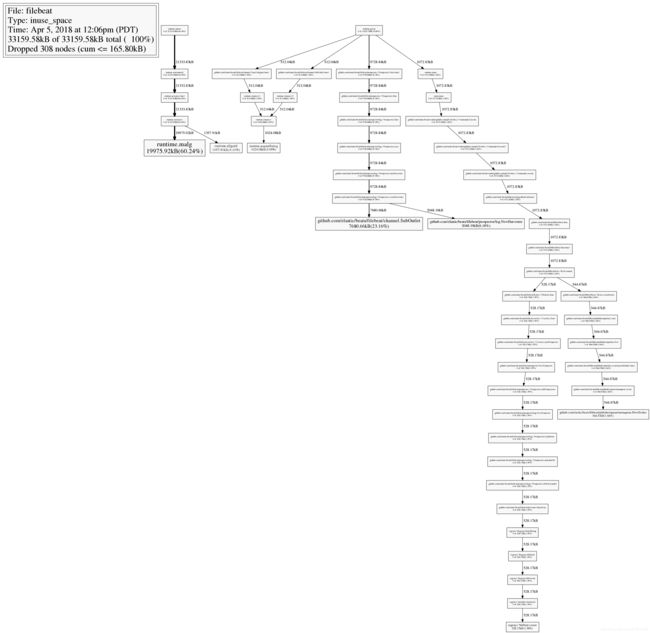
查看堆栈调用图
输入web命令,会生产堆栈调用关系的svg图,在这个svg图中,你可以结合top命令一起查看,在top中,我们已经知道github.com/elastic/beats/filebeat/channel.SubOutlet占用了很多的内存,在图中,展现的是调用关系栈,你可以看到这个类是怎么被实例化的,并且在整个堆中,内存是怎么分布的。最直观的是,实例所处的长方形面积越大,代表占用的内存越多。:
查看源码
通过list命令,可以迅速查看可以实例的问题源码,比如在之前的top10命令中,我们已经看到github.com/elastic/beats/filebeat/channel.SubOutlet这个类的实例占用了大量的内存,我们可以通过list做进一步的分析,看看这个类内部在哪个语句开始出现内存的占用:
(pprof) list SubOutlet
Total: 32.38MB
ROUTINE ======================== github.com/elastic/beats/filebeat/channel.SubOutlet in /home/jeremy/src/go/src/github.com/elastic/beats/filebeat/channel/util.go
7.50MB 7.50MB (flat, cum) 23.16% of Total
. . 15:// SubOutlet create a sub-outlet, which can be closed individually, without closing the
. . 16:// underlying outlet.
. . 17:func SubOutlet(out Outleter) Outleter {
. . 18: s := &subOutlet{
. . 19: isOpen: atomic.MakeBool(true),
1MB 1MB 20: done: make(chan struct{}),
2MB 2MB 21: ch: make(chan *util.Data),
4.50MB 4.50MB 22: res: make(chan bool, 1),
. . 23: }
. . 24:
. . 25: go func() {
. . 26: for event := range s.ch {
. . 27: s.res <- out.OnEvent(event)
如何调优
其实调优的过程就是调整参数的过程,之前说过了,和内存相关的参数, max_message_bytes,queue.mem.events,queue.mem.flush.min_events,以及队列占用内存的公式:max_message_bytes * queue.mem.events
output.kafka:
enabled: true
# max_message_bytes: 1000000
hosts: ["10.60.x.x:9092"]
topic: '%{[fields][topic]}'
max_procs: 1
#queue.mem.events: 256
#queue.mem.flush.min_events: 128
但其实,不同的环境下,不同的原因都可能会造成filebeat占用的内存过大,此时,需要仔细的确认你的上下文环境:
- 是否因为通配符的原因,造成同时监控数量巨大的文件,这种情况应该避免用通配符监控无用的文件。
- 是否文件的单行内容巨大,确定是否需要改造文件内容,或者将其过滤
- 是否过多的匹配了multiline的pattern,并且多行的event是否单条体积过大。这时,就需要暂时关闭multiline,修改文件内容或者multiline的pattern。
- 是否output经常阻塞,event queue里面总是一直缓存event。这时要检查你的网络环境或者消息队列等中间件是否正常