你了解欧拉回路吗?(附Java实现代码)
文章目录
- 一:什么是欧拉回路?
- 二: 无向图中欧拉回路存在的条件
- 三:如何得到欧拉回路
- 四:Java实现
一:什么是欧拉回路?
不知道你有没有玩过这样一种叫“一笔画”,从某一点开始画一个图形或图案,期间笔不能从纸上离开而且每条边只能画一次。
下面有三个例子,你可以先试一试看看能不能“一笔画”
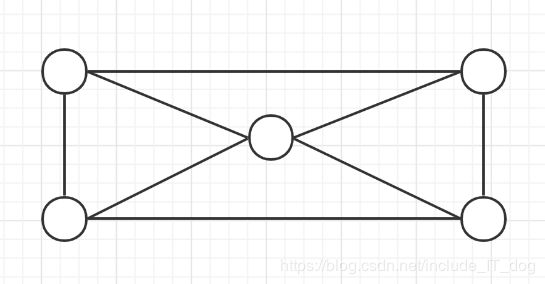

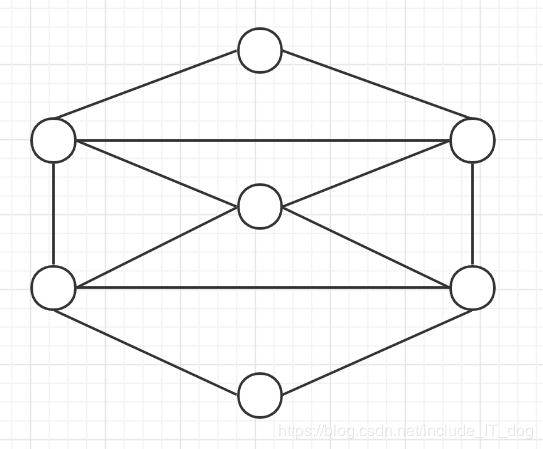
第一个图其实是根本画不出来的,第二个图可以画出,但是不存在起点和终点为同一点的情况,第三个图可以轻松画出,而且存在起点和终点为同一点的情况
欧拉回路问题:
如果图G中的一个路径包括每个边恰好一次,则该路径称为欧拉路径(Euler path)。
如果一个回路是欧拉路径,则称为欧拉回路(Euler circuit)。
具有欧拉回路的图称为欧拉图(简称E图)。具有欧拉路径但不具有欧拉回路的图称为半欧拉图。
二: 无向图中欧拉回路存在的条件
什么情况下才存在欧拉回路呢?
充要条件:当且仅当图是连通的而且每个顶点的度是偶数
想想一下,如果一个节点v的度为1,那么进入v后只能留在v中,不可能再出来。
但是当有两个度为奇数的节点分别作为起点和终点,欧拉路径还是有可能存在的,如果奇数度的顶点多余两个,连欧拉路径都不可能存在。
三:如何得到欧拉回路
求解起点和终点重合的欧拉回路问题可以基于深度优先思想来实现,与DFS算法的区别就是,DFS算法中每个节点基本上只会访问一遍,而欧拉回路算法中要求放宽,只是每个边只能访问一边,但是某一个节点可以多次访问,但基本思想是一致的。DFS算法
深度优先搜索的主要问题在于当访问返回开始节点时,可能还剩下某些边没有访问到,也就是访问提前结束了,比较好补救方法就是,在那些没有访问到的路径的第一个节点重新开始新一轮深度优先搜索,将新的回路加到原来回路中,继续此过程直到所有的边都被遍历为止
四:Java实现
public class EulerCircuit {
private List<Integer> path;
/**
* this cost O(|E| + |V|) time
* @param unDirectedEdges [1,2] represents edge from node1 to node2
* @param n represents the num of nodes
* @param k the start node of Euler Circuit
* @return
* @throws NotFoundException
*/
public List<Integer> EulerCircuitByDFS(int[][] unDirectedEdges, int n, int k)
throws NotFoundException{
if (unDirectedEdges==null||unDirectedEdges.length<=1||n<=2)
throw new NotFoundException();
//init undirected graph
//{key:1, value:<[2, 1], [3, 0]>} represents edge from node1 to node2
//has been visited but node1 to node3 not yet.
Map<Integer, List<int[]>> graph = new HashMap<>();
//nodes' degrees, if degrees(1) == 0 means all edges around node1
//have been visited
int[] degrees = new int[n];
//making graph takes O(E)
for(int i = 0; i<unDirectedEdges.length; i++) {
int[] edge = unDirectedEdges[i];
//set node's degrees
degrees[edge[0]-1]++;
degrees[edge[1]-1]++;
//add (edge[0], edge[1])
if (!graph.containsKey(edge[0])) {
graph.put(edge[0], new ArrayList<>());
}
graph.get(edge[0]).add(new int[]{edge[1], 0});
//add (edge[1], edge[0])
if (!graph.containsKey(edge[1])) {
graph.put(edge[1], new ArrayList<>());
}
graph.get(edge[1]).add(new int[]{edge[0], 0});
}
path = new ArrayList<>();
//ECDFS takes O(V)
try {
ECDFS(graph, k, k, path, degrees);
}catch (NotFoundException e){
throw e;
}
return path;
}
/**
* special dfs for Euler Circuit
* @param graph
* @param k
* @param origin
* @param currentPath
* @param degrees
* @throws NotFoundException
*/
public void ECDFS(Map<Integer, List<int[]>> graph, int k, int origin,
List<Integer> currentPath, int[] degrees)
throws NotFoundException{
currentPath.add(k);
for(int i = 0; i<graph.get(k).size(); i++){
if(degrees[k-1]==0) return;
int[] w = graph.get(k).get(i);
//if edge(k, w) has not been visited yet
if (w[1]==0){
degrees[k-1]--;
degrees[w[0]-1]--;
graph.get(k).set(i, new int[]{w[0], 1});
for(int[] j : graph.get(w[0])){
if(j[0] == k){
j[1] = 1;break;
}
}
//and the degree of node w is oven except the last one(origin node)
if(degrees[w[0]-1]%2==0 && w[0]!=origin){
throw new NotFoundException();
}
//father circuit is done
else if(w[0]==origin){
currentPath.add(origin);
boolean allSeen;
do{
boolean tmp = true;
for(int j = 0; j<currentPath.size(); j++) {
int entryNode = currentPath.get(j);
tmp &= degrees[entryNode-1]==0;
if(degrees[entryNode-1]!=0) {
List<Integer> tempPath = new ArrayList<>();
ECDFS(graph, entryNode, entryNode , tempPath, degrees);
//add child circuit
int index = currentPath.indexOf(entryNode);
currentPath.remove(index);
currentPath.addAll(index, tempPath);
}
}
allSeen = tmp;
}while (!allSeen);
return;
}
else ECDFS(graph, w[0], origin, currentPath, degrees);
}
}
}
public static class NotFoundException extends Exception{
public NotFoundException(){
super("Euler Circuit Not Found");
}
}
}

输入:
| unDirectedEdges | n | k |
|---|---|---|
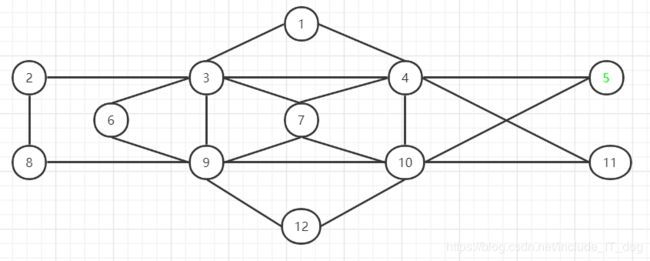
| {{1,3}, {1,4}, {2,3}, {2,8}, {3,4}, {3,6}, {3,7},{3,9}, {4,5}, {4,7}, {4,10}, {4,11}, {5,10}, {6,9}, {7,9},{7,10}, {8,9}, {9,10}, {9,12}, {10,11}, {10,12}} | 12 | 5 |
| {{1,3},{1,2},{3,4}, {2,3}, {2,4}}; | 4 | 4 |
预计输出:
某一条从节点5开始节点5结束的欧拉回路
Euler Circuit Not Found
实际输出:
[5, 4, 1, 3, 2, 8, 9, 10, 12, 9, 3, 4, 7, 3, 6, 9, 7, 10, 4, 11, 10, 5]
Euler Circuit Not Found
测试通过
你可能还敢兴趣的图论算法(均附Java实现代码):
-
算法实验–主函数只有五行的Floyed的算法以及最短路径输出
-
你必须会的–Dijkstra算法–单源最短路径问题
-
你必须会的DFS的递归实现与堆栈实现
-
你必须会的启发式搜索算法–A*算法