内存分配器的设计与实现
内存分配器(Memory Allocator)负责内存管理,实现动态内存的分配和释放。内存分配器分为两级。第一级分配器直接调用C函数分配内存,第二级分配器则采用内存池来管理内存。如果申请的内存块足够大,那么启动第一级分配器,否则启动第二级分配器。这种设计的优点是可以快速分配和释放小块内存,同时避免内存碎片;缺点是内存池的生命周期比较长,并且很难显式释放。
一些平台对某些特定类型的数据只能从某些特定地址开始存取,这就要求内存分配器可以由使用者指定对齐字节数。在通常情况下,考虑数据类型bool、char、short、int、long long、float、double的最大数据长度为64bit,可以采用8字节对齐,这也是内存分配器的默认对齐参数。但是,使用__m128、__m128i、__m128d时需要16字节对齐,使用__m256则需要32字节对齐。
第一级分配器只是简单的调用函数malloc()、realloc()和free()。为了保证内存按照指定字节数对齐,则需要调用函数_aligned_malloc()、_aligned_realloc()和_aligned_free(),因此实际分配的内存块可能大于申请内存的大小。
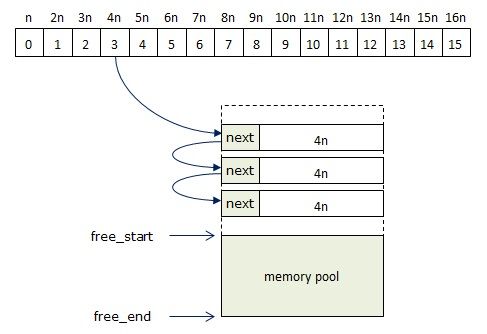
第二级分配器需要维护16个空闲块链表和一个内存池。每个链表中的空闲块的大小都是固定的,假定对齐字节数为n,则各个链码空闲块大小依次为n、2n、3n、4n、5n、6n、7n、8n、9n、10n、11n、12n、13n、14n、15n、16n。内存池由两个指针来描述,free_start记录起始地址,free_end记录结束地址。另外两个变量heap_size和used_size分别纪录堆大小和已用内存大小。
内存池管理的内存块大小只有固定的16个规格, 当所需内存块大于16n时,则使用第一级分配器进行内存分配。否则,按照以下步骤进行内存分配:
-
申请内存的大小上调至n的倍数,根据此大小查找对应的空闲链表;
-
如果空闲链表中有可用的内存块,则直接返回此空闲块,并从空闲链表中删除该块,否则继续下面的步骤;
-
计算内存池中所剩空间的大小,如果足以分配16个内存块,则从中取出16个内存块,调整内存池起始地址,返回第一个内存块,并将剩余的15个块并入空闲链表,否则继续下面的步骤;
-
如果剩余空间足以分配至少1个内存块,则从中取出尽可能多的内存块,调整内存池起始地址,返回第一个内存块,并将剩余的内存块并入空闲链表,否则继续下面的步骤;
-
如果内存池中还有一些内存,则将剩余空间并入其对应大小的空闲链表中;
-
向系统申请一个较大的内存块,如果申请成功,返回第一个内存块,调整内存池起始地址,否则继续下面的步骤;
-
遍历空闲链表,如果存在更大的空闲内存块,则从空闲链表中删除该块,返回该块首地址,并将剩余的部分内存交给内存池管理,否则分配失败。
内存池向系统申请的内存空间,在使用过程中会被划分为更小的内存块,而这些小内存块的使用和归还几乎是随机的。如果试图对这些小内存块进行合并和释放,其高昂的代价会大幅降低内存池的性能。但在内存池的已用内存大小为0时,释放内存是安全的。内存分配器维护一个指针链表,用于内存空间的统一释放。
内存分配器的对齐字节数决定了空闲链表中的内存块大小,这就意味着对齐字节数不同的分配器所维护的空闲链表是不相同的。因此,对齐字节数相同的分配器被认为是同一个分配器,否则被认为是不同的分配器。这与C++标准中对内存分配器的规定是不一样的,标准中的内存分配器没有考虑内存对齐,所有分配器都被视为相等。这也是C++标准容器不支持有内存对齐要求的数据类型的原因,如:__m128、__m128i、__m128d和__m256等数据。
template
class alloc_base
{
private:
// 剩余内存节点
union free_node
{
union free_node* next;
char buffer[1];
};
// 内存指针节点
struct ptr_node
{
ptr_node* next;
char* ptr;
};
private:
static const size_t max_bytes = align << 4;
static const size_t list_count = 16;
static const size_t chunk_count = 16;
static const size_t heap_threshold = (max_bytes * chunk_count) << 5;
static const size_t ptr_node_size = (sizeof(ptr_node) + align - 1) & ~(align - 1);
static free_node* volatile free_list[list_count]; // 空闲内存链表
static ptr_node* volatile ptr_list; // 指针链表
static char* free_start; // 内存池起始地址
static char* free_end; // 内存池结束地址
static size_t heap_size; // 内存池容量
static size_t used_size; // 已用内存大小
private:
// 获取对齐大小
static size_t round_up(size_t bytes)
{
return ((bytes + align - 1) & ~(align - 1));
}
// 获取链表索引
static size_t free_list_index(size_t bytes)
{
return (bytes + align - 1) / align - 1;
}
// 分配多个内存块
static char* chunk_alloc(size_t align_bytes, size_t& count)
{
char* result = nullptr;
size_t memory_size;
size_t total_bytes = align_bytes * count;
// 从堆空间重新分配内存
if (heap_size < heap_threshold)
memory_size = total_bytes << 1;
else
memory_size = (heap_size >> 7) << 3;
while (memory_size >= total_bytes)
{
// 从系统获取内存
char* ptr = reinterpret_cast (_aligned_malloc(ptr_node_size + memory_size, align));
if (ptr != nullptr)
{
result = ptr + ptr_node_size;
free_start = result + total_bytes;
free_end = result + memory_size;
heap_size += memory_size;
// 指针链表
reinterpret_cast (ptr)->next = ptr_list;
reinterpret_cast (ptr)->ptr = ptr;
ptr_list = reinterpret_cast (ptr);
break;
}
// 请求空间大小减半
memory_size >>= 1;
}
// 如果堆空间无可用内存
if (result == nullptr)
{
// 在空闲链表中搜索可用空间
for (size_t size = align_bytes; size <= max_bytes; size += align)
{
free_node* volatile* current_list = free_list + free_list_index(size);
if (*current_list != nullptr)
{
count = 1;
result = (*current_list)->buffer;
free_start = result + align_bytes;
free_end = result + size;
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
public:
// 返回容积
static size_t capacity(void)
{
return heap_size;
}
// 返回大小
static size_t size(void)
{
return used_size;
}
// 分配内存
static void* allocate(size_t size)
{
// 一级分配器
if (size > max_bytes)
{
void* result = _aligned_malloc(size, align);
if (result == nullptr)
throw std::bad_alloc();
return result;
}
// 二级分配器
else
{
char *result = nullptr;
size_t count = chunk_count;
free_node* volatile* current_list = free_list + free_list_index(size);
// 在空闲链表中搜索可用空间
if (*current_list != nullptr)
{
result = (*current_list)->buffer;
*current_list = (*current_list)->next;
}
// 在内存池中搜索可用空间
else
{
size_t align_bytes = round_up(size);
size_t total_bytes = align_bytes * count;
size_t free_bytes = free_end - free_start;
if (free_bytes >= total_bytes)
{
result = free_start;
free_start += total_bytes;
}
else if (free_bytes >= align_bytes)
{
count = free_bytes / align_bytes;
total_bytes = align_bytes * count;
result = free_start;
free_start += total_bytes;
}
else
{
// 将剩余内存编入空闲链表
if (free_bytes > 0)
{
free_node* volatile* free_list_left = free_list + free_list_index(free_bytes);
reinterpret_cast (free_start)->next = *free_list_left;
*free_list_left = reinterpret_cast (free_start);
free_start = free_end;
}
// 分配多个内存块
result = chunk_alloc(align_bytes, count);
}
// 填充空闲链表
if (result != nullptr && count > 1)
{
char *cur, *next = result + align_bytes;
*current_list = reinterpret_cast (next);
for (size_t i = 2; i < count; ++i)
{
cur = next;
next += align_bytes;
reinterpret_cast (cur)->next = reinterpret_cast (next);
}
reinterpret_cast (next)->next = nullptr;
}
}
if (result != nullptr)
used_size += size;
else
throw std::bad_alloc();
return reinterpret_cast (result);
}
}
// 释放内存
static void deallocate(void* ptr, size_t size)
{
if (size > max_bytes)
{
_aligned_free(ptr);
}
else
{
free_node* volatile* current_list = free_list + free_list_index(size);
reinterpret_cast (ptr)->next = *current_list;
*current_list = reinterpret_cast (ptr);
used_size -= size;
}
}
// 重新分配内存
static void* reallocate(void *ptr, size_t old_size, size_t new_size)
{
void *result = nullptr;
size_t copy_size;
if (old_size > max_bytes && new_size > max_bytes)
{
result = _aligned_realloc(ptr, new_size, align);
}
if (round_up(old_size) == round_up(new_size))
{
result = ptr;
used_size -= old_size;
used_size += new_size;
}
else
{
result = allocate(new_size);
if (result == nullptr)
{
copy_size = new_size > old_size ? old_size : new_size;
memcpy(result, ptr, copy_size);
deallocate(ptr, old_size);
}
}
if (result == nullptr)
throw std::bad_alloc();
return result;
}
// 释放全部内存
static void release(void)
{
if (used_size != 0)
return;
while (ptr_list != nullptr)
{
ptr_node *next = ptr_list->next;
_aligned_free(ptr_list->ptr);
ptr_list = next;
}
heap_size = 0;
used_size = 0;
}
};