观察者模式
上周公司内部的培训讲到了微服务的注册中心Eureka的部分源码,在实例的注册和注销到Eureka的过程中很多都是用到了观察者模式,监听Spring容器的初始化与销毁事件,来触发Eureka Client更新实例的相关信息到Eureka Server。
所以决定来复习下观察者模式。
定义:观察者模式是一种行为设计模式,也称为监听器模式,允许提供一种发布订阅的机制,当发布者的状态发生改变,就会提醒所有的订阅者。
现实生活中的例子:
商店 与 顾客
顾客想要关注某件商品是否到货,需要一直去商店查看
或者是商家在商品到货之后 就要对关注该商品的顾客进行消息推送。
思路:
商店 需要维护 关注商品的顾客信息 以及商品的数量
并且提供新的顾客进行注册的方法,以及老顾客注销的方法
在商品到货时对所有进行关注的顾客进行消息推送
对这个模式进行抽象就得到
商店 称为 发布者 Publisher,在属性改变时通知订阅者
顾客 称为 订阅者 Subscribers,监听发布者的某种属性或者状态
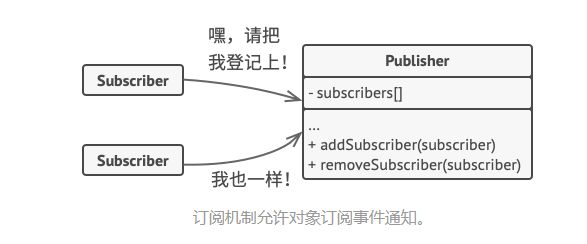
每个订阅者,接受到通知后的行为并不一致,可以定义一个通用的接口,来实现发布者与订阅者的解耦
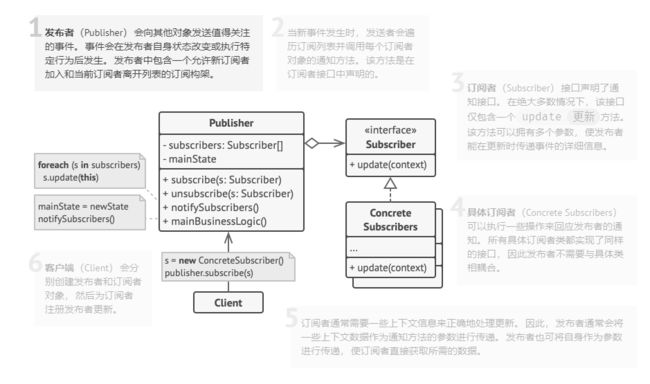
所有的订阅者实现Subscriber接口,实现update方法,进行自己的业务处理逻辑
商店中还有不同的商品,为了维护不同的商品,与不同的订阅者的关系
可以再抽象出一个事件处理器,用于维护订阅者与事件的关联关系,并进行消息提醒。

顾客的实现
//顾客接口
public interface Customer {
void update();
}
//想买苹果的顾客
public class AppleCustomer implements Customer{
@Override
public void update() {
System.out.println("AppleCustomer:爷要马上去买苹果");
}
}
//想买书的顾客
public class BookCustomer implements Customer{
@Override
public void update() {
System.out.println("BookCustomer:今天有点懒了 明天再买书吧");
}
}
事件处理器实现
public class EventManager {
public Map> customers = new HashMap<>();
//初始化 事件与监听器集合
public EventManager(String... operations) {
for (String operation : operations) {
this.customers.put(operation, new ArrayList<>());
}
}
//监听者注册
public void subscribe(String eventType,Customer customer){
ArrayList customerArrayList = customers.get(eventType);
if(customerArrayList == null){
customerArrayList = new ArrayList<>();
customers.put(eventType,customerArrayList);
}
customerArrayList.add(customer);
}
//监听者取消注册
public void unsubscribe(String eventType,Customer customer){
ArrayList customerArrayList = customers.get(eventType);
if(customerArrayList !=null ){
customerArrayList.remove(customer);
}
}
//消息通知
public void notify(String eventType){
ArrayList customerArrayList = customers.get(eventType);
for(Customer customer:customerArrayList){
customer.update();
}
}
}
商店的实现
public class Shop {
private EventManager eventManager;//事件处理器
private Integer bookCounts = 0;//书的数量
private Integer appleCounts = 0;//苹果数量
public Shop(EventManager eventManager) {
this.eventManager = eventManager;
}
public void applePurchase(Integer appleCounts){
//苹果进货了
this.appleCounts += appleCounts;
System.out.println("商店到了"+appleCounts+"斤苹果");
eventManager.notify("apples");
}
public void bookPurchase(Integer bookCounts){
this.bookCounts += bookCounts;
System.out.println("商店到了"+bookCounts+"本书");
eventManager.notify("books");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始化事件处理器
EventManager eventManager = new EventManager("apples","books");
//初始化商店
Shop shop = new Shop(eventManager);
//初始化顾客
AppleCustomer appleCustomer = new AppleCustomer();
BookCustomer bookCustomer = new BookCustomer();
//事件注册
eventManager.subscribe("apples",appleCustomer);
eventManager.subscribe("books",bookCustomer);
//还就那个进货
shop.applePurchase(20);
shop.bookPurchase(1);
}
}
后续将会结合部分Eureka源码来学习观察者模式.....