opencv3 目标运动检测
基本的运动检测
一种最直观的方法就是计算帧之间的差异,或考虑“背景”帧与其他帧之间的差异
basic_motion_detection.py
import cv2
import numpy as np
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
es = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (10,10))#返回指定形状和尺寸的结构元素
kernel = np.ones((5,5),np.uint8)
background = None
while (True):
ret, frame = camera.read()
if background is None:
background = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
background = cv2.GaussianBlur(background, (21, 21), 0)
continue
gray_frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray_frame = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray_frame, (21, 21), 0)
diff = cv2.absdiff(background, gray_frame)#得到一个差分图
diff = cv2.threshold(diff, 25, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]#固定阈值处理黑白图
diff = cv2.dilate(diff, es, iterations = 2)#膨胀处理图像
image, cnts, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(diff.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for c in cnts:
if cv2.contourArea(c) < 1500:
continue
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (255, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow("contours", frame)
cv2.imshow("dif", diff)
if cv2.waitKey(int(1000 / 12)) & 0xff == ord("q"):
break
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
camera.release()存在的问题:这个方法需要提前设置“默认”帧作为背景,在一些光照变化频繁的情况下,这种方法就不灵活。所以后面引入背景分割器
背景分割器:KNN、MOG2和GMG
BackgroundSubtractor类是专门用于视频分析的,即BackgroundSubtractor类会对每帧的环境进行‘学习’,他的另一个特征是它可以计算阴影。通过检测阴影,可排除检测图像的阴影区域(采用阈值方式),从而关注实际特征。
mog
import cv2
import numpy as np
bs = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorKNN(detectShadows = True)
camera = cv2.VideoCapture("movie.mpg")
while True:
ret, frame = camera.read()
fgmask = bs.apply(frame)
th = cv2.threshold(fgmask.copy(), 244, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
th = cv2.erode(th, cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (3,3)), iterations = 2)
dilated = cv2.dilate(th, cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (8,3)), iterations = 2)
image, contours, hier = cv2.findContours(dilated, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for c in contours:
if cv2.contourArea(c) > 1000:
(x,y,w,h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x,y), (x+w, y+h), (255, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow("mog", fgmask)
cv2.imshow("thresh", th)
cv2.imshow("diff", frame & cv2.cvtColor(fgmask, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR))
cv2.imshow("detection", frame)
k = cv2.waitKey(30) & 0xff
if k == 27:
break
camera.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()

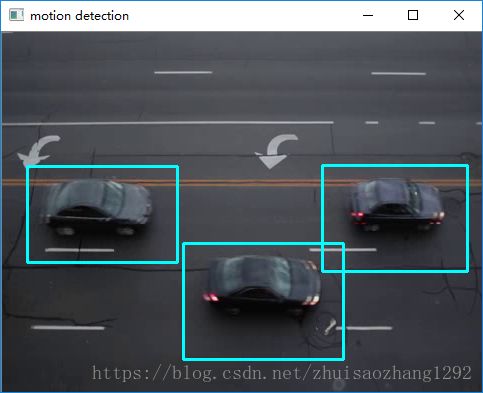
用BackgroundSubtractorKNN来实现运动检测的例子
import cv2
import numpy as np
knn = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorKNN(detectShadows = True)
es = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (20,12))
camera = cv2.VideoCapture("traffic.flv")
def drawCnt(fn, cnt):
if cv2.contourArea(cnt) > 1400:
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
cv2.rectangle(fn, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (255, 255, 0), 2)
while True:
ret, frame = camera.read()
if not ret:
break
fg = knn.apply(frame.copy()) #计算了前景掩码
fg_bgr = cv2.cvtColor(fg, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
bw_and = cv2.bitwise_and(fg_bgr, frame)
draw = cv2.cvtColor(bw_and, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
draw = cv2.GaussianBlur(draw, (21, 21), 0)
draw = cv2.threshold(draw, 20, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
draw = cv2.dilate(draw, es, iterations = 2)
image, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(draw.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for c in contours:
drawCnt(frame, c)
cv2.imshow("motion detection", frame)
if cv2.waitKey(int(1000 / 12)) & 0xff == ord("q"):
break
camera.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
均值漂移:
均值漂移是一种目标跟踪算法,该算法寻找概率函数离散样本的最大密度(例如感兴趣的图像区域),并且重新计算在下一帧种的最大密度,该算法给出了目标的移动。
meanshit.py
import numpy as np
import cv2
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# capture the first frame
ret,frame = cap.read()
# mark the ROI
r,h,c,w = 10, 200, 10, 200
# wrap in a tuple
track_window = (c,r,w,h)
# extract the ROI for tracking
roi = frame[r:r+h, c:c+w]
# switch to HSV
hsv_roi = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
# create a mask with upper and lower boundaries of colors you want to track
mask = cv2.inRange(hsv_roi, np.array((100., 30.,32.)), np.array((180.,120.,255.)))
# calculate histograms of roi
roi_hist = cv2.calcHist([hsv_roi],[0],mask,[180],[0,180])
cv2.normalize(roi_hist,roi_hist,0,255,cv2.NORM_MINMAX)
# Setup the termination criteria, either 10 iteration or move by atleast 1 pt
term_crit = ( cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS | cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_COUNT, 10, 1 )
while(1):
ret ,frame = cap.read()
if ret == True:
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
dst = cv2.calcBackProject([hsv],[0],roi_hist,[0,180],1)
#print (dst)
# apply meanshift to get the new location
ret, track_window = cv2.meanShift(dst, track_window, term_crit)
# Draw it on image
x,y,w,h = track_window
img2 = cv2.rectangle(frame, (x,y), (x+w,y+h), 255,2)
cv2.imshow('img2',img2)
k = cv2.waitKey(60) & 0xff
if k == 27:
break
else:
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
cap.release()如果在计算机上运行这些代码,会观察到均值漂移窗口是怎么搜索指定颜色范围的;如果没有找到,就只能看到串口抖动。如果有指定颜色范围的目标进入窗口,该窗口就会开始跟踪这个目标
CAMShit
在调用CAMShit以后,会根据具体的旋转来绘制矩阵,这种旋转会与被跟踪对象一起旋转;其中boxPoint函数会找到被旋转的顶点,而折现函数会在帧上绘制矩形线段
import numpy as np
import cv2
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# take first frame of the video
ret,frame = cap.read()
# setup initial location of window
r,h,c,w = 300,200,400,300 # simply hardcoded the values
track_window = (c,r,w,h)
roi = frame[r:r+h, c:c+w]
hsv_roi = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
mask = cv2.inRange(hsv_roi, np.array((100., 30.,32.)), np.array((180.,120.,255.)))
roi_hist = cv2.calcHist([hsv_roi],[0],mask,[180],[0,180])
cv2.normalize(roi_hist,roi_hist,0,255,cv2.NORM_MINMAX)
term_crit = ( cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS | cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_COUNT, 10, 1 )
while(1):
ret ,frame = cap.read()
if ret == True:
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
dst = cv2.calcBackProject([hsv],[0],roi_hist,[0,180],1)
ret, track_window = cv2.CamShift(dst, track_window, term_crit)
pts = cv2.boxPoints(ret)
pts = np.int0(pts)
img2 = cv2.polylines(frame,[pts],True, 255,2)
cv2.imshow('img2',img2)
k = cv2.waitKey(60) & 0xff
if k == 27:
break
else:
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
cap.release()
卡尔曼滤波器
主要包含预测和更新
预测:卡尔曼滤波器使用当前点计算的协方差来估计目标的新位置
更新:卡尔曼滤波器记录目标的位置,并为下一次循环计算修正协方差
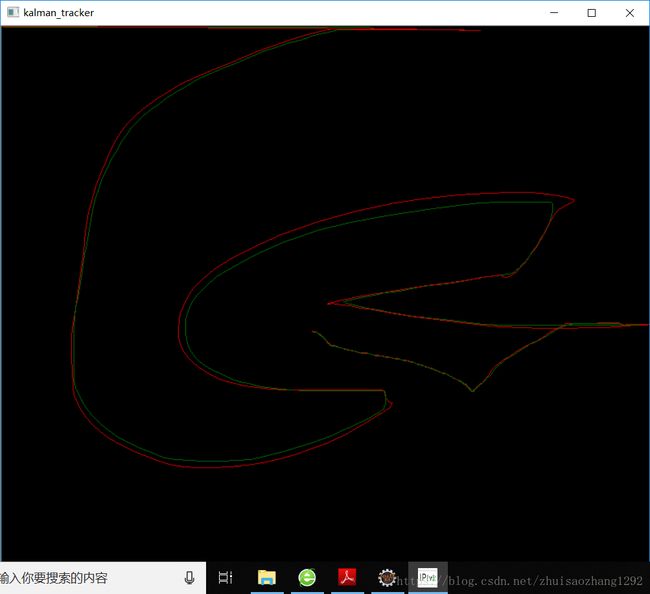
Kalman.py
import cv2, numpy as np
measurements = []
predictions = []
frame = np.zeros((800, 800, 3), np.uint8)
last_measurement = current_measurement = np.array((2,1), np.float32)
last_prediction = current_prediction = np.zeros((2,1), np.float32)
def mousemove(event, x, y, s, p):
global frame, current_measurement, measurements, last_measurement, current_prediction, last_prediction
last_prediction = current_prediction
last_measurement = current_measurement
current_measurement = np.array([[np.float32(x)],[np.float32(y)]])
kalman.correct(current_measurement)
current_prediction = kalman.predict()
lmx, lmy = last_measurement[0], last_measurement[1]
cmx, cmy = current_measurement[0], current_measurement[1]
lpx, lpy = last_prediction[0], last_prediction[1]
cpx, cpy = current_prediction[0], current_prediction[1]
cv2.line(frame, (lmx, lmy), (cmx, cmy), (0,100,0))
cv2.line(frame, (lpx, lpy), (cpx, cpy), (0,0,200))
cv2.namedWindow("kalman_tracker")
cv2.setMouseCallback("kalman_tracker", mousemove);
kalman = cv2.KalmanFilter(4,2,1)
kalman.measurementMatrix = np.array([[1,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0]],np.float32)
kalman.transitionMatrix = np.array([[1,0,1,0],[0,1,0,1],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,1]],np.float32)
kalman.processNoiseCov = np.array([[1,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,1]],np.float32) * 0.03
while True:
cv2.imshow("kalman_tracker", frame)
if (cv2.waitKey(30) & 0xFF) == 27:
break
if (cv2.waitKey(30) & 0xFF) == ord('q'):
cv2.imwrite('kalman.jpg', frame)
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()输出:
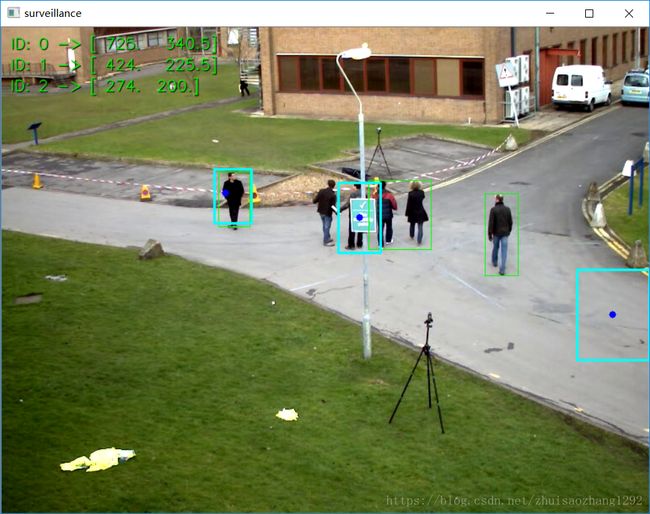
一个基于行人跟踪的例子
#! /usr/bin/python
"""Surveillance Demo: Tracking Pedestrians in Camera Feed
The application opens a video (could be a camera or a video file)
and tracks pedestrians in the video.
"""
# __author__ = "joe minichino"
# __copyright__ = "property of mankind."
# __license__ = "MIT"
# __version__ = "0.0.1"
# __maintainer__ = "Joe Minichino"
# __email__ = "[email protected]"
# __status__ = "Development"
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os.path as path
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("-a", "--algorithm",
help = "m (or nothing) for meanShift and c for camshift")
args = vars(parser.parse_args())
def center(points):
"""calculates centroid of a given matrix"""
x = (points[0][0] + points[1][0] + points[2][0] + points[3][0]) / 4
y = (points[0][1] + points[1][1] + points[2][1] + points[3][1]) / 4
return np.array([np.float32(x), np.float32(y)], np.float32)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
class Pedestrian():
"""Pedestrian class
each pedestrian is composed of a ROI, an ID and a Kalman filter
so we create a Pedestrian class to hold the object state
"""
def __init__(self, id, frame, track_window):
"""init the pedestrian object with track window coordinates"""
# set up the roi
self.id = int(id)
x,y,w,h = track_window
self.track_window = track_window
self.roi = cv2.cvtColor(frame[y:y+h, x:x+w], cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
roi_hist = cv2.calcHist([self.roi], [0], None, [16], [0, 180])
self.roi_hist = cv2.normalize(roi_hist, roi_hist, 0, 255, cv2.NORM_MINMAX)
# set up the kalman
self.kalman = cv2.KalmanFilter(4,2)
self.kalman.measurementMatrix = np.array([[1,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0]],np.float32)
self.kalman.transitionMatrix = np.array([[1,0,1,0],[0,1,0,1],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,1]],np.float32)
self.kalman.processNoiseCov = np.array([[1,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,1]],np.float32) * 0.03
self.measurement = np.array((2,1), np.float32)
self.prediction = np.zeros((2,1), np.float32)
self.term_crit = ( cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS | cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_COUNT, 10, 1 )
self.center = None
self.update(frame)
def __del__(self):
print ("Pedestrian %d destroyed" % self.id)
def update(self, frame):
# print "updating %d " % self.id
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
back_project = cv2.calcBackProject([hsv],[0], self.roi_hist,[0,180],1)
if args.get("algorithm") == "c":
ret, self.track_window = cv2.CamShift(back_project, self.track_window, self.term_crit)
pts = cv2.boxPoints(ret)
pts = np.int0(pts)
self.center = center(pts)
cv2.polylines(frame,[pts],True, 255,1)
if not args.get("algorithm") or args.get("algorithm") == "m":
ret, self.track_window = cv2.meanShift(back_project, self.track_window, self.term_crit)
x,y,w,h = self.track_window
self.center = center([[x,y],[x+w, y],[x,y+h],[x+w, y+h]])
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x,y), (x+w, y+h), (255, 255, 0), 2)
self.kalman.correct(self.center)
prediction = self.kalman.predict()
cv2.circle(frame, (int(prediction[0]), int(prediction[1])), 4, (255, 0, 0), -1)
# fake shadow
cv2.putText(frame, "ID: %d -> %s" % (self.id, self.center), (11, (self.id + 1) * 25 + 1),
font, 0.6,
(0, 0, 0),
1,
cv2.LINE_AA)
# actual info
cv2.putText(frame, "ID: %d -> %s" % (self.id, self.center), (10, (self.id + 1) * 25),
font, 0.6,
(0, 255, 0),
1,
cv2.LINE_AA)
def main():
# camera = cv2.VideoCapture(path.join(path.dirname(__file__), "traffic.flv"))
camera = cv2.VideoCapture("768x576.avi")
# camera = cv2.VideoCapture(path.join(path.dirname(__file__), "..", "movie.mpg"))
# camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
history = 20
# KNN background subtractor
bs = cv2.createBackgroundSubtractorKNN()
# MOG subtractor
# bs = cv2.bgsegm.createBackgroundSubtractorMOG(history = history)
# bs.setHistory(history)
# GMG
# bs = cv2.bgsegm.createBackgroundSubtractorGMG(initializationFrames = history)
cv2.namedWindow("surveillance")
pedestrians = {}
firstFrame = True
frames = 0
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID')
out = cv2.VideoWriter('output.avi',fourcc, 20.0, (640,480))
while True:
print (" -------------------- FRAME %d --------------------" % frames)
grabbed, frame = camera.read()
if (grabbed is False):
print ("failed to grab frame.")
break
fgmask = bs.apply(frame)
# this is just to let the background subtractor build a bit of history
if frames < history:
frames += 1
continue
th = cv2.threshold(fgmask.copy(), 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
th = cv2.erode(th, cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (3,3)), iterations = 2)
dilated = cv2.dilate(th, cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (8,3)), iterations = 2)
image, contours, hier = cv2.findContours(dilated, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
counter = 0
for c in contours:
if cv2.contourArea(c) > 500:
(x,y,w,h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x,y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 1)
# only create pedestrians in the first frame, then just follow the ones you have
if firstFrame is True:
pedestrians[counter] = Pedestrian(counter, frame, (x,y,w,h))
counter += 1
for i, p in pedestrians.items():
p.update(frame)
firstFrame = False
frames += 1
cv2.imshow("surveillance", frame)
out.write(frame)
if cv2.waitKey(110) & 0xff == 27:
break
out.release()
camera.release()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()输出:蓝色矩形框为CAMShit检测的结果,绿色矩形框是卡尔曼滤波器预测的结果,其中心为蓝色圆圈