Leetcode题解------C++语言实现
283. 移动零
// 时间复杂度: O(n)
// 空间复杂度: O(n)
class Solution {
public:
// 通过引用的方式传入一个vector类型的数组 可以对其进行修改
void moveZeroes(vector& nums) {
vector nonZeroElements;
// 对数组进行遍历 将vec中所有非0元素放入nonZeroElements中
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.size() ; i ++)
if(nums[i]) // 如果当前元素不为0
nonZeroElements.push_back(nums[i]);
// 将nonZeroElements中的所有元素依次放入到nums开始的位置
for(int i = 0 ; i < nonZeroElements.size() ; i ++)
nums[i] = nonZeroElements[i];
// 将nums剩余的位置放置为0
for(int i = nonZeroElements.size() ; i < nums.size() ; i ++)
nums[i] = 0;
}
}; // 时间复杂度: O(n)
// 空间复杂度: O(1) 原地(in place)解决,降低空间的使用
class Solution {
public:
void moveZeroes(vector& nums) {
int k = 0; // nums中, [0...k)的元素均为非0元素
// 遍历到第i个元素后,保证[0...i]中所有非0元素 都按照顺序排列在[0...k)中
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.size() ; i ++)
if(nums[i]) // 如果当前元素不为0 将其赋给K位置 K向后移一位
nums[k++] = nums[i]; // 先赋值 再自增
// 将nums剩余的位置放置为0
for(int i = k ; i < nums.size() ; i ++)
nums[i] = 0;
}
}; // 时间复杂度: O(n)
// 空间复杂度: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
void moveZeroes(vector& nums) {
int k = 0; // nums中, [0...k)的元素均为非0元素
// 遍历到第i个元素后,保证[0...i]中所有非0元素
// 都按照顺序排列在[0...k)中 同时, [k...i] 为 0
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.size() ; i ++)
if(nums[i])
// 对于不存在0的情况进行优化
if(k != i)
swap(nums[k++] , nums[i]);
else
k ++; // 如果K与当前索引相同 k与i同时向后移动
}
}; 75. 颜色分类
// 计数排序的思路 对整个数组遍历了两遍
// 时间复杂度: O(n)
// 空间复杂度: O(k), k为元素的取值范围
class Solution {
public:
void sortColors(vector &nums) {
int count[3] = {0}; // 存放0, 1, 2三个元素的次数
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.size() ; i ++){
assert(nums[i] >= 0 && nums[i] <= 2);
count[nums[i]] ++; // 对相应元素的次数进行 ++操作
}
int index = 0; // 声明一个指针 从头开始遍历
for(int i = 0 ; i < count[0] ; i ++)
nums[index++] = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < count[1] ; i ++)
nums[index++] = 1;
for(int i = 0 ; i < count[2] ; i ++)
nums[index++] = 2;
}
}; // 三路快速排序的思想 对整个数组只遍历了一遍
// 时间复杂度: O(n)
// 空间复杂度: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
void sortColors(vector &nums) {
int zero = -1; // [0...zero] == 0
int two = nums.size(); // [two...n-1] == 2
for(int i = 0 ; i < two ; ){
if(nums[i] == 1)
i ++;
else if (nums[i] == 2)
swap( nums[i] , nums[--two]);
else{
assert(nums[i] == 0);
swap(nums[++zero] , nums[i++]);
}
}
}
}; 167. 两数之和 II - 输入有序数组
// 对撞指针
// 时间复杂度: O(n)
// 空间复杂度: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
vector twoSum(vector& numbers, int target) {
assert(numbers.size() >= 2);
int l = 0, r = numbers.size() - 1;
while(l < r){
if(numbers[l] + numbers[r] == target){
int res[2] = {l+1, r+1};
return vector(res, res+2);
}
else if(numbers[l] + numbers[r] < target)
l ++;
else // numbers[l] + numbers[r] > target
r --;
}
throw invalid_argument("the input has no solution");
}
}; 209. 长度最小的子数组
// 滑动窗口的思路
// 时间复杂度: O(n)
// 空间复杂度: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int minSubArrayLen(int s, vector& nums) {
assert(s > 0);
int l = 0 , r = -1; // nums[l...r]为我们的滑动窗口
int sum = 0;
int res = nums.size() + 1; //子数组的最小长度
while(l < nums.size()){ // 窗口的左边界在数组范围内,则循环继续
if( sum < s && r + 1 < nums.size())
sum += nums[++r]; // 右指针向前走一步 sum加入该值
else // sum >= s 或者 r已经到头
sum -= nums[l++]; // 左指针向前走一步 sum减去该值
if(sum >= s) //满足条件 更新最小长度
res = min(res, r - l + 1);
}
// 最小长度没有被更新 则返回0
if(res == nums.size() + 1)
return 0;
return res;
}
}; 3. 无重复字符的最长子串
// 滑动窗口
// 时间复杂度: O(len(s))
// 空间复杂度: O(len(charset))
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
// 整个循环从 l == 0; r == -1 这个空窗口开始
// 到l == s.size(); r == s.size()-1 这个空窗口截止
// 在每次循环里逐渐改变窗口, 维护freq, 并记录当前窗口中是否找到了一个新的最优值
int freq[256] = {0}; // 初始化一个数组 用于记录ASC码出现的次数
int l = 0, r = -1; // 滑动窗口为s[l...r]
int res = 0;
while(l < s.size()){
// 如果右指针还能向前走 并且不重复
if(r + 1 < s.size() && freq[s[r+1]] == 0)
freq[s[++r]] ++; // 向前走一步 次数加一
else // r已经到头 或者 freq[s[r+1]] == 1重复
freq[s[l++]] --; // 不是一次走到不重复的位置 是一步一步走的!
res = max(res, r-l+1); // 每走一步都对结果进行更新
}
return res;
}
};349. 两个数组的交集
// 使用unordered_set(底层实现为哈希表)时间复杂度可降为O(n)
// 时间复杂度: O(nlogn) CPP set的底层实现是平衡二叉树
// 空间复杂度: O(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector intersection(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {
set record(nums1.begin(), nums1.end()); // 将nums1转换为set
set resultSet;
for( int i = 0 ; i < nums2.size() ; i ++ )
if( record.find(nums2[i]) != record.end())// 在set中找到了当前遍历nums2的元素
resultSet.insert( nums2[i] ); // 结果存入set中 只出现一次
// 将结果转换为vector返回
return vector(resultSet.begin(), resultSet.end());
}
}; 350. 两个数组的交集 II
// 使用unordered_map(底层实现为哈希表)时间复杂度可降为O(n)
// 时间复杂度: O(nlogn) CPP map的底层实现是平衡二叉树
// 空间复杂度: O(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector intersect(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {
map record;
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums1.size() ; i ++)
// CPP中set未出现的key默认值0 但查询一次后 会对该key进行初始化 即key : 0
record[nums1[i]] ++; // 统计每个元素出现的次数
vector resultVector;
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums2.size() ; i ++)
if(record[nums2[i]] > 0){ // 对nums2进行遍历 如果当前值在map中出现的次数大于0
resultVector.push_back(nums2[i]);
record[nums2[i]] --; // 匹配一次 map中的count值就减少一次
}
return resultVector;
}
}; 1. 两数之和
// 时间复杂度:O(n)
// 空间复杂度:O(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector twoSum(vector& nums, int target) {
unordered_map record;
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.size() ; i ++){
// 对于有重复值的特殊情况,若查找成功直接返回,查找失败对索引进行更新,不会影响后续查找
if(record.find(target - nums[i]) == record.end())
record[nums[i]] = i;
else{
int res[] = {i, record[target - nums[i]]};
return vector(res, res + 2);
}
}
throw invalid_argument("the input has no solution");
}
}; 454. 四数相加 II
// 时间复杂度: O(n^2)
// 空间复杂度: O(n^2)
class Solution {
public:
int fourSumCount(vector& A, vector& B, vector& C, vector& D) {
unordered_map hashtable;
for(int i = 0 ; i < C.size() ; i ++)
for(int j = 0 ; j < D.size() ; j ++)
hashtable[C[i]+D[j]] += 1;
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < A.size() ; i ++)
for(int j = 0 ; j < B.size() ; j ++)
if(hashtable.find(-A[i]-B[j]) != hashtable.end())
res += hashtable[-A[i]-B[j]];
return res;
}
}; 447. 回旋镖的数量
class Solution {
public:
int numberOfBoomerangs(vector>& points) {
int res = 0;
for( int i = 0 ; i < points.size() ; i ++ ){
// record中存储 点i 到所有其他点的距离出现的频次
unordered_map record;
for(int j = 0 ; j < points.size() ; j ++)
if(j != i)
// 计算距离时不进行开根运算, 以保证精度
record[dis(points[i], points[j])] += 1;
for(unordered_map::iterator iter = record.begin() ; iter != record.end() ; iter ++)
res += (iter->second) * (iter->second - 1);
}
return res;
}
private:
int dis(const vector &pa, const vector &pb){
return (pa[0] - pb[0]) * (pa[0] - pb[0]) +
(pa[1] - pb[1]) * (pa[1] - pb[1]);
}
}; 219. 存在重复元素 II
// 时间复杂度: O(n)
// 空间复杂度: O(k)
class Solution {
public:
bool containsNearbyDuplicate(vector& nums, int k) {
if(nums.size() <= 1)
return false;
if(k <= 0)
return false;
unordered_set record;
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.size() ; i ++){
// 每次都是在滑动窗口内部进行寻找
if(record.find(nums[i]) != record.end())
return true;
record.insert(nums[i]); // 没有找到将该元素添加到滑动窗口中
if(record.size() == k + 1) // 判断滑动窗口中元素个数 最多有k个元素
record.erase(nums[i - k]);
}
return false;
}
}; 220
206. 反转链表
// 时间复杂度: O(n)
// 空间复杂度: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* pre = NULL;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur){
ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
};
203. 移除链表元素
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
// 使用虚拟头结点
// 时间复杂度: O(n)
// 空间复杂度: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
// 创建虚拟头结点(在堆区开辟的空间 要手动删除)
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode* cur = dummyHead;
while(cur->next){
if(cur->next->val == val)
cur->next = cur->next->next;
else
cur = cur->next;
}
// 因为要对堆区数据进行删除,先给它的next指针起个别名(引用)
ListNode* retNode = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return retNode;
}
};24. 两两交换链表中的节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
// 时间复杂度: O(n)
// 空间复杂度: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
// 交换 删除 一般都需要申请一个虚拟头结点
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode* p = dummyHead;
while(p->next && p->next->next){ // 需要保证要交换的两个节点存在
ListNode* node1 = p->next;
ListNode* node2 = node1->next;
node1->next = node2->next;
node2->next = node1;
p->next = node2;
p = node1; // 对p进行更新 进行下一次的循环
}
ListNode* retHead = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead; // 在栈区保存一下要返回的地址,并将堆区的数据释放
return retHead;
}
};
237. 删除链表中的节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
// 时间复杂度: O(1)
// 空间复杂度: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {
// 注意: 这个方法对尾节点不适用。题目中要求了给定的node不是尾节点
// 在assert中, 我们使用node->next != NULL确保了node不是尾节点
assert(node != NULL && node->next != NULL);
node->val = node->next->val;
node->next =node->next->next;
}
};19. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
// 使用双指针, 对链表只遍历了一遍
// 时间复杂度: O(n)
// 空间复杂度: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* pHead = new ListNode(0);
pHead->next = head;
ListNode* pre = pHead;
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
for( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ){
assert(fast);
fast = fast->next;
}
while(fast){
pre = pre->next;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
pre->next = slow->next;
ListNode* retNode = pHead->next;
delete pHead;
return retNode;
}
};20. 有效的括号
// 时间复杂度: O(n)
// 空间复杂度: O(n)
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
stack stack;
for( int i = 0 ; i < s.size() ; i ++ )
if( s[i] == '(' || s[i] == '{' || s[i] == '[')
stack.push(s[i]);
else{
if( stack.size() == 0 ) // 如果当前字符为右括号 并且栈为空
return false;
char c = stack.top(); // 栈不空 则从栈顶弹出一个字符与当前字符匹配
stack.pop();
char match;
if( s[i] == ')' )
match = '(';
else if( s[i] == ']' )
match = '[';
else{
assert( s[i] == '}' );
match = '{';
}
if(c != match) // 若有一次不匹配就直接返回false
return false;
}
return stack.size() == 0;
}
};
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector res;
if(root==NULL)
return res;
stack stack;
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.empty()) {
TreeNode* node=stack.top();
stack.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
if(node->right)
stack.push(node->right);
if(node->left)
stack.push(node->left);
}
return res;
}
};
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector res;
stack stack;
while(root != NULL || !stack.empty()){ // 循环执行如下操作,直到栈空为止
while(root){ // 如果栈顶结点左孩子存在,则左孩子入栈
stack.push(root);
root = root->left;
}
root = stack.top(); // 如果栈顶结点左孩子不存在,则出栈并输出栈顶结点
stack.pop();
res.push_back(root->val); // 检查其右孩子是否存在,如果存在,则右孩子入栈
root = root->right;
}
return res;
}
};
145. 二叉树的后序遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector res;
if(root==NULL)
return res;
stack stack;
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.empty()) {
TreeNode* node=stack.top();
stack.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
// 后续遍历和前序遍历代码几乎相同 这里这是改变了 遍历左右结点的顺序 得到逆后续遍历结果
if(node->left)
stack.push(node->left);
if(node->right)
stack.push(node->right);
}
// 将得到的逆后序遍历结果反转 就可得到后序遍历结果
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
};
102. 二叉树的层次遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector > res;
if(root == NULL)
return res;
queue queue;
queue.push(root);
while(!queue.empty())
{
int k = queue.size();
vector tmp;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
TreeNode* node = queue.front();
queue.pop();
tmp.push_back(node->val);
if(node->left)
queue.push(node->left);
if(node->right)
queue.push(node->right);
}
res.push_back(tmp);
}
return res;
}
};
279
347
104. 二叉树的最大深度
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(not root)
return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};226. 翻转二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(not root)
return NULL;
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
swap(root->left, root->right);
return root;
}
};112. 路径总和
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
if(not root)
return false;
if(not root->left && not root->right)
return sum == root->val;
return hasPathSum(root->left, sum - root->val)
or hasPathSum(root->right, sum - root->val);
}
};257. 二叉树的所有路径
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void find_paths(TreeNode* root, vector& res, string path) {
if (not root)
return;
path += to_string(root->val);
if (not root->left and not root->right) {
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
path += "->";
find_paths(root->left, res, path);
find_paths(root->right, res, path);
}
vector binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector res;
string path;
find_paths(root, res, path);
return res;
}
}; 437. 路径总和 III
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
// 在以node为根节点的二叉树中,寻找包含node的路径,和为sum
int findPath(TreeNode* node, int num){
if(not node)
return 0;
int count = 0;
if(node->val == num)
count += 1;
count += findPath(node->left , num - node->val);
count += findPath(node->right , num - node->val);
return count;
}
// 在以root为根节点的二叉树中,寻找和为sum的路径,返回这样的路径个数
int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
if(not root)
return 0;
return findPath(root, sum) + pathSum(root->left , sum)
+ pathSum(root->right , sum);
}
};235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(not root)
return NULL;
if(p->val < root->val and q->val < root->val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
if(p->val > root->val and q->val > root->val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
return root;
}
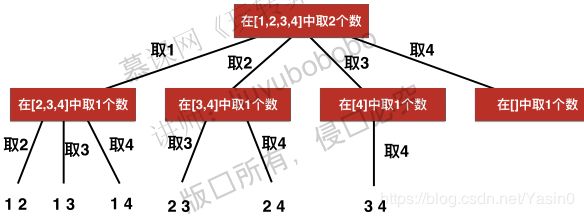
};17. 电话号码的字母组合
![]()
/// 时间复杂度: O(2^len(s))
/// 空间复杂度: O(len(s))
class Solution {
private:
// 声明一个数组 索引为数字 该索引位置为数字对应的不同字符
const string letterMap[10] = {
" ", //0
"", //1
"abc", //2
"def", //3
"ghi", //4
"jkl", //5
"mno", //6
"pqrs", //7
"tuv", //8
"wxyz" //9
};
vector res; // 声明一个vector容器 用于结果的存放
// s中保存了此时从digits[0...index-1]翻译得到的一个字母字符串
// 寻找和digits[index]匹配的字母, 获得digits[0...index]翻译得到的解
void findCombination(const string &digits, int index, const string &s){
if(index == digits.size()){
res.push_back(s); // 如果数字字符串已经遍历完成 将其放入结果容器中
return;
}
char c = digits[index]; // 当前要映射的数字
string letters = letterMap[c - '0']; // 获得当前要映射数字在数组letterMap对应的字符串
for(int i = 0 ; i < letters.size() ; i ++){ // 遍历该数字对应的每一个字符
findCombination(digits, index+1, s + letters[i]); // 保持上一层字符不变 依次将该层字符添加到s中
}
return;
}
public:
vector letterCombinations(string digits) {
if(digits == "")
return res;
findCombination(digits, 0, ""); // index = 0表示从第一个数字的位置 index为数字的索引
return res;
}
}; 46
![]()
/// 时间复杂度: O(n^n)
/// 空间复杂度: O(n)
class Solution {
private:
vector> res; // 初始化一个vector容器 用于存放结果
vector used; // 初始化一个bool型数组 用于记录当前数字是否已经被使用
// p中保存了一个有index-1个元素的排列。
// 向这个排列的末尾添加第index个元素, 获得一个有index个元素的排列
void helper(const vector& nums, int index, vector& p){
if(index == nums.size()){
res.push_back(p);
return;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.size() ; i ++)
if(!used[i]){ // 如果当前字符 未被使用的话
used[i] = true; // 标记为已使用
p.push_back(nums[i]); // 将当前字符添加到p中
helper(nums, index + 1, p ); // 对下一个数字进行全排列 并将对应数字 添加到p中
p.pop_back();
used[i] = false;
}
return;
}
public:
vector> permute(vector& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 0)
return res;
used = vector(nums.size(), false); // 将数组进行填充
vector p;
helper(nums, 0, p);
return res;
}
}; 77. 组合
class Solution {
private:
vector> res;
// 求解C(n,k), 当前已经找到的组合存储在c中, 需要从start开始搜索新的元素
void generateCombinations(int n, int k, int first, vector &c){
if(c.size() == k){
res.push_back(c);
return;
}
// 还有k - c.size()个空位, 所以, [i...n] 中至少要有 k - c.size() 个元素
// i最多为 n - (k - c.size()) + 1
for(int i = first; i <= n-(k-c.size())+1; i ++){
c.push_back(i);
generateCombinations(n, k, i + 1 ,c);
c.pop_back();
}
return;
}
public:
vector> combine(int n, int k) {
if(n < 1 or k < 1 or k > n)
return res;
vector c;
generateCombinations(n, k, 1, c);
return res;
}
}; 79
/// 时间复杂度: O(m*n*m*n)
/// 空间复杂度: O(m*n)
class Solution {
private:
int d[4][2] = {{-1, 0}, {0,1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}};
int m, n;
vector> visited;
bool inArea(int x, int y){
return x >= 0 and x < m and y >= 0 and y < n;
}
// 从board[startx][starty]开始, 寻找word[index...word.size())
bool searchWord(const vector> &board, const string& word, int index,
int startx, int starty ){
if(index == word.size() - 1)
return board[startx][starty] == word[index];
if(board[startx][starty] == word[index]){
visited[startx][starty] = true;
// 从startx, starty出发,向四个方向寻
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i ++){
int newx = startx + d[i][0];
int newy = starty + d[i][1];
if(inArea(newx, newy) && !visited[newx][newy] &&
searchWord(board, word, index + 1, newx, newy))
return true;
}
visited[startx][starty] = false;
}
return false;
}
public:
bool exist(vector>& board, string word) {
m = board.size();
n = board[0].size();
for(int i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++)
visited.push_back(vector(n, false));
for(int i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++)
for(int j = 0 ; j < board[i].size() ; j ++)
if(searchWord(board, word, 0, i, j))
return true;
return false;
}
}; 200
/// 时间复杂度: O(n*m)
/// 空间复杂度: O(n*m)
class Solution {
private:
int d[4][2] = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
int m, n;
vector> visited;
bool inArea(int x, int y){
return x >= 0 and x < m and y >= 0 and y < n;
}
// 从grid[x][y]的位置开始,进行floodfill
// 保证(x,y)合法,且grid[x][y]是没有被访问过的陆地
void dfs(vector>& grid, int x, int y){
visited[x][y] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++){
int newx = x + d[i][0];
int newy = y + d[i][1];
if(inArea(newx, newy) and !visited[newx][newy] and grid[newx][newy] == '1')
dfs(grid, newx, newy);
}
return;
}
public:
int numIslands(vector>& grid) {
m = grid.size();
if(m == 0)
return 0;
n = grid[0].size();
if(n == 0)
return 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++)
visited.push_back(vector(n, false));
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++)
for(int j = 0 ; j < n ; j ++)
if(grid[i][j] == '1' and !visited[i][j]){
dfs(grid, i, j);
res ++;
}
return res;
}
}; 51
/// 时间复杂度: O(n^n)
/// 空间复杂度: O(n)
class Solution {
private:
vector col, dia1, dia2;
vector> res;
// 尝试在一个n皇后问题中, 摆放第index行的皇后位置
void putQueen(int n, int index, vector &row){
if(index == n){
res.push_back(generateBoard(n, row));
return;
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++)
// 尝试将第index行的皇后摆放在第i列
if(!col[i] and !dia1[index + i] and !dia2[index - i + n - 1]){
row.push_back(i);
col[i] = true;
dia1[index + i] = true;
dia2[index - i + n - 1] = true;
putQueen(n, index + 1, row);
col[i] = false;
dia1[index + i] = false;
dia2[index - i + n - 1] = false;
row.pop_back();
}
return;
}
vector generateBoard(int n, vector &row){
vector board(n, string(n, '.'));
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++)
board[i][row[i]] = 'Q';
return board;
}
public:
vector> solveNQueens(int n) {
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++)
col.push_back(false);
for(int i = 0 ; i < 2 * n - 1 ; i ++){
dia1.push_back(false);
dia2.push_back(false);
}
vector row;
putQueen(n, 0, row);
return res;
}
}; 70
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n<=3)
return n;
int a[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=3;i++)
a[i]=i;
for(int i=4;i<=n;i++)
a[i]=a[i-1]+a[i-2];
return a[n];
}
};343
198
416
300
455
435