Springmv知识六------拦截器&异常处理
拦截器
拦截器概念
拦截器的主要作用就是拦截用户的请求,在所匹配的目标方法之前进行执行。一般情况下,用作权限验证来判断用户是否登陆,还有就是商城中不登录不让购买也可以利用拦截器进行验证。
我们可以自定义拦截器来实现特定的功能,自定义的拦截器必须实现HandlerInterceptor接口。
并且实现以下方法:
preHandle():这个方法在业务处理器处理请求之前被调用,在该方法中可以对用户请求Request进行处理。需要注意的是这个方法的返回值,如果我们在该拦截器对请求进行拦截处理后还要调用其他的拦截器,或者是业务处理器去进行处理,则返回true;如果我们不再需要调用其他的组件去处理请求,则返回false。
postHandle():*在业务处理器执行完目标方法后,但是是在DispatcherServlet向客户端返回响应前被调用*,在该方法中对用户请求Request进行处理。
afterCompletion():这个方法在DispatcherServlet完全处理完请求后被调用,可以在该方法中进行一些资源清理的操作。
配置自定义的拦截器
二步走:
第一步:编写自定义拦截器
第二步:注册自定义拦截器
public class FirstIntercept implements HandlerInterceptor{
/* 该方法在目标方法之前之前进行拦截调用
* 若该方法返回true,则会继续调用后续的拦截器和目标方法
* 若方法返回false,则会终止后续拦截器和目标方法的执行。
* preHandle--》目标方法 --》postHandle--》afterCompletion
*
* 权限 日志 事务
*/
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("FirstIntercept preHandle ");
//return false;
return true;
}
/*调用目标方法之后渲染视图之前
* 可以对请求域中的属性或者视图做出修改
* */
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("FirstIntercept postHandle ");
}
/*渲染视图之后
* 释放资源
* */
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("FirstIntercept afterCompletion ");
}
}
<mvc:interceptors>
<bean class="com.wf.springmvc.crud.intercept.FirstIntercept">bean>
<bean class="com.wf.springmvc.crud.intercept.SecondIntercept">bean>
mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/list"/>
<bean class="com.wf.springmvc.crud.intercept.SecondIntercept">bean>
mvc:interceptor>
mvc:interceptors>
注意:
在配置拦截器时,我们可以利用【mvc:interceptor】子节点,进行指定拦截器去作用在那些请求上面,例如上面的配置自定义拦截器 方法二 ,其实这样可以大大优化我们的性能,因为这样的话,我们可以指定在某些需要拦截器的目标方法上进行拦截,而对于不需要拦截的目标方法则不进行拦截。
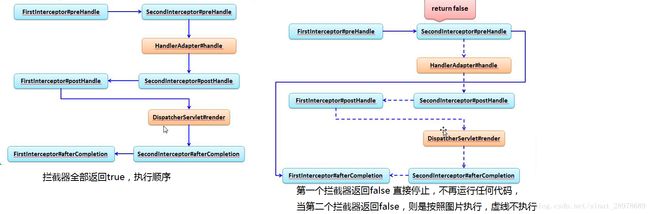
拦截器执行顺序
对于 单个拦截器,拦截的顺序是按照下列顺序进行,但是要注意的是此时的preHandle的返回值是true,如果返回值为false,则执行完HandlerAdapter的目标方法 之后就直接进行渲染视图,而不再进行其他的处理
FirstIntercept的 preHandle—-》HandlerAdapter的目标方法 —-》FirstIntercept的postHandle—-》DispatcherServlet的渲染视图 —-》FirstIntercept的afterCompletion
对于多个拦截器,执行顺序就像剥洋葱那样层层递进。是根据注册自定义拦截器的顺序进行执行。注意的是,下图中的停止是直接停止,连目标方法都不会执行。
异常处理
Springmvc 通过HandlerExceptionResolver接口 处理程序的异常,包括Handler映射,数据绑定以及目标方法执行时发生的异常。
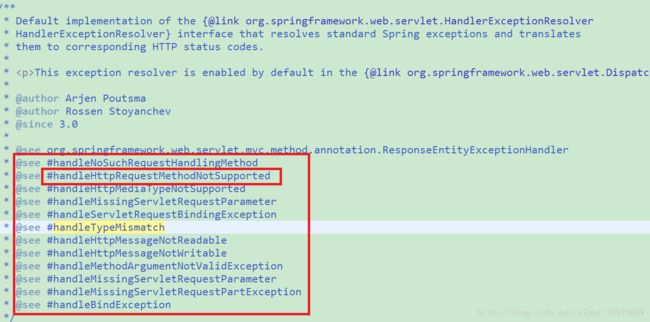
HandlerExceptionResolver接口的实现类有以下几种,但是我们常用的是四个:

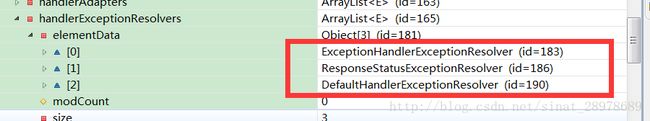
其中在我们配置了【mvc:annotation-driven】时,DispatcherServlet 会给我们装配以下的三个默认的异常实现类,加断点,查看【DispatcherServlet 】的this变量中的【handlerExceptionResolver】
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
1、ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver主要处理Handler中用@ExceptionHandler注解定义的方法。
2、对于@ExceptionHandler注解的方法,如果是发生的NullPointException,但是在我们的声明异常有RuntimeException和Exception,那么此时会根据异常的最近继承关系,找继承深度最浅的那个,(就近原则) 。
3、ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver内部如果找不到@ExceptionHandler注解的话,就会找@ControllerAdvice中的@ExceptionHandler注解方法。
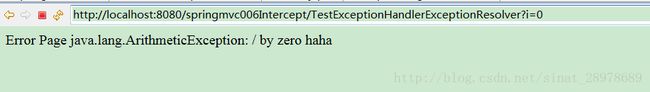
一般情况下,在我们的运行中出现异常的话,直接会在页面进行报错显示,如果我们利用了我们的异常处理,就可以避免这样。
<a href="TestExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver?i=2">Test ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver a> <br>
@RequestMapping("TestExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver")
public String TestExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver(@RequestParam("i") int i){
System.out.println("result : "+10/i);
return "success";
}当我们运行上述代码时,如果我们没有进行异常处理的话,跳转的页面如下:(我们可以吧传递参数设置为0,让其强制出错)

但是如果我们在这个方法下面新增一个异常处理方法,即被@ExceptionHandler注解修饰的方法。则运行效果如下:
添加的代码:
@ExceptionHandler(value={ArithmeticException.class,IOException.class})
public ModelAndView TestExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver(Exception ex){
System.out.println("01----出异常了:"+ex);
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView("error");
model.addObject("exception", ex);
return model;
}
@ExceptionHandler({ClassNotFoundException.class,ClassCastException.class})
public ModelAndView TestExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver02(Exception ex){
System.out.println("02----出异常了:"+ex);
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView("error");
model.addObject("exception", ex);
return model;
}
注意:
1、上述我们定义了两个@ExceptionHandler修饰的方法,但是一定要注意两个方法的异常类型不能相同,这样做的目的,是为了测试,当我们抛出的异常不在这预定义的异常之中,会进行就近选择进行处理。
2、@ExceptionHandler 注解 可以指定异常,可以为多个
3、@ExceptionHandler 修饰的方法,不能使用Map作为与前台交互的数据存储, 如果希望将错误新城传递到前台,我们需要使用ModelAndView 作为视图返回值 在model中进行异常的交互与显示
4、@ExceptionHandler 方法有异常的优先级,一般都是匹配相似度较高的
5、如果出现异常在本类中找不到@ExceptionHandler修饰的方法进行异常处理,则会进入到 有@ControllerAdvice修饰的类中去查找@ExceptionHandler修饰的方法进行匹配
6、注意@ExceptionHandler可以匹配多个异常,但是在不同的方法中不能处理相同的异常,因为会不知道该用哪个方法进行处理,回报500异常
或者我们单独写出来一个类,用来存放异常处理,如下:
@ControllerAdvice
public class HandlerExceptionController {
@ExceptionHandler({ArithmeticException.class,IOException.class})
public ModelAndView TestExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver(Exception ex){
System.out.println("03----ControllerAdvice出异常了:"+ex);
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView("error");
model.addObject("exception", ex);
return model;
}
}注意使用类注解@ControllerAdvice和异常注解@ExceptionHandler。
这样的话,当发生异常时,异常在本类中找不到@ExceptionHandler修饰的方法进行异常处理,则会进入到 有@ControllerAdvice修饰的类中去查找@ExceptionHandler修饰的方法进行匹配。
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver一般用于自己制定特定的响应状态和错误信息信息显示上面。一般我们在向外抛出异常进行处理时,我们可以抛出我们自己定义的异常类。
在处理器方法中抛出了上述异常,若【ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver】不解析我们的异常类,这是由于触发的自定义异常带有【@ResponseStatus注解】,因此,会被ResponseStatusExceptionResolver解析到。最后响应【@ResponseStatus注解】属性值给客户端。
"TestResponseStatusExceptionResolver?i=10">Test ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
// 测试ResponseStatusExceptionResolver 注意自定义异常类NameNOTINPasswordException
@RequestMapping("TestResponseStatusExceptionResolver")
public String TestResponseStatusExceptionResolver(@RequestParam("i") int i){
if(i==13 ){
throw new NameNOTINPasswordException(); // 更改浏览器参数i为13
// throw new RuntimeErrorException(null);
}
System.out.println("TestResponseStatusExceptionResolver ...");
return "success";
}
// reason指定显示信息 value http的状状态码 屏蔽此注解对比 拿到外部浏览器进行显示
// 不要标在方法上面,尽管可以,会造成应该正常的显示页面也产生错误页面上
@ResponseStatus(value=HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN,reason="用户名与密码不匹配")
public class NameNOTINPasswordException extends RuntimeException {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
}
注意:ResponseStatusExceptionResolver只处理带有@ResponseStatus注解的异常并将其映射为状态码。
第一次我们抛出RuntimeErrorException,由于没有注解@ResponseStatus,所以返回的为500
第二次我们修改我们抛出的异常为自定义的异常,并且利用注解@ResponseStatus,所以返回我们特定的状态码和信息。

DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver这个主要是处理Spring一些特定的异常并且把他们转化为状态码。在源码中我们可以看到。
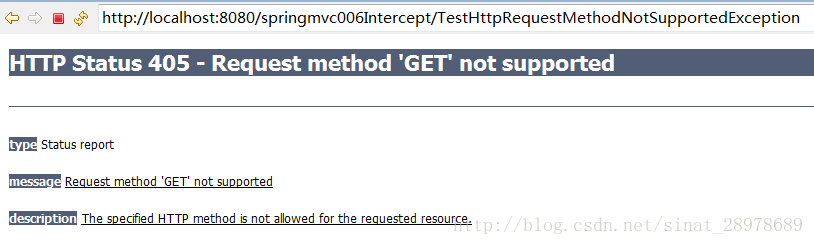
测试上述HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException。他的意思是不支持我们提交的方法方式。
我们的超链接是GET方式,我们在后台处理时,将方法指定为处理POST请求,这样的话,就会交给我们的这个DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver进行处理。
<a href="TestHttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException">Test HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException a> <br>
@RequestMapping(value="/TestHttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException",method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String TestHttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(){
System.out.println("TestHttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException...");
return "success";
}
注意: 显然,从这里我们可以看出以前再出现错误页面时,都是经过框架给我们处理过的。
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver
这个异常处理,主要是解决当发生我们所指定的异常情况时,跳转到我们所指定的页面。这个异常我们在Springmvc.xml文件中进行注册。
<a href="TestSimpleMappingExceptionResolver?i=10">Test SimpleMappingExceptionResolver a> <br>
@RequestMapping("/TestSimpleMappingExceptionResolver")
public String TestSimpleMappingExceptionResolver(@RequestParam("i") Integer i){
int [] vals = new int[20];
System.out.println(vals[i]); // 传递参数 21 让其发生 java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
return"success";
}
<bean class=" org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver">
<property name="exceptionMappings">
<props>
<prop key="java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException">errorprop>
props>
property>
<property name="exceptionAttribute" value="ex">property>
bean>
<body>
Error Page <br>
默认存储域: ${exception } <br>
haha <br>
配置修改存储域:${ex}<br>
body>
注意:配置指定的异常到指定的位置,依然经过我们的视图解析器进行配置,所以要在指定位置编写错误页面。