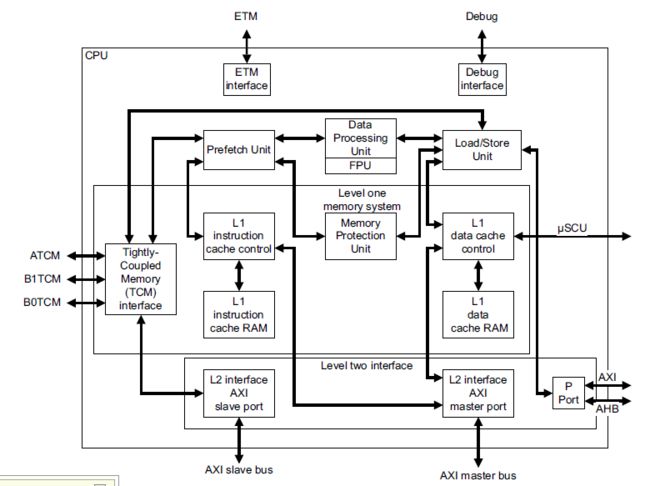
TCM:Tightly Coupled Memory,连接到RAM等memory中,但是CPU读写速度很快。
ECC:Error Checking and Correction
PMU:Performance Monitoring Unit
VIC:Vectored Interrupt Controller
ACP:Accelerator Coherency Port(AXI Coherency Port)
架构:Single Instruction Multiple Data(SIMD)
Vector Floating-Point version3(VFPv3)
Multiprocessing Extensions
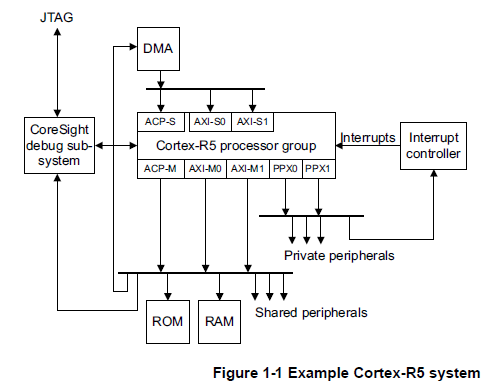
CR5的外部接口:
1)64bit的AXI Master接口
2)32bit的AXI/AHB
3)64bit的AXI Slave接口
4)TCM接口
5)ACP接口,AXI的master和slave
6)VIC接口
7)Configuration信号接口
8)interrupt,event接口
9)32bit的debug APB接口
10)ETM接口
11)MBIST信号和scan信号
CPU的集成过程:
1)Build Config:设置最终AP的Frequency,Area,Feature,比如TCM模块的个数选择。
2)Config inputs/outputs:设置一些interface的值,用于配置,tie0/tie1。
3)SoftWare Config:硬件上电后的cpu初始化设置,cache,register等。
多核结构:
单核结构:
PFU:Prefetch Unit,指令预取单元。
DFU:Data Processing Unit,数据处理单元。
LSU:Load/Store Unit,存储器数据访问。
PFU和LSU都有接口接到L1 Cache,访问L1和TCM。
CR5内debug,每个CPU都通过APB总线来传输数据,如设置watchpoint / breakpoint。
CR5的每个CPU有四种Power mode:
Run mode:正常工作模式。
Standby mode:CPU的一些clock gate。通过WFI/WFE来表征进入该模式
Dormant mode:除了cache和TCM,其他逻辑掉电。
ShutDown mode:整个cpu掉电,cache和TCM的信息必须存储在外部。
CR5中的reset:
1)nRESET:复位non-debug cpu logic
2)DBGRESET:复位core-domain debug logic
3)PRESETDBG:复位debug-domain logic和APB interface
4)ACPRESET:复位ACP的slave和master AXI 接口
5)SYSPORESET:整个cpu系统复位
6)CPUHALT:CPU停止取指令
CR5中的clock:
一个core一个CLKIN,其他的所有时钟,AXI,ACP,D-APB,AHB时钟都必须与它同步。
ARM的CPU内核,除了user mode,其他都为Privileage mode,处理中断,异常,security。
多核系统中的Coherency问题:
1)Data并不shared的情况下,没问题。
2)Data shared但是没有cache,没问题。
3)Data shared,也被cache了,但是都是在自己的L1 cache,没问题。
4)软件,使用Write-Through cache。
处理器内部设计了很多逻辑来检测发生的event,做性能分析,如cache miss等。并且有输出信号EVNTBUS来直接输出信号。
PMU通过对jiance到的event进行计数,控制来表征性能。