前期博客
基于CentOS6.5下Suricata(一款高性能的网络IDS、IPS和网络安全监控引擎)的搭建(图文详解)(博主推荐)
基于Ubuntu14.04下Suricata(一款高性能的网络IDS、IPS和网络安全监控引擎)的搭建(图文详解)(博主推荐)
参考官网
https://redmine.openinfosecfoundation.org/projects/suricata/wiki/_Logstash_Kibana_and_Suricata_JSON_output
注意,这官网,默认是适合Ubuntu系统的安装手法。
首先,
Make sure your Suricata is compiled/installed with libjansson support enabled:
[root@suricata ~]# suricata --build-info This is Suricata version 3.1 RELEASE Features: PCAP_SET_BUFF LIBPCAP_VERSION_MAJOR=1 AF_PACKET HAVE_PACKET_FANOUT LIBCAP_NG LIBNET1.1 HAVE_HTP_URI_NORMALIZE_HOOK HAVE_NSS HAVE_LIBJANSSON TLS SIMD support: SSE_4_2 SSE_4_1 SSE_3 Atomic intrisics: 1 2 4 8 16 byte(s) 64-bits, Little-endian architecture GCC version 4.4.7 20120313 (Red Hat 4.4.7-18), C version 199901 compiled with _FORTIFY_SOURCE=0 L1 cache line size (CLS)=64 thread local storage method: __thread compiled with LibHTP v0.5.20, linked against LibHTP v0.5.20 Suricata Configuration: AF_PACKET support: yes PF_RING support: no NFQueue support: no NFLOG support: no IPFW support: no Netmap support: no DAG enabled: no Napatech enabled: no Unix socket enabled: yes Detection enabled: yes libnss support: yes libnspr support: yes libjansson support: yes hiredis support: no Prelude support: no PCRE jit: no LUA support: no libluajit: no libgeoip: no Non-bundled htp: no Old barnyard2 support: no CUDA enabled: no Hyperscan support: no Libnet support: yes Suricatasc install: yes Profiling enabled: no Profiling locks enabled: no Development settings: Coccinelle / spatch: no Unit tests enabled: no Debug output enabled: no Debug validation enabled: no Generic build parameters: Installation prefix: /usr/local Configuration directory: /usr/local/etc/suricata/ Log directory: /usr/local/var/log/suricata/ --prefix /usr/local --sysconfdir /usr/local/etc --localstatedir /usr/local/var Host: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu Compiler: gcc (exec name) / gcc (real) GCC Protect enabled: no GCC march native enabled: yes GCC Profile enabled: no Position Independent Executable enabled: no CFLAGS -g -O2 -march=native PCAP_CFLAGS SECCFLAGS [root@suricata ~]#
然后,需要配置
Configure suricata
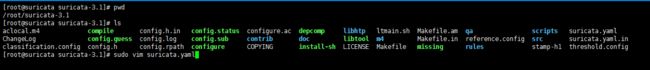
[root@suricata suricata-3.1]# pwd /root/suricata-3.1 [root@suricata suricata-3.1]# ls aclocal.m4 compile config.h.in config.status configure.ac depcomp libhtp ltmain.sh Makefile.am qa scripts suricata.yaml ChangeLog config.guess config.log config.sub contrib doc libtool m4 Makefile.in reference.config src suricata.yaml.in classification.config config.h config.rpath configure COPYING install-sh LICENSE Makefile missing rules stamp-h1 threshold.config [root@suricata suricata-3.1]# sudo vim suricata.yaml
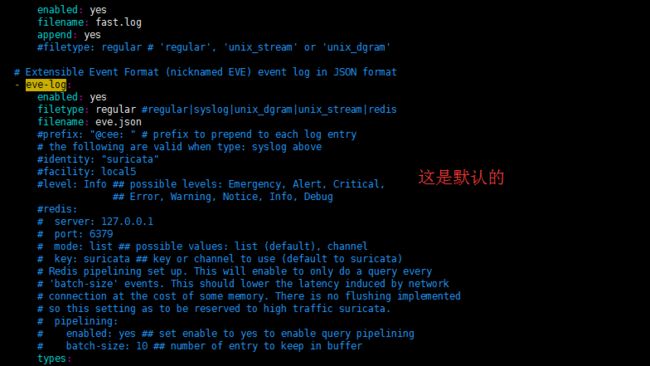
# Extensible Event Format (nicknamed EVE) event log in JSON format - eve-log: enabled: yes filetype: regular #regular|syslog|unix_dgram|unix_stream|redis filename: eve.json #prefix: "@cee: " # prefix to prepend to each log entry # the following are valid when type: syslog above #identity: "suricata" #facility: local5 #level: Info ## possible levels: Emergency, Alert, Critical, ## Error, Warning, Notice, Info, Debug #redis: # server: 127.0.0.1 # port: 6379 # mode: list ## possible values: list (default), channel # key: suricata ## key or channel to use (default to suricata) # Redis pipelining set up. This will enable to only do a query every # 'batch-size' events. This should lower the latency induced by network # connection at the cost of some memory. There is no flushing implemented # so this setting as to be reserved to high traffic suricata. # pipelining: # enabled: yes ## set enable to yes to enable query pipelining # batch-size: 10 ## number of entry to keep in buffer types: - alert: # payload: yes # enable dumping payload in Base64 # payload-buffer-size: 4kb # max size of payload buffer to output in eve-log # payload-printable: yes # enable dumping payload in printable (lossy) format # packet: yes # enable dumping of packet (without stream segments) http: yes # enable dumping of http fields tls: yes # enable dumping of tls fields ssh: yes # enable dumping of ssh fields smtp: yes # enable dumping of smtp fields # HTTP X-Forwarded-For support by adding an extra field or overwriting # the source or destination IP address (depending on flow direction) # with the one reported in the X-Forwarded-For HTTP header. This is # helpful when reviewing alerts for traffic that is being reverse # or forward proxied. xff: enabled: no # Two operation modes are available, "extra-data" and "overwrite". mode: extra-data # Two proxy deployments are supported, "reverse" and "forward". In # a "reverse" deployment the IP address used is the last one, in a # "forward" deployment the first IP address is used. deployment: reverse # Header name where the actual IP address will be reported, if more # than one IP address is present, the last IP address will be the # one taken into consideration. header: X-Forwarded-For - http: extended: yes # enable this for extended logging information # custom allows additional http fields to be included in eve-log # the example below adds three additional fields when uncommented #custom: [Accept-Encoding, Accept-Language, Authorization] - dns - tls: extended: yes # enable this for extended logging information - files: force-magic: no # force logging magic on all logged files force-md5: no # force logging of md5 checksums #- drop: # alerts: no # log alerts that caused drops - smtp: #extended: yes # enable this for extended logging information # this includes: bcc, message-id, subject, x_mailer, user-agent # custom fields logging from the list: # reply-to, bcc, message-id, subject, x-mailer, user-agent, received, # x-originating-ip, in-reply-to, references, importance, priority, # sensitivity, organization, content-md5, date #custom: [received, x-mailer, x-originating-ip, relays, reply-to, bcc] # output md5 of fields: body, subject # for the body you need to set app-layer.protocols.smtp.mime.body-md5 # to yes #md5: [body, subject] - ssh - stats: totals: yes # stats for all threads merged together threads: no # per thread stats deltas: no # include delta values # bi-directional flows - flow # uni-directional flows #- netflow
改为
# "United" event log in JSON format - eve-log: enabled: yes type: file #file|syslog|unix_dgram|unix_stream filename: eve.json # the following are valid when type: syslog above #identity: "suricata" #facility: local5 #level: Info ## possible levels: Emergency, Alert, Critical, ## Error, Warning, Notice, Info, Debug types: - alert - http: extended: yes # enable this for extended logging information - dns - tls: extended: yes # enable this for extended logging information - files: force-magic: yes # force logging magic on all logged files force-md5: yes # force logging of md5 checksums #- drop - ssh - smtp
然后,接下是安装
Install ELK (elasticsearch, logstash, kibana)
先卸载自带的openjdk
rpm -qa|grep java
rpm -e --nodeps tzdata-java-2013g-1.el6.noarch rpm -e --nodeps java-1.7.0-openjdk-1.7.0.45-2.4.3.3.el6.x86_64 rpm -e --nodeps java-1.6.0-openjdk-1.6.0.0-1.66.1.13.0.el6.x86_64
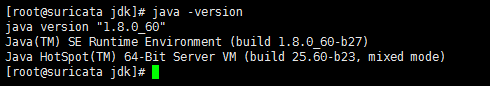
注意:这里一定要是jdk1.8,不然会报如下错误
[root@suricata ~]# sudo /etc/init.d/elasticsearch start Starting elasticsearch: Elasticsearch requires at least Java 8 but your Java version from /usr/local/jdk/jdk1.7.0_79/bin/java does not meet this requirement [FAILED] [root@suricata ~]#
官网提示了,建议安装orcal 的 jdk。
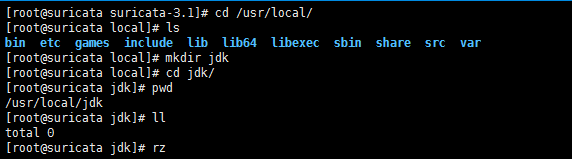
我这里安装jdk18。
[root@suricata suricata-3.1]# cd /usr/local/ [root@suricata local]# ls bin etc games include lib lib64 libexec sbin share src var [root@suricata local]# mkdir jdk [root@suricata local]# cd jdk/ [root@suricata jdk]# pwd /usr/local/jdk [root@suricata jdk]# ll total 0 [root@suricata jdk]# rz
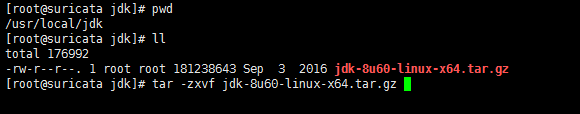
[root@suricata jdk]# pwd /usr/local/jdk [root@suricata jdk]# ll total 176992 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 181238643 Sep 3 2016 jdk-8u60-linux-x64.tar.gz [root@suricata jdk]# tar -zxvf jdk-8u60-linux-x64.tar.gz
然后,再vim /etc/profile
#java export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk/jdk1.8.0_60 export CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/rt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin
文件生效
source /etc/profile
然后,接下来就是安装ELk和配置JDK。(注意以下只是个例子)
wget https://download.elasticsearch.org/kibana/kibana/kibana-3.0.0.tar.gz wget https://download.elasticsearch.org/elasticsearch/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-1.6.1.deb wget https://download.elastic.co/logstash/logstash/packages/debian/logstash_1.5.3-1_all.deb tar -C /var/www/ -xzf kibana-3.0.0.tar.gz dpkg -i elasticsearch-1.6.1.deb dpkg -i logstash_1.5.3-1_all.deb
我这里啊,Elasticsearch选取5.5.0
所以,总的是
[root@suricata ~]# wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-5.5.0.deb
[root@suricata ~]# wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-5.5.0.deb
[root@suricata ~]# wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-5.5.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
最后下载,得到
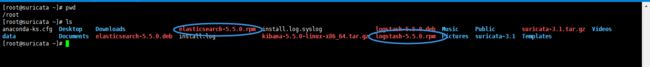
[root@suricata ~]# pwd /root [root@suricata ~]# ls anaconda-ks.cfg Desktop Downloads install.log kibana-5.5.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz Music Public suricata-3.1.tar.gz Videos data Documents elasticsearch-5.5.0.deb install.log.syslog logstash-5.5.0.deb Pictures suricata-3.1 Templates [root@suricata ~]#
然后,进行对kibana的安装
[root@suricata ~]# pwd /root [root@suricata ~]# ls anaconda-ks.cfg Desktop Downloads install.log kibana-5.5.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz Music Public suricata-3.1.tar.gz Videos data Documents elasticsearch-5.5.0.deb install.log.syslog logstash-5.5.0.deb Pictures suricata-3.1 Templates [root@suricata ~]# tar -C /var/www/ -xzf kibana-5.5.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
得到
[root@suricata www]# pwd /var/www [root@suricata www]# ls cgi-bin error html icons kibana-5.5.0-linux-x86_64 [root@suricata www]#
若大家没安装过这个命令,则安装下即可。
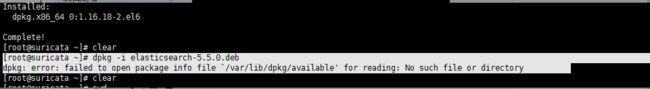
[root@suricata ~]# yum -y install dpkg
然后,进行对elasticsearch的安装
[root@suricata ~]# pwd /root [root@suricata ~]# ls anaconda-ks.cfg Desktop Downloads install.log kibana-5.5.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz Music Public suricata-3.1.tar.gz Videos data Documents elasticsearch-5.5.0.deb install.log.syslog logstash-5.5.0.deb Pictures suricata-3.1 Templates [root@suricata ~]# dpkg -i elasticsearch-5.5.0.deb
这里啊,我建议大家还是去安装tar.gz包,这种方式比较好。
所以,后面,我还是下载了,rpm包,以这种方式来进行安装。
[root@suricata ~]# wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm
[root@suricata ~]# wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-5.5.0.rpm
进行elasticsearch-5.5.0的安装
[root@suricata ~]# pwd /root [root@suricata ~]# ls anaconda-ks.cfg Desktop Downloads elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm install.log.syslog logstash-5.5.0.deb Music Public suricata-3.1.tar.gz Videos data Documents elasticsearch-5.5.0.deb install.log kibana-5.5.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz logstash-5.5.0.rpm Pictures suricata-3.1 Templates
[root@suricata ~]# rpm -ivh elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm
warning: elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm: Header V4 RSA/SHA512 Signature, key ID d88e42b4: NOKEY
Preparing... ########################################### [100%]
Creating elasticsearch group... OK
Creating elasticsearch user... OK
1:elasticsearch ########################################### [100%]
### NOT starting on installation, please execute the following statements to configure elasticsearch service to start automatically using chkconfig
sudo chkconfig --add elasticsearch
### You can start elasticsearch service by executing
sudo service elasticsearch start
安装完,默认即有
然后,进行logstash的安装
[root@suricata ~]# pwd /root [root@suricata ~]# ls anaconda-ks.cfg Desktop Downloads elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm install.log.syslog logstash-5.5.0.deb Music Public suricata-3.1.tar.gz Videos data Documents elasticsearch-5.5.0.deb install.log kibana-5.5.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz logstash-5.5.0.rpm Pictures suricata-3.1 Templates [root@suricata ~]# rpm -ivh logstash-5.5.0.rpm warning: logstash-5.5.0.rpm: Header V4 RSA/SHA512 Signature, key ID d88e42b4: NOKEY Preparing... ########################################### [100%] 1:logstash ########################################### [100%] Using provided startup.options file: /etc/logstash/startup.options /usr/share/logstash/vendor/jruby/bin/jruby: line 388: /usr/bin/java: No such file or directory /usr/share/logstash/vendor/jruby/bin/jruby: line 388: exec: /usr/bin/java: cannot execute: No such file or directory Unable to install system startup script for Logstash. [root@suricata ~]#
安装完,默认即有
然后,下面是
Logstash configuration
[root@suricata conf.d]# pwd /etc/logstash/conf.d [root@suricata conf.d]# ll total 0 [root@suricata conf.d]# touch /etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash.conf
插入如下内容
input { file { path => ["/var/log/suricata/eve.json"] sincedb_path => ["/var/lib/logstash/"] codec => json type => "SuricataIDPS" } } filter { if [type] == "SuricataIDPS" { date { match => [ "timestamp", "ISO8601" ] } ruby { code => "if event['event_type'] == 'fileinfo'; event['fileinfo']['type']=event['fileinfo']['magic'].to_s.split(',')[0]; end;" } } if [src_ip] { geoip { source => "src_ip" target => "geoip" #database => "/opt/logstash/vendor/geoip/GeoLiteCity.dat" add_field => [ "[geoip][coordinates]", "%{[geoip][longitude]}" ] add_field => [ "[geoip][coordinates]", "%{[geoip][latitude]}" ] } mutate { convert => [ "[geoip][coordinates]", "float" ] } if ![geoip.ip] { if [dest_ip] { geoip { source => "dest_ip" target => "geoip" #database => "/opt/logstash/vendor/geoip/GeoLiteCity.dat" add_field => [ "[geoip][coordinates]", "%{[geoip][longitude]}" ] add_field => [ "[geoip][coordinates]", "%{[geoip][latitude]}" ] } mutate { convert => [ "[geoip][coordinates]", "float" ] } } } } } output { elasticsearch { host => localhost #protocol => http } }
然后,再
Configure the start-up services
update-rc.d elasticsearch defaults 95 10 (这两个是ubuntu系统里的做法,我这里是centos系统,不需要) update-rc.d logstash defaults
service httpd start 启动apache
service elasticsearch start
service logstash start
或者
启动服务sudo /etc/init.d/elasticsearch start 停止服务sudo /etc/init.d/elasticsearch stop
启动服务sudo /etc/init.d/logstash/start
停止服务sudo /etc/init.d/logstashstop
如果大家在启动过程中,出现如下问题。
[root@suricata ~]# sudo /etc/init.d/elasticsearch start which: no java in (/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin) Could not find any executable java binary. Please install java in your PATH or set JAVA_HOME [root@suricata ~]#
则见
ElasticSearch里JAVA环境丢失的问题
-rwxr-x---. 1 root root 5113 Jul 1 07:20 elasticsearch ,经过
[root@suricata init.d]# chmod 755 elasticsearch [root@suricata init.d]# pwd /etc/init.d [root@suricata init.d]#
改为
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 5113 Jul 1 07:20 elasticsearch
大家,自行按照自己的jdk位置。
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk/jdk1.8.0_60
然后,就可以成功了。
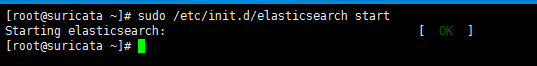
[root@suricata ~]# sudo /etc/init.d/elasticsearch start
Starting elasticsearch: [ OK ]
[root@suricata ~]#
然后,大家也许在启动,会遇到这样的问题:
Logstash默认的配置文件位置为./config和/etc/logstash/,后者已经存在,但直接运行依然会报错:
WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash.
见
Logstash使用grok解析IIS日志
简单起见,直接在Logstash根目录创建软链接即可:
cd /usr/share/logstash
[root@suricata logstash]# pwd
/usr/share/logstash
[root@suricata logstash]# ln -s /etc/logstash ./config
[root@suricata logstash]#
设置配置文件实时生效,从而不用频繁地启停Logstash。
修改/etc/logstash/logstash.yml
config.reload.automatic: true
Logstash的运行
与Elasticsearch、Kibana不同,Logstash默认并不作为系统服务安装,我们也不建议作为服务启动。主要原因为:大多数情况下,Elasticsearch、Kibana在每台服务器上只有一个实例,可以作为服务启动;而一个Logstash实例一般只服务于一个数据流,因此一台服务器上经常运行多个实例 。编写一个配置文件helloworld.conf进行测试。注意,不要把该文件放在/etc/logstash/conf.d下,以避免不同实例间产生混淆,因为该文件夹是Logstash默认读取的文件夹。简单起见,可直接放在Logstash根目录下。
input {
stdin {}
}
output {
stdout {}
}
这是一个命令行输入、命令行输出的Logstash实例,运行成功则说明已配置正确:
bin/logstash -f helloworld.conf
虽然如此,很多时候我们还是希望各个Logstash实例能随系统而启动并在后台运行。将其加入计划任务即可:
nohup /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f /usr/share/logstash/helloworld.conf > /dev/null &
然后,
Now make sure Suricata is running and you have logs written in your JSON log files
http://localhost/kibana-5.5.0
https://redmine.openinfosecfoundation.org/projects/suricata/wiki/_Logstash_Kibana_and_Suricata_JSON_output
继续