faster rcnn中RPN网络源码分析(pytorch)
最近刚入坑检测,初步看了RGB大佬的faster rcnn文章,再看看源码
本次分析的源码是陈云大佬pytorch版本的GITHUB地址
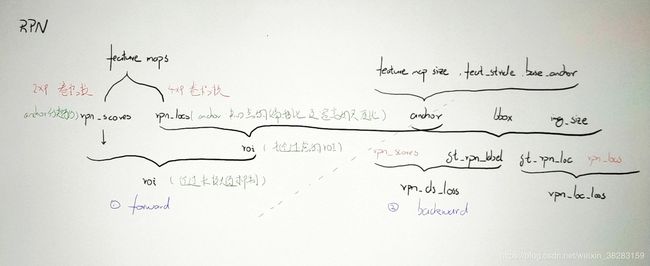
一、forward
主文件./model/region_proposal_network.py
- rpn_scores & rpn_locs
input : feature maps
output : rpn_scores 、 rpn_locs
(1)、feature maps过 n_anchor * 2个卷积核得到每个anchor的前景背景的分类得分rpn_locs
(2)、feature maps过 n_anchor * 4个卷积核得到每个anchor的中心点坐标和宽高的尺度变换比值rpn_locs
#rpn中初始化定义的Layer
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, mid_channels, 3, 1, 1)
self.score = nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, n_anchor * 2, 1, 1, 0) #n_anchor * 2 ,作为每个anchor的前景背景的分类得分,二分类所以*2
self.loc = nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, n_anchor * 4, 1, 1, 0) #n_anchor * 4,为每个anchor的中心坐标偏移比例和宽、高的各自的尺寸比
#rpn前传网络中连接
h = F.relu(self.conv1(x)) #x是extractor提取的feature maps
rpn_locs = self.loc(h)
rpn_scores = self.score(h)
- anchor
# 生成anchor_base,即feature map第一个点对应的anchors
#使用的函数(path:./model/utils/bbox_tool.py)
def generate_anchor_base(base_size=16, ratios=[0.5, 1, 2],anchor_scales=[8, 16, 32])
#以(8,8)为中心,长宽比分别为[0.5, 1, 2],面积分别为16*16 *[8, 16, 32],共9个anchor
input : feature map size、feat_stride、anchor_base
output : anchor
# height, width为feature map 尺寸
# feat_stride为image 和 feature map 尺寸比
# 将anchor_base经过平移变换和等比变换,得到对应于image的anchors
# 使用的函数(path:./model/region_proposal_network.py)
def _enumerate_shifted_anchor(anchor_base, feat_stride, height, width)
下面3、4主体都在ProposalCreator类(path:./model/utils/creator_tool.py)的def __call__中实现
- 未经过滤的roi
input : rpn_locs、anchor
output : 未经过滤的roi
通过rpn_locs(dy,dx,dh,dw)对anchor做坐标变换,得到未经过滤的roi。变换公式如下
#x,y,w,h为anchor的中心点坐标(x,y)及宽w、高h
#x',y',w',h'为未经过滤的roi的中心点坐标(x',y')及宽w'、高h'
dx = (x' - x) / w
dy = (y' - y) / h
dw = ln(w' / w) #使用ln是为了是w'/w为一个正数
dh = ln(h' / h)
#使用的函数(path:./model/utils/bbox_tool.py)
#src_bbox : anchor
#loc : rpn_locs
def loc2bbox(src_bbox, loc)
- roi
input : 未经过滤的roi、rpn_scores
output : roi
#1、尺寸过滤(只保留尺寸大于阈值的roi)
min_size = self.min_size * scale
hs = roi[:, 2] - roi[:, 0]
ws = roi[:, 3] - roi[:, 1]
keep = np.where((hs >= min_size) & (ws >= min_size))[0]
roi = roi[keep, :]
score = score[keep]
#2、前期前景得分过滤(只保留得分最高的n_pre_nms 个roi)
order = score.ravel().argsort()[::-1]
if n_pre_nms > 0:
order = order[:n_pre_nms]
roi = roi[order, :]
#3、非极大值抑制
keep = non_maximum_suppression(
cp.ascontiguousarray(cp.asarray(roi)),
thresh=self.nms_thresh)
#4、后期前景得分过滤(只保留得分最高的n_post_nms 个roi)
if n_post_nms > 0:
keep = keep[:n_post_nms]
roi = roi[keep]
至此前传基本就结束了,之后就是将roi送入roi pooling…
二、backward
主文件./trainer.py
- gt_rpn_label
input : bbox、anchor
output : gt_rpn_label
# 主要就是计算bbox个各个anchor的iou值
# 使用的函数(path:./model/utils/creator_tool.py)
# bbox :目标真实位置
def _create_label(self, inside_index, anchor, bbox)
...
# iou小于阈值为背景
label[max_ious < self.neg_iou_thresh] = 0
...
# iou大于阈值为前景
label[max_ious >= self.pos_iou_thresh] = 1
...
# 前景个数大于n_pos,就将n_pos后的忽略,即label=-1
if len(pos_index) > n_pos:
disable_index = np.random.choice(
pos_index, size=(len(pos_index) - n_pos), replace=False)
label[disable_index] = -1
...
# 背景个数大于n_neg,就将n_neg后的忽略,即label=-1
if len(neg_index) > n_neg:
disable_index = np.random.choice(
neg_index, size=(len(neg_index) - n_neg), replace=False)
label[disable_index] = -1
-
gt_rpn_loc
input : bbox、anchor
output : gt_rpn_loc
# 使用的函数(path:./model/utils/bbox_tool.py)
# src_bbox : anchor
# dst_bbox: bbox
# 利用每个anchor分别与bbox计算(公式见一中的3),得到每个anchor的中心点坐标和宽高的尺度变换比值的GT
def bbox2loc(src_bbox, dst_bbox)
- rpn_cls_loss
input : gt_rpn_label、rpn_scores
output : rpn_cls_loss
# 交叉熵
rpn_cls_loss = F.cross_entropy(rpn_score, gt_rpn_label.cuda(), ignore_index=-1)
- rpn_loc_loss
input : gt_rpn_loc、rpn_locs、gt_rpn_label
output : rpn_loc_loss
#使用的函数(path:./trainer.py)
def _fast_rcnn_loc_loss(pred_loc, gt_loc, gt_label, sigma)
至此反向传播需要的两项loss就计算结束了,之后就是和roi pooling的两项loss 求和,再反向传播