数据结构与算法C++之堆排序
首先需要介绍一下一个新的数据结构:堆
堆使用了优先队列
普通队列:先进先出,后进后出
优先队列:出队顺序与入队顺序无关,与优先级有关,一般取出优先级最高的元素,堆入队出队的算法复杂度都为O(nlogn)
最常使用的是二叉堆(Binary Heap)
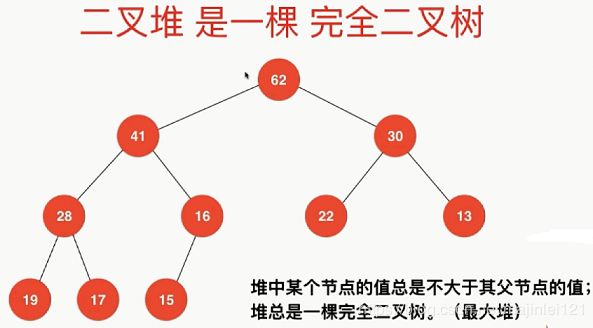
如上图所示,62称为41和30的父节点,41称为左节点,30称为右节点,以此类推,41又是28和16的父节点,等等,二叉堆有如下性质:
- 父节点大于左右子节点
- 堆总是一棵完全二叉树,即最后一层上面的所有层都是完整的,即因为上图有四层,那么30一定同时存在左右节点,否则就不满足堆的性质,倒数第二层的父节点可以左右节点都没有,如22,也可以只有一个节点,但这个节点必须是左节点,如16
用数组来存储二叉堆,如下图所示
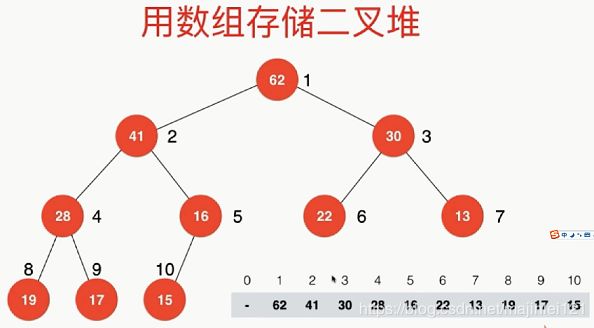
习惯于将最上面的父节点62编号为1,然后从上到下,从左到右依次编号,因为编号从1开始,所以用来存储堆的数组需要10+1个存储空间
- 定义某个节点 i i i 的父节点为 p a r e n t ( i ) = i / 2 parent(i)=i/2 parent(i)=i/2
- 定义该节点 i i i 的左节点为 l e f t c h i l d ( i ) = 2 ∗ i left child (i) = 2*i leftchild(i)=2∗i
- 定义该节点 i i i 的又节点为 r i g h t c h i l d ( i ) = 2 ∗ i + 1 right child (i) = 2*i + 1 rightchild(i)=2∗i+1
如节点4,它的值是28,他的父节点为 4 / 2 = 2 4/2 = 2 4/2=2,值是41
它的左节点为 2 ∗ 4 = 8 2*4 = 8 2∗4=8,值是19
它的右节点为 2 ∗ 4 + 1 = 9 2*4 + 1 = 9 2∗4+1=9, 值是17
Shift Up 堆中插入元素

如上图所示,插入元素值为52
(1)首先将52插入堆的最后一个位置,编号为11

(2)将52与其父节点16作比较,比16大,那么交换16和52的位置
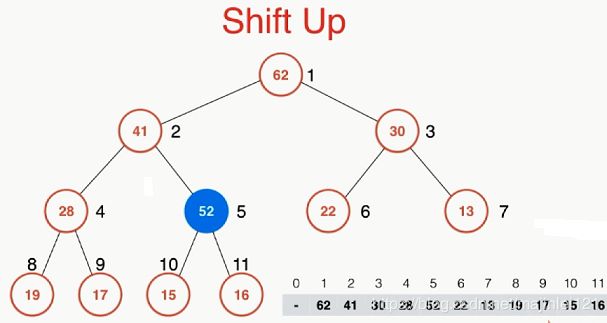
(3)将52再与其父节点41作比较,比41大,那么交换41和52的位置

(4)将52再与新的父节点62作比较,比62小,那么插入操作结束

Shift Down 堆中取出最大元素
(1)首先将最上面的父节点62取出

(2)将最后一个节点16填补到最上面的位置,同时将堆的元素总数count减1
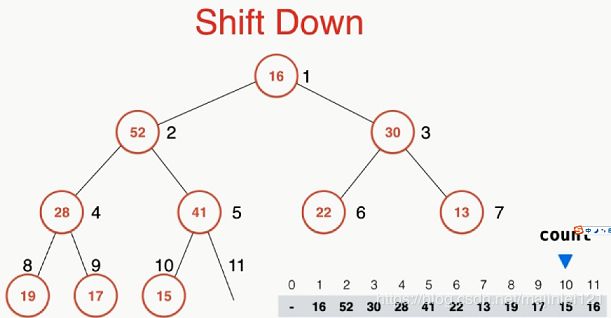
(3)然后将父节点16与其他两个子节点52和30作比较,16比52小,那么交换16与52的位置

(4)继续比较16与它的两个新的子节点28和41的大小,比41小,那么交换16和41的位置

(4)继续比较16与其子节点15的大小,16比15大,那么不用交换位置,Shift Down结束

下面就先使用ShiftUp和ShiftDown进行插入元素和取出元素
#include int main(){
MaxHeap<int> maxheap = MaxHeap<int>(100);
srand(time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
maxheap.insert(rand()%100);
}
//maxheap.testPrint();
while(!maxheap.isEmpty()){
cout<<maxheap.extractMax()<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
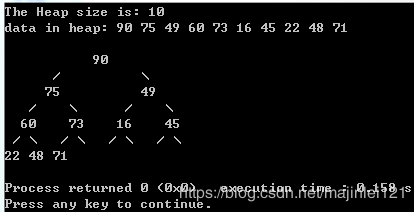
输出为

下面使用堆实现排序
其实就是先将数组中元素挨个放入堆中,然后挨个将堆中元素取出来逆序再放入数组中就可以
首先将堆的实现放入 Heap.h 中
//Heap.h
#include 实现程序如下,程序中实现的快速排序与归并排序可以参考前几篇博客
#include 输出为

可以看出堆排序要慢于归并排序和快速排序,但是计算复杂度也是在允许的范围内,数据结构堆主要用于数据的动态维护
Heapify
上面程序中是将数组元素一个个插入到堆中,如下
MaxHeap<T> maxheap = MaxHeap<T>(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
maxheap.insert(arr[i]);
其实还有更好的方式,即 Heapify
(1)首先将数组按顺序放入堆中,如下图所示,此时是不满足堆的性质的

(2)可以看出所有的叶子节点都是满足堆的性质的,即30,41,62,16,28

(3)第一个非叶子节点的编号为 c o u n t / 2 count / 2 count/2,也就是 10 / 2 = 5 10/2=5 10/2=5也就是编号为5的22
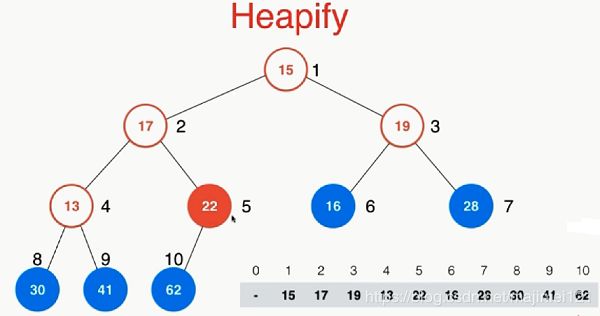
(5)找到第一个非叶子节点5后,按照5,4,3,2,1的顺序不断对他们进行ShiftDown即可,比如22比其子节点62小,那么交换22和62的位置,然后比较13和子节点30和41的大小,13比41小,交换13和41的位置,然后比较19和子节点16,28的大小,交换19和28的位置,然后比较17和子节点62,41的大小,交换17和62的位置,17继续和他的子节点比较,17比22小,那么继续交换位置,以此类推,最后就可将元素都放入正确的位置

程序实现如下,函数取名为 heapSorting2()
首先在Heap.h中添加构造函数MaxHeap(Item arr[], int n)
//Heap.h
MaxHeap(Item arr[], int n){
data = new Item[n+1];
capacity = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
data[i+1] = arr[i];
count = n;
for (int i = count / 2; i >= 1; i--)
ShiftDown(i);
}
测试程序为
#include 输出为
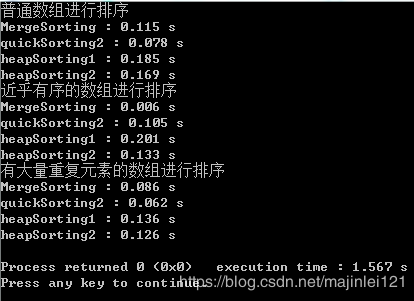
可以看出使用Heapify来将数组构造成堆后,时间变短了
- 将n个元素逐个插入到一个空堆中,算法复杂度为O(nlogn)
- heapify的过程,算法复杂度为O(n)