先来了解关于Runtime的一些主要的数据结构。
- objc_object
- objc_class
- isa指针
- method_t
objc_object
首先我们要了解的是,在OC中,我们常用的id类型,对应到runtime中就是objc_object这样的结构体。
objc_object包含以下几个成员部分:
- isa_t(共用体)
- 关于isa操作相关方法
- 弱引用相关方法
- 关联对象相关方法
- 内存管理相关方法
objc_class
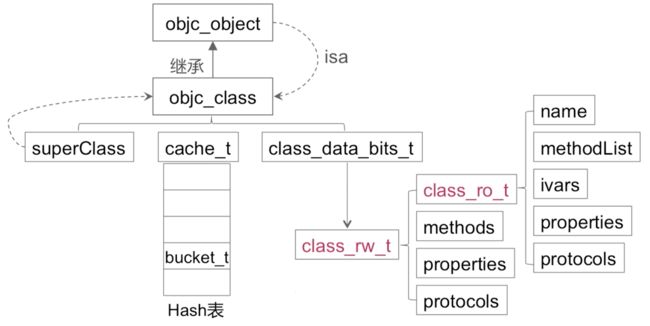
在OC中我们使用到Class在runtime中对应的就是objc_class结构体。
objc_class继承自objc_object,由此我们可以了解,Class实际上也是一个对象类型,objc_class包含以下部分:
- Class superClass(指向父类)
-
cache_tcache(方法缓存结构) -
class_data_bits_tbits;(类定义的变量,属性,方法都在这个成员结构当中)
isa指针
isa指针是一个C++当中的共用体isa_t,现在大多数系统都是64位的,因此我们按照isa_t在64位系统下的内存表现情况来对其做讲解。
isa指针分为2种,一种是指针型的isa(isa的值代表Class的地址),另一种是非指针型的isa(isa的值的部分代表Class的地址)。这种做法的目的是,通常在内存中40位左右的内存就已经可以满足内存查找的目的,剩下的内存可以存储一些其他的信息,以节省内存。
isa指针的指向
- 对于
对象类型,其isa指针指向类对象(我们之前说过,任何对象的类对象实际上也是一个对象)。 - 对于
类对象类型,其isa指针指向元类对象(MetaClass)。
cache_t
- cache_t用于快速查找方法执行函数(例如执行一个方法,此方法在缓存中,就不需要重新去方法列表中查找)
- cache_t是可
增量扩展的哈希表结构 - 是
局部性原理(局部性原理: 在我们调用方法时,可能调用频次最高的就那么几个方法,因此将几个调用频次高的方法缓存起来,达到优化的目的)的最佳应用
下面说明一下cache_t的结构,这是一个由bucket_t结构体组成的数组
而bucket_t中的结构是
struct bucket_t {
private:
cache_key_t _key;
IMP _imp;
public:
inline cache_key_t key() const { return _key; }
inline IMP imp() const { return (IMP)_imp; }
inline void setKey(cache_key_t newKey) { _key = newKey; }
inline void setImp(IMP newImp) { _imp = newImp; }
void set(cache_key_t newKey, IMP newImp);
};
我们可以看到是由key和IMP组成的一个结构体,key对应于OC中的方法选择器(SEL),IMP可以理解为一个无类型的函数指针。我们查找方法时,由上层传入一个key,就可以根据key定位到函数的实现实现调用。
class_data_bits_t
- class_data_bits_t主要是对class_rw_t(可读写)的封装
- class_rw_t代表了类相关的
读写信息,对class_ro_t(只读)的封装
public:
class_rw_t* data() {
return (class_rw_t *)(bits & FAST_DATA_MASK);
}
void setData(class_rw_t *newData)
{
assert(!data() || (newData->flags & (RW_REALIZING | RW_FUTURE)));
// Set during realization or construction only. No locking needed.
// Use a store-release fence because there may be concurrent
// readers of data and data's contents.
uintptr_t newBits = (bits & ~FAST_DATA_MASK) | (uintptr_t)newData;
atomic_thread_fence(memory_order_release);
bits = newBits;
}
class_rw_t
下面是class_rw_t中的主要属性
struct class_rw_t {
// Be warned that Symbolication knows the layout of this structure.
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t version;
const class_ro_t *ro;
method_array_t methods;
property_array_t properties;
protocol_array_t protocols;
Class firstSubclass;
Class nextSiblingClass;
char *demangledName;
}
我们重点关注以下几个属性
- class_ro_t *ro(只读列表)
- property_array_t properties(属性列表)
- protocol_array_t protocols(协议列表)
- method_array_t methods(方法列表)
关于这个二维数组的更多理解,可以结合这段代码。
比如,我们在分类A中定义的方法,就作为一个数组,存在于methods中。分类B又作为新的数组对象,存在于methods中。
class method_array_t :
public list_array_tt
{
typedef list_array_tt Super;
public:
method_list_t **beginCategoryMethodLists() {
return beginLists();
}
method_list_t **endCategoryMethodLists(Class cls);
method_array_t duplicate() {
return Super::duplicate();
}
};
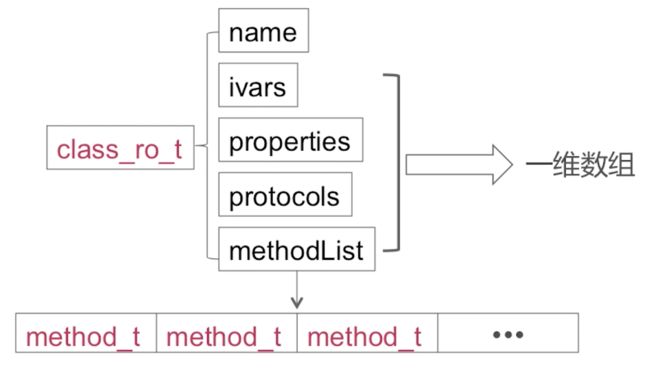
class_ro_t
我们再看看class_ro_t是什么样的数据结构
struct class_ro_t {
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t instanceStart;
uint32_t instanceSize;
#ifdef __LP64__
uint32_t reserved;
#endif
const uint8_t * ivarLayout;
const char * name; // 类名 NSClassFromString(这里就是这个类名)
method_list_t * baseMethodList; // 方法
protocol_list_t * baseProtocols; // 协议
const ivar_list_t * ivars; // 定义的成员变量
const uint8_t * weakIvarLayout;
property_list_t *baseProperties; // 属性
method_list_t *baseMethods() const {
return baseMethodList;
}
};
总结来说,class\_rw\_t中一般来说存储的是分类的内容,class\_ro\_t存储的是原始类中的内容
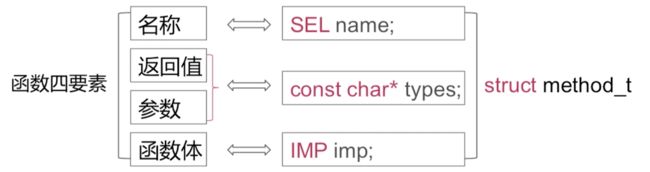
method_t
上面见到了这么多method_t,那么method_t是什么样的数据结构呢?
struct method_t {
SEL name; // 方法选择器
const char *types; // 返回值,参数
IMP imp; // 指向方法实现地址的指针
struct SortBySELAddress :
public std::binary_function
{
bool operator() (const method_t& lhs,
const method_t& rhs)
{ return lhs.name < rhs.name; }
};
};
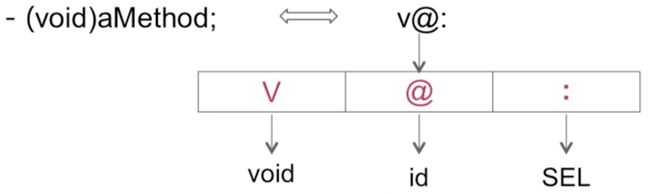
我们先来看看types是怎么表述返回值和参数的,这里涉及到Apple的Type Encodings技术。
我们来看const char* types结构的数据
我们可以很直观的理解。无参的返回值为void。
比如方法-(void)aMethod;,对应的types的值是v@:,v表示void,@代表参数1,:表示参数2。
下面整体的看一下这些内容的关系图