【Android】图文解密Android AIDL
文章目录
- 1、简介
- 2、用法
- 1)创建.aidl文件。
- 2)实现接口
- 3)公开接口
- 4)实现客户端
- 5)支持自定义类型
- 6)服务端通知客户端
- 3、aidl自动生成的java代码
- 4、aidl流程
1、简介
AIDL是一种接口描述语言,用于进程间通信,有如下几个特点。
1)AIDL用于多个客户端跨进程访问服务端,且服务端需要处理多线程的场合。否则,同一进程内的通信可以使用Binder,跨进程的通信可以使用Messager。
2)AIDL调用如果来自本地进程,即客户端和服务端在同一进程,则服务端的执行过程与发起调用的客户端在一个线程,此时完全没必要使用AIDL,而是使用上面提到的Binder即可。
3)AIDL调用如果来自远程进程,即客户端和服务端在不同进程,则服务端必须考虑并发AIDL调用,保证线程安全,因为每次远程调用可能在服务端的不同线程中执行。
4)oneway关键字。本地调用为同步调用,不受oneway影响。oneway用于远程调用时,不会阻塞。
5)in、out、inout关键字。这三个关键字表示数据流向,in表示客户端的数据可以流向服务端,out表示服务端的数据可以流向客户端,inout表示客户端和服务的数据流是双向的。基本数据类型默认为in,不可以为别的;非基本数据类型需要指定一个实际需要的关键字,因为这个关键字会影响数据的打包规则,从而影响性能。
2、用法
如何使用AIDL,包括以下几个步骤。
1)创建.aidl文件。
aidl语法类似于Java,数据类型支持boolean、char、byte、short、int、long、float、double八个基本类型,以及String、CharSequence、List和Map,也支持自定义类型,如AIDL生成的接口、parcelable类,但即使是同一package的自定义类型也必须使用import。下面是一个简单的例子,形式为远程调用,使用了AndroidStudio,App名字为AIDLTest,package名字为com.example.aidltest。
// IRemoteService.aidl
package com.example.aidltest;
import com.example.aidltest.IRemoteServiceCallback;
import com.example.aidltest.User;
interface IRemoteService {
int add(int a, int b);
void print(String string);
void printUser(in User user);
void printUser2(out User user);
void printUser3(inout User user);
void registerCallback(IRemoteServiceCallback callback);
}
然后,AndroidStudio编译时会自动生成一个文件IRemoteService.java,其中定义了一个非常重要的抽象类Stub,本质上是一个IBinder。Debug编译时这个文件的位置为AIDLTest/app/build/generated/aidl_source_output_dir/debug/compileDebugAidl/out/com/example/myserver,稍后再解释这个文件中代码。
另外,还定义了两个aidl文件,User.aidl和// IRemoteServiceCallback.aidl,代码如下,稍后会解释它们的作用。
// User.aidl
package com.example.aidltest;
parcelable User;
// IRemoteServiceCallback.aidl
package com.example.aidltest;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface IRemoteServiceCallback {
void hello(int flag);
}
2)实现接口
实现接口,即我们在.aidl文件中声明的接口,这些接口出现在了Stub中。代码如下所示。
private final IRemoteService.Stub mBinder = new IRemoteService.Stub() {
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) {
int ret = a + b;
Log.d("RemoteService", "add ret:" + ret);
return ret;
}
@Override
public void print(String string) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "print string:" + string);
}
@Override
public void printUser(User user) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "printUser user:" + user);
try {
if (null != mCallback) {
mCallback.hello(111);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "callback Exception:" + e);
}
}
@Override
public void printUser2(User user) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "printUser2 user:" + user);
try {
if (null != mCallback) {
mCallback.hello(222);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "callback Exception:" + e);
}
}
@Override
public void printUser3(User user) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "printUser3 user:" + user);
try {
if (null != mCallback) {
mCallback.hello(333);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "callback Exception:" + e);
}
}
@Override
public void registerCallback(IRemoteServiceCallback callback) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "registerCallback callback:" + callback);
mCallback = callback;
}
};
3)公开接口
公开接口,即提供Service,在onBind函数中返回我们实现的Stub类对象。代码如下所示,重点就一个地方,Override onBind,返回上一步实现的接口。
// RemoteService.java
package com.example.aidltest;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.res.Configuration;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class RemoteService extends Service {
private IRemoteServiceCallback mCallback;
private final IRemoteService.Stub mBinder = new IRemoteService.Stub() {
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) {
int ret = a + b;
Log.d("RemoteService", "add ret:" + ret);
return ret;
}
@Override
public void print(String string) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "print string:" + string);
}
@Override
public void printUser(User user) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "printUser user:" + user);
try {
if (null != mCallback) {
mCallback.hello(111);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "callback Exception:" + e);
}
}
@Override
public void printUser2(User user) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "printUser2 user:" + user);
try {
if (null != mCallback) {
mCallback.hello(222);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "callback Exception:" + e);
}
}
@Override
public void printUser3(User user) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "printUser3 user:" + user);
try {
if (null != mCallback) {
mCallback.hello(333);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "callback Exception:" + e);
}
}
@Override
public void registerCallback(IRemoteServiceCallback callback) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "registerCallback callback:" + callback);
mCallback = callback;
}
};
public RemoteService() {
Log.d("RemoteService", "RemoteService");
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.d("RemoteService", "onCreate");
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
int ret = super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
Log.d("RemoteService", "onStartCommand intent:" + intent);
Log.d("RemoteService", "onStartCommand flags:" + flags);
Log.d("RemoteService", "onStartCommand startId:" + startId);
Log.d("RemoteService", "onStartCommand ret:" + ret);
return ret;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.d("RemoteService", "onDestroy");
mCallback = null;
}
@Override
public void onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "onConfigurationChanged newConfig:" + newConfig);
}
@Override
public void onLowMemory() {
Log.d("RemoteService", "onLowMemory");
}
@Override
public void onTrimMemory(int level) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "onTrimMemory level:" + level);
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "onBind intent:" + intent);
return mBinder;
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "onUnbind intent:" + intent);
mCallback = null;
return false;
}
@Override
public void onRebind(Intent intent) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "onRebind intent:" + intent);
}
@Override
public void onTaskRemoved(Intent rootIntent) {
Log.d("RemoteService", "onTaskRemoved intent:" + rootIntent);
}
}
在早期的Android版本中,开启关联启动后,一个App可以绑定另一个App的Service,这就是一种远程调用,不过现在的Android禁止了这种做法。在同一个app内,Service默认在app所属的进程,在AndroidManifest.xml中给Service配置android:process某个属性后,Service就会是一个独立的进程,这时候在同一个app内绑定Service,也是远程调用。
4)实现客户端
客户端使用bindService通过显式Intent绑定Service,这时需要一个ServiceConnection对象,当绑定成功、Service连接后会收到onServiceConnected通知,其中的参数IBinder就是与服务端通信的桥梁,然后使用IRemoteService.Stub.asInterface把这个IBinder转换为IRemoteService,接着就可以调用aidl中声明的接口了,代码如下所示。
// MainActivity.java
package com.example.aidltest;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.content.res.Configuration;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.Message;
import android.os.Process;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private static final int HELLO = 0;
private IRemoteService mRemoteService;
private final ServiceConnection mRemoteConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
Log.d("MainActivity", "onServiceConnected className:" + className);
Log.d("MainActivity", "onServiceConnected service:" + service);
mRemoteService = IRemoteService.Stub.asInterface(service);
if (null != mRemoteService) {
try {
mRemoteService.registerCallback(mRemoteServiceCallback);
Log.d("MainActivity", "add:" + mRemoteService.add(100, 200));
mRemoteService.print("Called from client");
User user = new User("AAA", 111);
mRemoteService.printUser(user);
mRemoteService.printUser2(user);
mRemoteService.printUser3(user);
Log.d("MainActivity", "User:" + user);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.d("MainActivity", "Remote Exception:" + e);
}
}
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) {
Log.d("MainActivity", "onServiceDisconnected className:" + className);
mRemoteService = null;
}
@Override
public void onBindingDied(ComponentName name) {
Log.d("MainActivity", "onBindingDied className:" + name);
}
@Override
public void onNullBinding(ComponentName name) {
Log.d("MainActivity", "onNullBinding className:" + name);
}
};
private IRemoteServiceCallback mRemoteServiceCallback = new IRemoteServiceCallback.Stub() {
@Override
public void hello(int flag) {
Log.d("MainActivity", "hello flag:" + flag);
mRemoteServiceHandler.sendMessage(mRemoteServiceHandler.obtainMessage(HELLO, flag));
}
};
private Handler mRemoteServiceHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case HELLO:
Log.d("MainActivity", "handleMessage hello flag:" + msg.arg1);
break;
default:
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Log.d("MainActivity", "onCreate");
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
try {
boolean ret = bindService(new Intent(this, RemoteService.class), mRemoteConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
Log.d("MainActivity", "bindService ret:" + ret);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.d("MainActivity", "bindService Exception:" + e);
}
}
@Override
protected void onRestart() {
super.onRestart();
Log.d("MainActivity", "onRestart");
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
Log.d("MainActivity", "onStart");
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
Log.d("MainActivity", "onResume");
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
Log.d("MainActivity", "onPause");
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
Log.d("MainActivity", "onStop");
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.d("MainActivity", "onDestroy");
}
@Override
public void onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig) {
super.onDestroy();
Log.d("MainActivity", "onConfigurationChanged newConfig:" + newConfig);
}
}
5)支持自定义类型
aidl中支持自定义类型,分三步。
第一步,比如说定义一个User类,需要实现接口Parcelable,包括两个函数,describeContents和writeToParcel,然后定义一个变量public static final Parcelable.Creator。代码如下所示,需要注意writeToParcel和readFromParcel的变量顺序一致。
// User.java
package com.example.aidltest;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
public class User implements Parcelable {
private String mName;
private int mAge;
public static final Parcelable.Creator CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator() {
@Override
public User createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new User(in);
}
@Override
public User[] newArray(int size) {
return new User[size];
}
};
public User() {
this("default", 0);
}
public User(String name, int age) {
mName = name;
mAge = age;
}
public User(Parcel in) {
readFromParcel(in);
}
public void readFromParcel(Parcel in) {
mName = in.readString();
mAge = in.readInt();
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel out, int flags) {
out.writeString(mName + "?");
out.writeInt(mAge * 100);
}
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString() + "/mName:" + mName + "/mAge:" + mAge;
}
}
Parcelable对象可以打包为Parcel,有了Parcel就可以通过IBinder进行进程间通信了,Parcel的主要目的就是IPC。
第二步,定义同名aidl文件,使用parceable标记自定义类型User。
第三步,在aidl文件中使用自定义类型User,需要注意参数流向。
6)服务端通知客户端
服务端通知客户端有两种方式,一种是aidl中接口的参数标记为out或inout,另一种是使用aidl,即上文代码中的IRemoteServiceCallback.aidl,客户端实现IRemoteServiceCallback.Stub,然后通过IRemoteService中提供的接口registerCallback向服务端注册callback,服务端可通过这个callback向客户端发送通知,客户端收到这个通知时可能不在主线程,有时候还会根据需要使用Handler进行转线程,可参考上面MainActivity中的代码。
3、aidl自动生成的java代码
上面定义了如下三个aidl文件。
├── IRemoteService.aidl
├── IRemoteServiceCallback.aidl
└── User.aidl
其中User.aidl对应的Java代码是我们手动写的,其它两个对应的Java代码是自动生成的。首先来看一下IRemoteServiceCallback.java,本质上就是个Binder实现,代码如下。
/*
* This file is auto-generated. DO NOT MODIFY.
* Original file: /evo/AIDLTest/app/src/main/aidl/com/example/aidltest/IRemoteServiceCallback.aidl
*/
package com.example.aidltest;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
public interface IRemoteServiceCallback extends android.os.IInterface
{
/** Local-side IPC implementation stub class. */
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.example.aidltest.IRemoteServiceCallback
{
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.example.aidltest.IRemoteServiceCallback";
/** Construct the stub at attach it to the interface. */
public Stub()
{
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
/**
* Cast an IBinder object into an com.example.aidltest.IRemoteServiceCallback interface,
* generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static com.example.aidltest.IRemoteServiceCallback asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj)
{
if ((obj==null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.example.aidltest.IRemoteServiceCallback))) {
return ((com.example.aidltest.IRemoteServiceCallback)iin);
}
return new com.example.aidltest.IRemoteServiceCallback.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder()
{
return this;
}
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException
{
java.lang.String descriptor = DESCRIPTOR;
switch (code)
{
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION:
{
reply.writeString(descriptor);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_hello:
{
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
int _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readInt();
this.hello(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
default:
{
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
}
}
private static class Proxy implements com.example.aidltest.IRemoteServiceCallback
{
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote)
{
mRemote = remote;
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder()
{
return mRemote;
}
public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor()
{
return DESCRIPTOR;
}
@Override
public void hello(int flag) throws android.os.RemoteException
{
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeInt(flag);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_hello, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
}
finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
}
static final int TRANSACTION_hello = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0);
}
public void hello(int flag) throws android.os.RemoteException;
}
下面是IRemoteServiceCallback相关的类图。
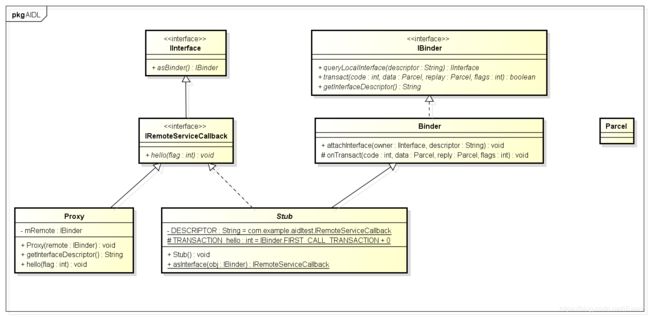
aidl中没有使用oneway,oneway的意思就是不阻塞,那么在自动生成的Java代码中,有两个区别,一个是Stub类的onTransact函数不作reply处理,另一个是Proxy类的函数如上文的hello不作reply处理。另外,如果函数有返回值,或者使用了不同的in、out、input关键字,生成的代码也是不同的。IRemoteService.java代码如下所示,可以看到对自定义数据类型User使用了in、out、input后的区别。
/*
* This file is auto-generated. DO NOT MODIFY.
* Original file: /evo/AIDLTest/app/src/main/aidl/com/example/aidltest/IRemoteService.aidl
*/
package com.example.aidltest;
public interface IRemoteService extends android.os.IInterface
{
/** Local-side IPC implementation stub class. */
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.example.aidltest.IRemoteService
{
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.example.aidltest.IRemoteService";
/** Construct the stub at attach it to the interface. */
public Stub()
{
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
/**
* Cast an IBinder object into an com.example.aidltest.IRemoteService interface,
* generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static com.example.aidltest.IRemoteService asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj)
{
if ((obj==null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.example.aidltest.IRemoteService))) {
return ((com.example.aidltest.IRemoteService)iin);
}
return new com.example.aidltest.IRemoteService.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder()
{
return this;
}
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException
{
java.lang.String descriptor = DESCRIPTOR;
switch (code)
{
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION:
{
reply.writeString(descriptor);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_add:
{
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
int _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readInt();
int _arg1;
_arg1 = data.readInt();
int _result = this.add(_arg0, _arg1);
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(_result);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_print:
{
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
java.lang.String _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readString();
this.print(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_printUser:
{
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
com.example.aidltest.User _arg0;
if ((0 != data.readInt())) {
_arg0 = com.example.aidltest.User.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
}
else {
_arg0 = null;
}
this.printUser(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_printUser2:
{
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
com.example.aidltest.User _arg0;
_arg0 = new com.example.aidltest.User();
this.printUser2(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
if ((_arg0 != null)) {
reply.writeInt(1);
_arg0.writeToParcel(reply, android.os.Parcelable.PARCELABLE_WRITE_RETURN_VALUE);
}
else {
reply.writeInt(0);
}
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_printUser3:
{
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
com.example.aidltest.User _arg0;
if ((0 != data.readInt())) {
_arg0 = com.example.aidltest.User.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
}
else {
_arg0 = null;
}
this.printUser3(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
if ((_arg0 != null)) {
reply.writeInt(1);
_arg0.writeToParcel(reply, android.os.Parcelable.PARCELABLE_WRITE_RETURN_VALUE);
}
else {
reply.writeInt(0);
}
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_registerCallback:
{
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
com.example.aidltest.IRemoteServiceCallback _arg0;
_arg0 = com.example.aidltest.IRemoteServiceCallback.Stub.asInterface(data.readStrongBinder());
this.registerCallback(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
default:
{
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
}
}
private static class Proxy implements com.example.aidltest.IRemoteService
{
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote)
{
mRemote = remote;
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder()
{
return mRemote;
}
public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor()
{
return DESCRIPTOR;
}
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) throws android.os.RemoteException
{
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
int _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeInt(a);
_data.writeInt(b);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_add, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.readInt();
}
finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
@Override
public void print(java.lang.String string) throws android.os.RemoteException
{
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeString(string);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_print, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
}
finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
@Override
public void printUser(com.example.aidltest.User user) throws android.os.RemoteException
{
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
if ((user != null)) {
_data.writeInt(1);
user.writeToParcel(_data, 0);
}
else {
_data.writeInt(0);
}
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_printUser, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
}
finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
@Override public void printUser2(com.example.aidltest.User user) throws android.os.RemoteException
{
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_printUser2, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
if ((0!=_reply.readInt())) {
user.readFromParcel(_reply);
}
}
finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
@Override
public void printUser3(com.example.aidltest.User user) throws android.os.RemoteException
{
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
if ((user != null)) {
_data.writeInt(1);
user.writeToParcel(_data, 0);
}
else {
_data.writeInt(0);
}
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_printUser3, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
if ((0 !=_reply.readInt())) {
user.readFromParcel(_reply);
}
}
finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
@Override public void registerCallback(com.example.aidltest.IRemoteServiceCallback callback) throws android.os.RemoteException
{
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeStrongBinder((((callback != null)) ? (callback.asBinder()) : (null)));
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_registerCallback, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
}
finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
}
static final int TRANSACTION_add = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0);
static final int TRANSACTION_print = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 1);
static final int TRANSACTION_printUser = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 2);
static final int TRANSACTION_printUser2 = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 3);
static final int TRANSACTION_printUser3 = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 4);
static final int TRANSACTION_registerCallback = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 5);
}
public int add(int a, int b) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public void print(java.lang.String string) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public void printUser(com.example.aidltest.User user) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public void printUser2(com.example.aidltest.User user) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public void printUser3(com.example.aidltest.User user) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public void registerCallback(com.example.aidltest.IRemoteServiceCallback callback) throws android.os.RemoteException;
}
最后,总结一下aidl中几个特殊关键字的用法。oneway表示数据流单方向流通,那么oneway标识的接口不能有返回值,参数类型不能是out和inout。对于8个基本数据类型来说,包括String类型,以及aidl接口,充当接口参数类型时默认为in,不能是out和inout。
4、aidl流程
aidl流程其实就是Binder进程间通信的流程,在Java客户端通过Proxy发起远程调用请求,然后经JNI、Native到Kernel后,再经Native、JNI到Java服务端的Stub.onTransact。如果需要数据回流或反向通知,数据再从服务端的Stub流向客户端的Proxy。