数据结构与算法---二叉堆和二叉堆排序(python实现)
一、什么是二叉堆
1. 堆的定义:
堆(heap),这里指的堆是一种数据结构,不是内存模型中的堆。堆通常可以看作为一棵树,但这棵树得满足以下条件:
a. 堆中任意节点的值总是不大于(不小于)其子节点的值;
b. 堆总是一颗完全树。
将任意节点不大于其子节点的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆,而将任意节点不小于其子节点的堆叫做最大堆或者大根堆。常见的堆有二叉堆,左倾堆,斜堆,二项堆,斐波那契堆等等。
2. 二叉堆:
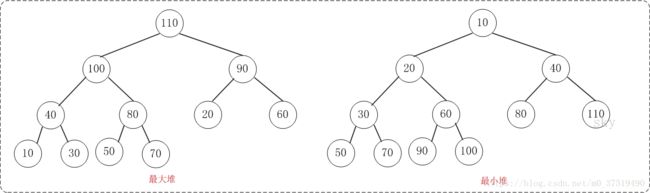
二叉堆是完全二叉树,它分为两种:最大堆和最小堆。
最大堆:父结点的键值总是大于或等于任何一个子节点的键值;最小堆:父结点的键值总是小于或等于任何一个子节点的键值。示意图如下:
二、二叉堆的存储
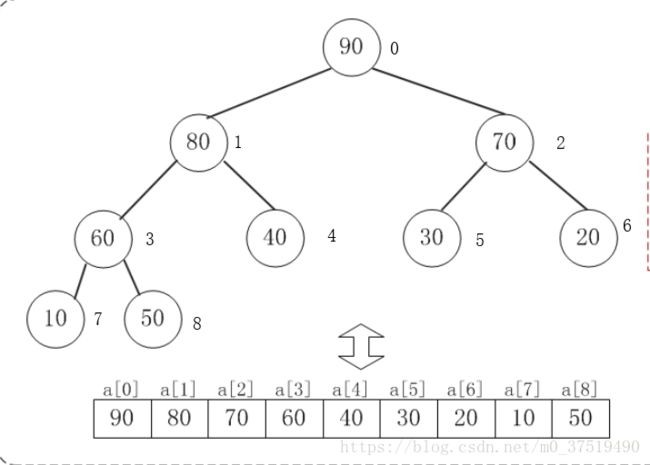
二叉堆是一颗二叉树,因此我们很容易想到使用链式存储,但是二叉堆是一颗完全二叉树,因此我们可以使用数组这种更简单高效的存储方式。
我们将二叉堆的第一个元素放在数组索引的0的位置,也可以放在索引为1的位置。当然,它们的本质是一样的。
当第一个元素放在索引为0的位置上时:
1. 索引为 i 的左孩子的索引为(2*i + 1)
2. 索引为 i 的右孩子的索引为 (2*i + 2)
3. 索引为 i 的父节点的索引为 (i - 1)/ 2(计算机里取整)
二叉堆及其数组存储方式如下:
当第一个元素放在索引为1的位置上时:
1. 索引为 i 的左孩子的索引为(2*i )
2. 索引为 i 的右孩子的索引为 (2*i + 1)
3. 索引为 i 的父节点的索引为 (i )/ 2(计算机里取整)
二叉堆及其数组存储方式如下:
三、二叉堆的基本操作:shift_up与shift_down
我们以最大堆来演示二叉堆的插入与删除对应的shift_up与shift_down操作
1. 插入数据---shift_up:
例如,在最大堆[90,80,70,60,40,30,20,10,50]中添加85,需要执行的步骤如下:
插入数据基本过程如下:
a. 将数据加入到最大堆的末尾,即数组最后
b. 然后通过shift_up操作把数据尽可能的往上挪,直到挪不动为止
因此,插入的最关键步骤为shift_up,最大堆插入的代码如下:
class MaxHeap:
heap = []
@staticmethod
def insert(num):
MaxHeap.heap.append(num)
MaxHeap.shift_up()
@staticmethod
def shift_up():
current_id = len(MaxHeap.heap) - 1
parent_id = (current_id - 1)//2
while current_id > 0:
if MaxHeap.heap[parent_id] >= MaxHeap.heap[current_id]:
break
else:
MaxHeap.heap[parent_id], MaxHeap.heap[current_id] = MaxHeap.heap[current_id], MaxHeap.heap[parent_id]
current_id = parent_id
parent_id = (current_id -1)//22. 删除数据---shift_down:
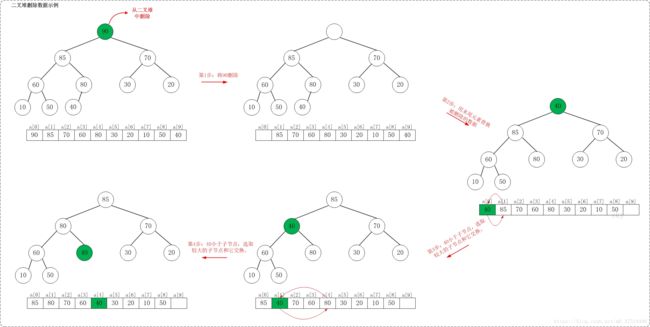
如例,从最大堆[90,85,70,60,80,30,20,10,50,40]中删除90,需要执行的步骤如下:
删除数据的步骤如下:
a. 删除该数据m,但数组结构不变,即其他数据位置不发生移动
b. 将数组最后一个数据n移动到刚才删除的数据m的索引处
c. 通过shift_down操作,把数据n,尽量往下挪,直到生于的数组重新成为最大堆
因此,删除的最关键步骤为shift_down,最大堆删除的代码如下:
class MaxHeap:
heap = [90,85,70,60,80,30,20,10,50,40]
@staticmethod
def insert(num):
MaxHeap.heap.append(num)
MaxHeap.shift_up()
@staticmethod
def shift_up():
current_id = len(MaxHeap.heap) - 1
parent_id = (current_id - 1)//2
while current_id > 0:
if MaxHeap.heap[parent_id] >= MaxHeap.heap[current_id]:
break
else:
MaxHeap.heap[parent_id], MaxHeap.heap[current_id] = MaxHeap.heap[current_id], MaxHeap.heap[parent_id]
current_id = parent_id
parent_id = (current_id -1)//2
@staticmethod
def delate(num):
temp = MaxHeap.heap.pop()
ind = MaxHeap.heap.index(num)
MaxHeap.heap[ind] = temp
MaxHeap.shift_down(ind)
@staticmethod
def shift_down(ind):
current_id = ind
child_id_left = current_id * 2 + 1
child_id_right = current_id * 2 + 2
while current_id < len(MaxHeap.heap) - 1:
#如果当前节点为叶子节点,shift_down完成
if current_id * 2 + 1 > len(MaxHeap.heap) - 1:
break
#如果当前节点只有左孩子没有右孩子
if current_id * 2 + 1 == len(MaxHeap.heap) - 1:
if MaxHeap.heap[current_id] > MaxHeap.heap[-1]:
break
else:
MaxHeap.heap[current_id], MaxHeap.heap[-1] = MaxHeap.heap[-1], MaxHeap.heap[current_id]
break
#如果当前节点既有左孩子又有右孩子
if MaxHeap.heap[current_id] > max(MaxHeap.heap[child_id_left], MaxHeap.heap[child_id_right]):
break
else:
if MaxHeap.heap[child_id_right] > MaxHeap.heap[child_id_left]:
MaxHeap.heap[child_id_right], MaxHeap.heap[current_id] = MaxHeap.heap[current_id], MaxHeap.heap[child_id_right]
current_id = child_id_right
child_id_left = current_id * 2 + 1
child_id_right = current_id * 2 + 2
else:
MaxHeap.heap[child_id_left], MaxHeap.heap[current_id] = MaxHeap.heap[current_id], MaxHeap.heap[child_id_left]
current_id = child_id_left
child_id_left = current_id * 2 + 1
child_id_right = current_id * 2 + 2四、基础堆排序和Heapify
1. 基础排序
有了堆的基本操作,实现堆的排序就比较简单了,用最大堆实现升序排序步骤如下:
a. 将待排序列表依次插入
b. 依次取出堆顶元素并放进原列表对应位置
代码实现如下:
class MaxHeap:
heap = []
@staticmethod
def insert(num):
MaxHeap.heap.append(num)
MaxHeap.shift_up()
@staticmethod
def shift_up():
current_id = len(MaxHeap.heap) - 1
parent_id = (current_id - 1)//2
while current_id > 0:
if MaxHeap.heap[parent_id] >= MaxHeap.heap[current_id]:
break
else:
MaxHeap.heap[parent_id], MaxHeap.heap[current_id] = MaxHeap.heap[current_id], MaxHeap.heap[parent_id]
current_id = parent_id
parent_id = (current_id -1)//2
@staticmethod
def delate(num):
temp = MaxHeap.heap.pop()
ind = MaxHeap.heap.index(num)
MaxHeap.heap[ind] = temp
MaxHeap.shift_down(ind)
@staticmethod
def shift_down(ind):
current_id = ind
child_id_left = current_id * 2 + 1
child_id_right = current_id * 2 + 2
while current_id < len(MaxHeap.heap) - 1:
#如果当前节点为叶子节点,shift_down完成
if current_id * 2 + 1 > len(MaxHeap.heap) - 1:
break
#如果当前节点只有左孩子没有右孩子
if current_id * 2 + 1 == len(MaxHeap.heap) - 1:
if MaxHeap.heap[current_id] > MaxHeap.heap[-1]:
break
else:
MaxHeap.heap[current_id], MaxHeap.heap[-1] = MaxHeap.heap[-1], MaxHeap.heap[current_id]
break
#如果当前节点既有左孩子又有右孩子
if MaxHeap.heap[current_id] > max(MaxHeap.heap[child_id_left], MaxHeap.heap[child_id_right]):
break
else:
if MaxHeap.heap[child_id_right] > MaxHeap.heap[child_id_left]:
MaxHeap.heap[child_id_right], MaxHeap.heap[current_id] = MaxHeap.heap[current_id], MaxHeap.heap[child_id_right]
current_id = child_id_right
child_id_left = current_id * 2 + 1
child_id_right = current_id * 2 + 2
else:
MaxHeap.heap[child_id_left], MaxHeap.heap[current_id] = MaxHeap.heap[current_id], MaxHeap.heap[child_id_left]
current_id = child_id_left
child_id_left = current_id * 2 + 1
child_id_right = current_id * 2 + 2
@staticmethod
def extract_max():
num = MaxHeap.heap[0]
try:
MaxHeap.delate(num)
return num
except:
return num
@staticmethod
def heap_sort(arr):
for n in arr:
MaxHeap.insert(n)
for i in range(len(arr)):
arr[i] = MaxHeap.extract_max()2. Heapify
基础堆排序中,将n个元素逐个插入到一个空堆中,算法复杂度是O(nlogn)
而下面介绍的Heapify,对n个元素的建堆,算法复杂度是O(n)
Heapify算法过程如下:
----堆的第一个元素从索引0开始,堆元素个数为n
a. 找到待建堆的二叉树最后一个非叶子节点,索引为 m =(n - 1)/2
b. 从索引m到0,依次执行shift_down 操作
二叉树的倒数第一层满足二叉堆性质,因此,从倒数第二层开始,通过shift_down 逐层的将其转换为二叉堆。
代码如下(附带通过heapify的排序算法):
@staticmethod
def heapify(arr):
MaxHeap.heap = arr
n = (len(arr) - 1)//2
while n >= 0:
MaxHeap.shift_down(n)
n -= 1
@staticmethod
def heap_sort2(arr):
MaxHeap.heapify(arr)
res = []
for i in range(len(arr)):
res.append(MaxHeap.extract_max())
return res五、原地堆排序
在上一节中,无论是堆的基础排序还是基于heapify的排序,都需要额外的开辟一片空间存放排序。空间复杂度为O(n),
接下来要讲的原地堆排序的空间复杂度为O(1), 算法过程分析如下:
a. 由heapify对n个元素的列表建堆
b. 将堆顶元素与堆尾元素互换,堆大小减一
c. 对堆顶元素执行shift_down操作
d. 依次循环b,c。当堆中元素个数为0时为止
代码如下:
@staticmethod
def heap_sort3(arr):
MaxHeap.heapify(arr)
for i in range(len(arr)-1, -1, -1):
MaxHeap.heap[i], MaxHeap.heap[0] = MaxHeap.heap[0], MaxHeap.heap[i] #将堆顶元素与堆尾元素互换
MaxHeap.shift_down(0, i)六、堆的优势
若使用堆做静态数组的排序,它的时间复杂度与快速排序相比并没有优势,实际上一般情况下要慢于快速排序。
那堆排序的优势在哪呢?
堆,在解决动态排序问题时,有较大优势。
问题1. 动态选择优先级最高的任务执行
很多情况下,我们需要使用优先队列来解决实际问题,如操作系统选择优先级最高的进程使用CPU,而进程随时都会有新进程产生,也会有老进程死亡,而且各进程的优先级也会动态变化。这种时候,如果每次都用排序算法对所有进程优先级进行排序,可以想象耗时是巨大的。而此时堆来解决优先队列就显示出巨大优势,插入新元素,重建最大堆,删除元素,这些操作的时间复杂度均为O(logn)。
问题2. 从N个元素中选出前M个(N巨大而M相对很小,如N=10000000,M=10)
用快速排序算法时间复杂度为NlogN, 而用堆排序时间复杂度为NlogM
当然对于问题2,对快排进行改进,也可提高效率,具体实现方法还没想太清楚。
综上:堆的最大优势就在使用堆实现优先队列。
参考博客:
https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3610187.html
https://coding.imooc.com/class/207.html