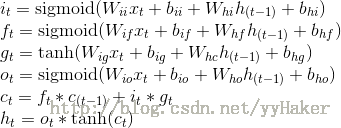Pytorch源码之RNN理解
Pytorch源码之RNN理解
我用的pytorch0.2,除了API的解释外,部分容易混淆。因此我依次整理了一下。下面是rnn.py的structure,
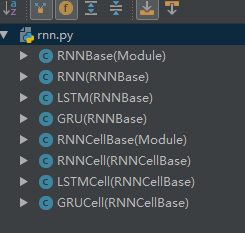
RNN类
该类实现了RNN, math公式如下:
ht=tanh(wih∗xt+bih+whh∗h(t−1)+bhh)(1) (1) h t = tanh ( w i h ∗ x t + b i h + w h h ∗ h ( t − 1 ) + b h h )
class RNN(RNNBase):
r"""Applies a multi-layer Elman RNN with tanh or ReLU non-linearity to an
input sequence.
For each element in the input sequence, each layer computes the following
function:
.. math::
h_t = \tanh(w_{ih} * x_t + b_{ih} + w_{hh} * h_{(t-1)} + b_{hh})
where :math:`h_t` is the hidden state at time `t`, and :math:`x_t` is
the hidden state of the previous layer at time `t` or :math:`input_t`
for the first layer. If nonlinearity='relu', then `ReLU` is used instead
of `tanh`.
Args:
input_size: The number of expected features in the input x
hidden_size: The number of features in the hidden state h
num_layers: Number of recurrent layers.
nonlinearity: The non-linearity to use ['tanh'|'relu']. Default: 'tanh'
bias: If False, then the layer does not use bias weights b_ih and b_hh.
Default: True
batch_first: If True, then the input and output tensors are provided
as (batch, seq, feature)
dropout: If non-zero, introduces a dropout layer on the outputs of each
RNN layer except the last layer
bidirectional: If True, becomes a bidirectional RNN. Default: False
Inputs: input, h_0
- **input** (seq_len, batch, input_size): tensor containing the features
of the input sequence. The input can also be a packed variable length
sequence. See :func:`torch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_padded_sequence`
for details.
- **h_0** (num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size): tensor
containing the initial hidden state for each element in the batch.
Outputs: output, h_n
- **output** (seq_len, batch, hidden_size * num_directions): tensor
containing the output features (h_k) from the last layer of the RNN,
for each k. If a :class:`torch.nn.utils.rnn.PackedSequence` has
been given as the input, the output will also be a packed sequence.
- **h_n** (num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size): tensor
containing the hidden state for k=seq_len.
Attributes:
weight_ih_l[k]: the learnable input-hidden weights of the k-th layer,
of shape `(input_size x hidden_size)`
weight_hh_l[k]: the learnable hidden-hidden weights of the k-th layer,
of shape `(hidden_size x hidden_size)`
bias_ih_l[k]: the learnable input-hidden bias of the k-th layer,
of shape `(hidden_size)`
bias_hh_l[k]: the learnable hidden-hidden bias of the k-th layer,
of shape `(hidden_size)`
Examples::
>>> rnn = nn.RNN(10, 20, 2)
>>> input = Variable(torch.randn(5, 3, 10))
>>> h0 = Variable(torch.randn(2, 3, 20))
>>> output, hn = rnn(input, h0)
"""
num_layers in RNN is just stacking RNNs on top of each other. So you get a hidden from each layer and an output only from the topmost layer.
如果numlayers=1, RNN图示如下:
![]()
如果numlayers=2, RNN图示如下:
![]()
LSTM
该类实现了LSTM, math公式如下:
class LSTM(RNNBase):
r"""Applies a multi-layer long short-term memory (LSTM) RNN to an input
sequence.
For each element in the input sequence, each layer computes the following
function:
.. math::
\begin{array}{ll}
i_t = \mathrm{sigmoid}(W_{ii} x_t + b_{ii} + W_{hi} h_{(t-1)} + b_{hi}) \\
f_t = \mathrm{sigmoid}(W_{if} x_t + b_{if} + W_{hf} h_{(t-1)} + b_{hf}) \\
g_t = \tanh(W_{ig} x_t + b_{ig} + W_{hc} h_{(t-1)} + b_{hg}) \\
o_t = \mathrm{sigmoid}(W_{io} x_t + b_{io} + W_{ho} h_{(t-1)} + b_{ho}) \\
c_t = f_t * c_{(t-1)} + i_t * g_t \\
h_t = o_t * \tanh(c_t)
\end{array}
where :math:`h_t` is the hidden state at time `t`, :math:`c_t` is the cell
state at time `t`, :math:`x_t` is the hidden state of the previous layer at
time `t` or :math:`input_t` for the first layer, and :math:`i_t`,
:math:`f_t`, :math:`g_t`, :math:`o_t` are the input, forget, cell,
and out gates, respectively.
Args:
input_size: The number of expected features in the input x
hidden_size: The number of features in the hidden state h
num_layers: Number of recurrent layers.
bias: If False, then the layer does not use bias weights b_ih and b_hh.
Default: True
batch_first: If True, then the input and output tensors are provided
as (batch, seq, feature)
dropout: If non-zero, introduces a dropout layer on the outputs of each
RNN layer except the last layer
bidirectional: If True, becomes a bidirectional RNN. Default: False
Inputs: input, (h_0, c_0)
- **input** (seq_len, batch, input_size): tensor containing the features
of the input sequence.
The input can also be a packed variable length sequence.
See :func:`torch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_padded_sequence` for details.
- **h_0** (num_layers \* num_directions, batch, hidden_size): tensor
containing the initial hidden state for each element in the batch.
- **c_0** (num_layers \* num_directions, batch, hidden_size): tensor
containing the initial cell state for each element in the batch.
Outputs: output, (h_n, c_n)
- **output** (seq_len, batch, hidden_size * num_directions): tensor
containing the output features `(h_t)` from the last layer of the RNN,
for each t. If a :class:`torch.nn.utils.rnn.PackedSequence` has been
given as the input, the output will also be a packed sequence.
- **h_n** (num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size): tensor
containing the hidden state for t=seq_len
- **c_n** (num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size): tensor
containing the cell state for t=seq_len
Attributes:
weight_ih_l[k] : the learnable input-hidden weights of the k-th layer
`(W_ii|W_if|W_ig|W_io)`, of shape `(4*hidden_size x input_size)`
weight_hh_l[k] : the learnable hidden-hidden weights of the k-th layer
`(W_hi|W_hf|W_hg|W_ho)`, of shape `(4*hidden_size x hidden_size)`
bias_ih_l[k] : the learnable input-hidden bias of the k-th layer
`(b_ii|b_if|b_ig|b_io)`, of shape `(4*hidden_size)`
bias_hh_l[k] : the learnable hidden-hidden bias of the k-th layer
`(b_hi|b_hf|b_hg|b_ho)`, of shape `(4*hidden_size)`
Examples::
>>> rnn = nn.LSTM(10, 20, 2)
>>> input = Variable(torch.randn(5, 3, 10))
>>> h0 = Variable(torch.randn(2, 3, 20))
>>> c0 = Variable(torch.randn(2, 3, 20))
>>> output, hn = rnn(input, (h0, c0))
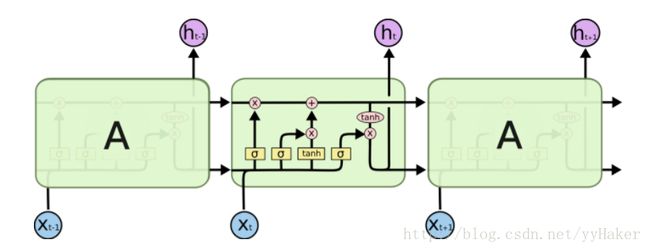
"""LSTM可以参考下图:
【1】pytorch官方文档:http://pytorch.org/docs/0.2.0/nn.html#recurrent-layers