程序员面试金典 - 面试题 16.19. 水域大小(BFS/DFS)
1. 题目
你有一个用于表示一片土地的整数矩阵 land,该矩阵中每个点的值代表对应地点的海拔高度。
若值为0则表示水域。由垂直、水平或对角连接的水域为池塘。
池塘的大小是指相连接的水域的个数。
编写一个方法来计算矩阵中所有池塘的大小,返回值需要从小到大排序。
示例:
输入:
[
[0,2,1,0],
[0,1,0,1],
[1,1,0,1],
[0,1,0,1]
]
输出: [1,2,4]
提示:
0 < len(land) <= 1000
0 < len(land[i]) <= 1000
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pond-sizes-lcci
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
2. 解题
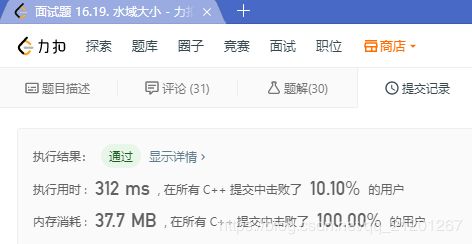
2.1 BFS
- 该题有8个可走方向,访问标志可以直接改地图为 1
class Solution {
int m, n;
int k, x, y, x0, y0;
vector<int> water;
queue<vector<int>> q;
vector<vector<int>> dir = {{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1},{-1,0},{1,1},{-1,-1},{1,-1},{-1,1}};
public:
vector<int> pondSizes(vector<vector<int>>& land) {
m = land.size(), n = land[0].size();
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if(land[i][j]==0)
{
bfs(land, i, j, 0);
}
}
}
sort(water.begin(), water.end());
return water;
}
void bfs(vector<vector<int>>& land, int i, int j, int count)
{
q.push({i,j});
land[i][j] = 1;//访问过了
count++;
while(!q.empty())
{
x0 = q.front()[0];
y0 = q.front()[1];
q.pop();
for(k = 0; k < 8; ++k)
{
x = x0 + dir[k][0];
y = y0 + dir[k][1];
if(x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 && y<n && land[x][y]==0)
{
count++;
q.push({x,y});
land[x][y] = 1;//访问过了
}
}
}
water.push_back(count);
}
};
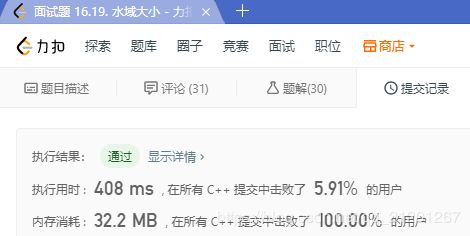
2.2 DFS
class Solution {
int m, n;
vector<int> water;
queue<vector<int>> q;
vector<vector<int>> dir = {{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1},{-1,0},{1,1},{-1,-1},{1,-1},{-1,1}};
public:
vector<int> pondSizes(vector<vector<int>>& land) {
m = land.size(), n = land[0].size();
int i, j, count;
for(i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if(land[i][j]==0)
{
count = 1;
land[i][j] = 1;//访问过了
dfs(land, i, j, count);
water.push_back(count);
}
}
}
sort(water.begin(), water.end());
return water;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& land, int i, int j, int& count)
{
int k, x, y;
for(k = 0; k < 8; ++k)
{
x = i + dir[k][0];
y = j + dir[k][1];
if(x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 && y<n && land[x][y]==0)
{
count++;
land[x][y] = 1;//访问过了
dfs(land,x,y,count);
}
}
}
};