python逻辑回归示例
# 逻辑回归示例 引用视频代码解释 背景: 通过数据库预测大学生成绩是否会被录取,使用逻辑回归的方法,重点在于建立逻辑回归的过程
求平均损失
#三大件
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
# 引入三个必要的包 分别是科学计算 文件读写以及作图import os
path = 'data' + os.sep + 'LogiReg_data.txt'
pdData = pd.read_csv(path, header=None, names=['Exam 1', 'Exam 2', 'Admitted'])
pdData.head()
.dataframe thead tr:only-child th { text-align: right; } .dataframe thead th { text-align: left; } .dataframe tbody tr th { vertical-align: top; }
| Exam 1 | Exam 2 | Admitted | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 34.623660 | 78.024693 | 0 |
| 1 | 30.286711 | 43.894998 | 0 |
| 2 | 35.847409 | 72.902198 | 0 |
| 3 | 60.182599 | 86.308552 | 1 |
| 4 | 79.032736 | 75.344376 | 1 |
pdData.shape
#打印表格维度(100, 3)
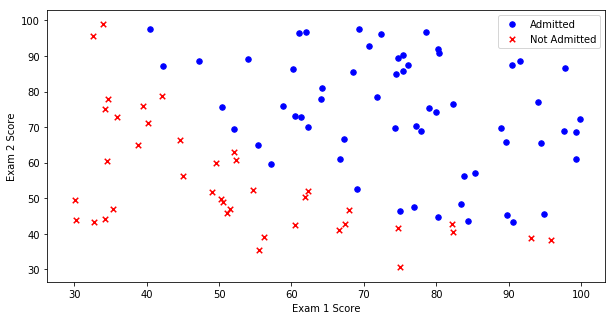
#绘制散点图 注意plt库的用法
positive = pdData[pdData['Admitted'] == 1] # returns the subset of rows such Admitted = 1, i.e. the set of *positive* examples
negative = pdData[pdData['Admitted'] == 0] # returns the subset of rows such Admitted = 0, i.e. the set of *negative* examples
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,5))
ax.scatter(positive['Exam 1'], positive['Exam 2'], s=30, c='b', marker='o', label='Admitted')
ax.scatter(negative['Exam 1'], negative['Exam 2'], s=30, c='r', marker='x', label='Not Admitted')
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel('Exam 1 Score')
ax.set_ylabel('Exam 2 Score')Text(0,0.5,'Exam 2 Score')
目标:建立分类器(求解出三个参数 θ0θ1θ2 θ 0 θ 1 θ 2 )
设定阈值,根据阈值判断录取结果
要完成的模块
sigmoid: 映射到概率的函数model: 返回预测结果值cost: 根据参数计算损失gradient: 计算每个参数的梯度方向descent: 进行参数更新accuracy: 计算精度
模块1 sigmoid函数
g(z)=11+e−z g ( z ) = 1 1 + e − z
属性:
- g:R→[0,1] g : R → [ 0 , 1 ]
- g(0)=0.5 g ( 0 ) = 0.5
- g(−∞)=0 g ( − ∞ ) = 0
- g(+∞)=1 g ( + ∞ ) = 1
def sigmoid(z):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
nums = np.arange(-10, 10, step=1) #creates a vector containing 20 equally spaced values from -10 to 10
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,4))
ax.plot(nums, sigmoid(nums), 'r')[]

模块2 model函数
def model(X, theta):
return sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta.T))
(θ0θ1θ2)×⎛⎝⎜1x1x2⎞⎠⎟=θ0+θ1x1+θ2x2 ( θ 0 θ 1 θ 2 ) × ( 1 x 1 x 2 ) = θ 0 + θ 1 x 1 + θ 2 x 2
这一步指将参数与变量之间的算法转换成矩阵算法
##构造相关的举证
#pdData.insert(0, 'Ones', 1) # in a try / except structure so as not to return an error if the block si executed several times
# set X (training data) and y (target variable)
orig_data = pdData.as_matrix() # convert the Pandas representation of the data to an array useful for further computations
cols = orig_data.shape[1]
X = orig_data[:,0:cols-1]
y = orig_data[:,cols-1:cols]
# convert to numpy arrays and initalize the parameter array theta
#X = np.matrix(X.values)
#y = np.matrix(data.iloc[:,3:4].values) #np.array(y.values)
theta = np.zeros([1, 3])X.shape, y.shape, theta.shape((100, 3), (100, 1), (1, 3))
模块3 损失函数
将对数似然函数去负号
D(hθ(x),y)=−ylog(hθ(x))−(1−y)log(1−hθ(x)) D ( h θ ( x ) , y ) = − y log ( h θ ( x ) ) − ( 1 − y ) log ( 1 − h θ ( x ) )
求平均损失
J(θ)=1n∑i=1nD(hθ(xi),yi) J ( θ ) = 1 n ∑ i = 1 n D ( h θ ( x i ) , y i )
def cost(X, y, theta):
left = np.multiply(-y, np.log(model(X, theta)))
right = np.multiply(1 - y, np.log(1 - model(X, theta)))
return np.sum(left - right) / (len(X))cost(X, y, theta)0.69314718055994529
模块4 梯度函数
∂J∂θj=−1m∑i=1n(yi−hθ(xi))xij ∂ J ∂ θ j = − 1 m ∑ i = 1 n ( y i − h θ ( x i ) ) x i j
def gradient(X, y, theta):
grad = np.zeros(theta.shape)# 创建一个3个元素的theta
error = (model(X, theta)- y).ravel()# error指-(y-h(Theta(Xi))),然后人ravel函数将矩阵平铺成一个向量list
for j in range(len(theta.ravel())): #for each parmeter 对于向量中的每一个元素
term = np.multiply(error, X[:,j]) #term=error[i]*X[i,j],q其中j是固定的,也就是说i号元素对应相乘
grad[0, j] = np.sum(term) / len(X)#i元素再相加求和
return gradSTOP_ITER = 0
STOP_COST = 1
STOP_GRAD = 2
def stopCriterion(type, value, threshold):
#设定三种不同的停止策略
if type == STOP_ITER: return value > threshold
elif type == STOP_COST: return abs(value[-1]-value[-2]) < threshold
elif type == STOP_GRAD: return np.linalg.norm(value) < thresholdimport numpy.random
#洗牌 注意shuffle的用法
def shuffleData(data):
np.random.shuffle(data)
cols = data.shape[1]
X = data[:, 0:cols-1]
y = data[:, cols-1:]
return X, yimport time
def descent(data, theta, batchSize, stopType, thresh, alpha):
#梯度下降求解
init_time = time.time()
i = 0 # 迭代次数
k = 0 # batch
X, y = shuffleData(data)
grad = np.zeros(theta.shape) # 计算的梯度
costs = [cost(X, y, theta)] # 损失值
while True:
grad = gradient(X[k:k+batchSize], y[k:k+batchSize], theta)
k += batchSize #取batch数量个数据
if k >= n:
k = 0
X, y = shuffleData(data) #重新洗牌
theta = theta - alpha*grad # 参数更新
costs.append(cost(X, y, theta)) # 计算新的损失
i += 1
if stopType == STOP_ITER: value = i
elif stopType == STOP_COST: value = costs
elif stopType == STOP_GRAD: value = grad
if stopCriterion(stopType, value, thresh): break
return theta, i-1, costs, grad, time.time() - init_timedef runExpe(data, theta, batchSize, stopType, thresh, alpha):
#import pdb; pdb.set_trace();
theta, iter, costs, grad, dur = descent(data, theta, batchSize, stopType, thresh, alpha)
name = "Original" if (data[:,1]>2).sum() > 1 else "Scaled"
name += " data - learning rate: {} - ".format(alpha)
if batchSize==n: strDescType = "Gradient"
elif batchSize==1: strDescType = "Stochastic"
else: strDescType = "Mini-batch ({})".format(batchSize)
name += strDescType + " descent - Stop: "
if stopType == STOP_ITER: strStop = "{} iterations".format(thresh)
elif stopType == STOP_COST: strStop = "costs change < {}".format(thresh)
else: strStop = "gradient norm < {}".format(thresh)
name += strStop
print ("***{}\nTheta: {} - Iter: {} - Last cost: {:03.2f} - Duration: {:03.2f}s".format(
name, theta, iter, costs[-1], dur))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,4))
ax.plot(np.arange(len(costs)), costs, 'r')
ax.set_xlabel('Iterations')
ax.set_ylabel('Cost')
ax.set_title(name.upper() + ' - Error vs. Iteration')
return theta#选择的梯度下降方法是基于所有样本的
n=100
runExpe(orig_data, theta, n, STOP_ITER, thresh=5000, alpha=0.000001)***Original data - learning rate: 1e-06 - Gradient descent - Stop: 5000 iterations
Theta: [[-0.00027127 0.00705232 0.00376711]] - Iter: 5000 - Last cost: 0.63 - Duration: 1.33s
array([[-0.00027127, 0.00705232, 0.00376711]])

之后可以基于不同的策略使用逻辑回归预测结果,见下一篇文档