贪心策略
文章目录
- 简介
- 贪心的特点
- 实际例子
- 硬币支付问题
- POJ_1700
- 区间调度问题(二维数组排序)
- 区间选点
- 区间覆盖问题
简介
- 无论是DFS还是BFS都是遍历解空间
- 动态规划和贪心算法都是一种递推算法,运用局部最优解来推到全局最优解
- 是对遍历解空间的一种优化
- 当问题具有最优子结构的时候,可以用动归,而贪心是动归的特例。
贪心的特点
- 只看眼前。根据某种规则,不断的选取当前策略,最终找到最优解
- 主要需要不断的举例,去猜测出一个贪心策略。
注意:当前最优的未必是整体最优
实际例子
硬币支付问题
硬币问题
有1元,5元,10元,50元,100元,500元的硬币各c1,c5,c10,c50,c100,c500枚.
现在要用这些硬币来支付A元,最少需要多少枚硬币?
假定本题至少存在一种支付方案.
0≤ci≤10^9
0≤A≤10^9
输入:
第一行有六个数字,分别代表从小到大6种面值的硬币的个数
第二行为A,代表需支付的A元
样例:
输入
3 2 1 3 0 2
620
输出
6
/**
* 尽量先用大面值,因为不用大面值,将使用更多的小面值硬币,一定得不到最优解
*/
public class Main {
static int [] cin = new int[6];
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int money ;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
cin[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
int [] coins = new int[]{1,5,10,50,100,500};
money = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = 5; i >=0; i--) {
int x = money/coins[i];//金额有多少个coins[i]
int t = Math.min(cin[i],x);//当前面值的硬币有cin[i]个
ans += t;
money -= t*coins[i];
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
POJ_1700
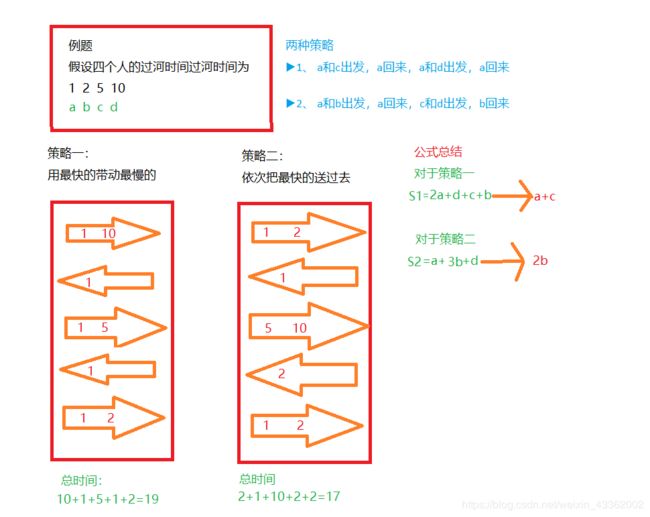
N个人过河,船每次最多只能坐两个人,船载每个人过河的所需时间不同,问最快的过河时间。
有N个人要渡河,但是只有一艘船,船上每次最多只能载两个人,渡河的速度由两个人中较慢的那个决定,小船来回载人直到所有人都渡河,求最短的渡河时间。
输入的每种情况的第一行包含N,第二行包含N个整数,表示每个人过河的时间。每个案例前面都有一个空行。不会有超过1000人,没有人会花超过100秒的时间穿越。
对于每个测试用例,打印一行,其中包含所有N个人过河所需的总秒数。
Sample Input
1
4
1 2 5 10
Sample Output
17
可以发现,4个人以上时,前四轮都是将最慢的两个渡过河。
public class Case02_POJ_1700 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int T = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < T; i++) {
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] speed = new int[n];
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
speed[j] = sc.nextInt();
}
//排序
Arrays.sort(speed);
f(n, speed);
}
}
/**
* speed已经排序
*
* @param n
* @param speed
*/
private static void f(int n, int[] speed) {
int left = n;
int ans = 0;
while (left > 0) {
if (left == 1) {//只有1人
ans += speed[0];
break;
} else if (left == 2) {//只有两人
ans += speed[1];
break;
} else if (left == 3) {//有三人
ans += speed[2] + speed[0] + speed[1];
break;
} else {//通过两种策略来回两趟,渡过最慢的两个人
//1,2出发,1返回,最后两名出发,2返回
int s1 = speed[1] + speed[0] + speed[left - 1] + speed[1];
//1,3出发,1返回,1,4出发,1返回,1,2过河
int s2 = speed[left - 1] + speed[left - 2] + 2 * speed[0];
ans += Math.min(s1, s2);
left -= 2;//左侧是渡河的起点,left代表左侧的剩余人数
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
区间调度问题(二维数组排序)
有n项工作,每项工作分别在si时间开始,在ti时间结束.
对于每项工作,你都可以选择参与与否.如果选择了参与,那么自始至终都必须全程参与.
此外,参与工作的时间段不能重复(即使是开始的瞬间和结束的瞬间的重叠也是不允许的).
你的目标是参与尽可能多的工作,那么最多能参与多少项工作呢?
1≤n≤100000
1≤si≤ti≤10^9
输入:
第一行:n
第二行:n个整数空格隔开,代表n个工作的开始时间
第三行:n个整数空格隔开,代表n个工作的结束时间
样例输入:
5
1 3 1 6 8
3 5 2 9 10
样例输出:
3
说明:选取工作1,3,5
面向对象的排序思想:
- 将不同的维度,比如说身高、体重、年龄,进行打包。
- 将对象的一些操作打包到一起,操作可以直接影响数据。
//贪心策略:选择结束时间最早的
public class Case03_区间调度问题 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] s = new int[n];
int[] t = new int[n];
//建立开始时间和终止时间的打包对象
Job[] jobs = new Job[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
s[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
t[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
jobs[i] = new Job(s[i], t[i]);
}
Arrays.sort(jobs);
//此时数据按照终止时间和开始时间由小到大排序
int res = f(n, jobs);
System.out.println(res);
}
private static int f(int n, Job[] jobs) {
int cnt = 1;
int y = jobs[0].t;//先选择最小的终止时间
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {//选择下一个终止时间最早的
if (jobs[i].s > y) {
cnt++;
y = jobs[i].t;
}
}
return cnt;
}
/**
* 必须实现排序规则
*/
private static class Job implements Comparable<Job> {
int s;
int t;
public Job(int s, int t) {
this.s = s;
this.t = t;
}
//排序规则
@Override
public int compareTo(Job other) {
int x = this.t - other.t;
if (x == 0)//如果终止的时间相同,则比较开始时间
return this.s - other.s;
else
return x;
}
}
}
区间选点
题意:有n个如下形式的条件:
ai bi ci,表示在区间[ai, bi]内至少要选择ci个整数点.(不同区间内含的点可以是同一个)
问你满足n个条件的情况下,最少需要选多少个点?
Sample Input
5
3 7 3
8 10 3
6 8 1
1 3 1
10 11 1
Sample Output
6

public class Case04_区间选点问题 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
Interval[] intervals = new Interval[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
intervals[i] = new Interval(sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt());
}
Arrays.sort(intervals);//按区间右端点排序
int max = intervals[n - 1].t;//右端最大值
int[] axis = new int[max + 1];//标记数轴上的点是否已经被选中
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
//1.查阅区间中有多少个点
int s = intervals[i].s;//起点
int t = intervals[i].t;//终点
int cnt = sum(axis, s, t);//找到这个区间已经选点的数量,sums[t] - sums[s - 1];//效率低
// 2.如果不够,从区间右端开始标记,遇标记过的就跳过
intervals[i].c -= cnt;//需要新增的点的数量
while (intervals[i].c > 0) {
if (axis[t] == 0) {//从区间终点开始选点
axis[t] = 1;
// updateSums(t,sums);//更新前缀和
intervals[i].c--;//进一步减少需要新增的点的数量
t--;
} else {//这个点已经被选过了,不选择重复的点
t--;
}
}
}
System.out.println(sum(axis, 0, max));
}
/**
* 统计数轴axis上s-t区间已经有多少个点被选中
* @param axis
* @param s
* @param t
* @return
*/
private static int sum(int[] axis, int s, int t) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = s; i <= t; i++) {
sum += axis[i];
}
return sum;
}
private static class Interval implements Comparable<Interval> {
int s;//起点
int t;//终点
int c;//区间需求
public Interval(int s, int t, int c) {
this.s = s;
this.t = t;
this.c = c;
}
//按照终点由小到大排序
@Override
public int compareTo(Interval other) {
int x = this.t - other.t;
if (x == 0)
return this.s - other.s;
else
return x;
}
}
}
区间覆盖问题
如果给定一堆线段,给定一个区间,看最少需要几个线段才能完全覆盖这个区间。
解决思路:
-
设区间起点为start,终点为end,所需线段数目为ans
-
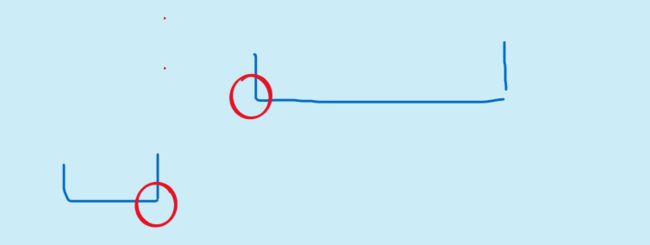
首先线段中的终点,小于区间的起点,则该线段肯定无法覆盖
-
同理如果区间的终点,大于线段的起点,则也一定无法覆盖
-
接着就需要保存线段终点大于等于区间起点且线段起点小于等于区间终点的线段
-
对上面的线段根据起点的大小排序
-
重复上述步骤直到找到终点大于end的
题目:给出n条线段,以及最大长度m,问最少需要多少条才能覆盖1-m这个区间,当无法全部覆盖的时候输出-1
Sample Input
3 10
1 7
3 6
6 10
Sample Output
2
public class Case05_区间覆盖问题 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int T = sc.nextInt();
Job[] jobs = new Job[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
jobs[i] = new Job(sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt());
}
Arrays.sort(jobs);
int start = 1;//要覆盖的目标点,end覆盖该点的所有区间中右端点最右
int end = 1;
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int s = jobs[i].s;
int t = jobs[i].t;
if (i == 0 && s > 1) break;//第一个起点比区间起点小,则一定无法覆盖
if (s <= start) {//当前区间有可能覆盖start
end = Math.max(t, end);//寻找起点小于start同时终点最远的线段
} else {//说明已经没有线段再比start小,开始下一个区间
ans++;//上一个目标覆盖已经达成,计数加1
start = end + 1;//更新起点,设置一个新的覆盖目标
if (s <= start) {
end = Math.max(t, end);
} else {//当前的起点如果比end大,则后面的都一定大,无法继续覆盖
break;
}
}
if (end >= T) {//当前的end超越了线段的右侧,则不需要继续判断了
break;
}
}
if (end < T)//如果没有覆盖
System.out.println(-1);
else
System.out.println(ans);
}
private static class Job implements Comparable<Job> {
int s;
int t;
public Job(int s, int t) {
this.s = s;
this.t = t;
}
/**按照区间起点排序*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Job other) {
int x = this.s - other.s;
if (x == 0)
return this.t - other.t;
else
return x;
}
}
}