编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
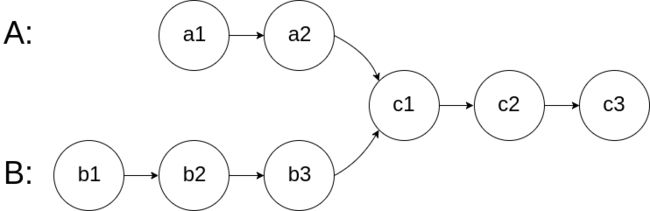
在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:
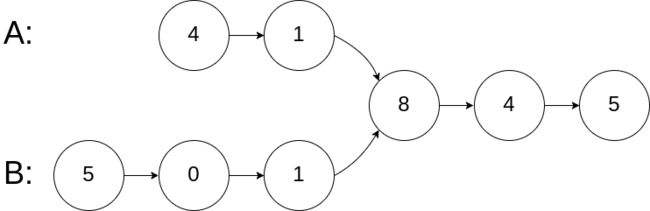
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
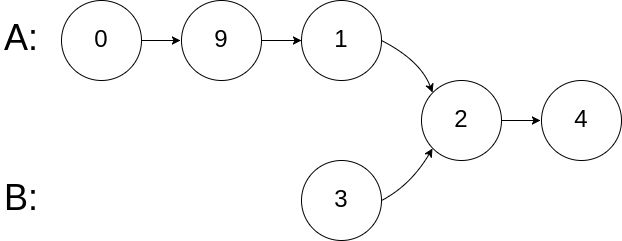
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
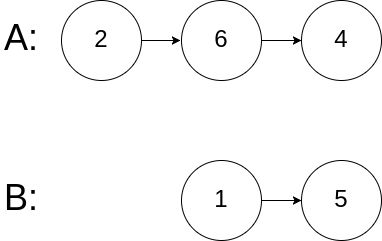
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
思路:用map标记即可
膜一波大佬,思路清晰到让我五体投地(我啥时候才能那么强)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/comments/3107
#include
#include
#include



