【数据结构java篇】- 队列
文章目录
- 1 队列的一个使用场景
- 2 队列介绍
- 3 数组模拟队列思路
- 4、数组模拟环形队列
1 队列的一个使用场景
2 队列介绍
3 数组模拟队列思路
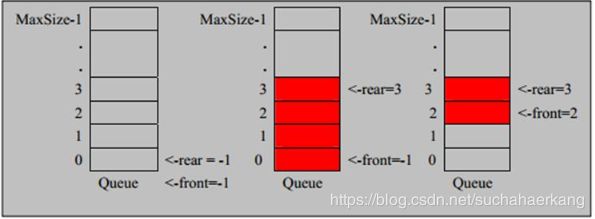
- 队列本身是有序列表,若使用数组的结构来存储队列的数据,则队列数组的声明如下图,其中maxSize是该队列的最大容量。
- 因为队列的输出、输入是分别从前后端来处理,因此需要两个变量front及rear分别记录队列前后端的下标,front会随着数据输出而改变,而rear则是随着数据输入而改变,如图所示
- 当我们将数据存入队列时称为”addQueue”,addQueue的处理需要有两个步骤:思路分析
- 将尾指针往后移:rear+1,当front==rear【空】
- 若尾指针rear小于队列的最大下标maxSize-1,则将数据存入rear所指的数组元素中,否则无法存入数据。rear==maxSize-1[队列满]
- 代码实现
package com.sukang.queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @description: 数组模拟队列
* @author: sukang
* @date: 2019-12-27 14:30
*/
public class ArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个队列
ArrayQueue queue = new ArrayQueue(3);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
char key = ' ';
boolean loop = true;
while (loop) {
System.out.println("e(exit):退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add):添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get):从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("f(first):查看队列头的数据");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (key) {
case 'a':
System.out.println("请数据一个数字");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g':
try {
int data = queue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("从队列中取出的值为:%d\n", data);
} catch ( Exception e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
case 'f':
try {
int data = queue.getFirst();
System.out.printf("查看队列头的数据为:%d\n", data);
} catch ( Exception e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
case 'e':
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("退出程序!");
}
}
//数组队列
class ArrayQueue {
//队列的容量
private int maxSize;
//队列头
private int front;
//队列尾
private int tail;
//声明一个数组充当队列
private int[] arr = {};
//构造函数
public ArrayQueue(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.front = -1;
this.tail = -1;
this.arr = new int[maxSize];
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
//如果头尾相等那么队列为空
if(front == tail){
return true;
}
return false;
}
//判断队列是否满了
public boolean isFull(){
if(tail == maxSize - 1){
return true;
}
return false;
}
//队列中添加数据
public void addQueue(int queue){
if(isFull()){
System.out.println("队列已经满了...");
return;
}
tail++;
arr[tail] = queue;
}
//从队列中取数据
public int getQueue(){
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,没有数据可取");
}
front ++;
return arr[front];
}
//展示队列的第一个数据,不是从队列中取出
public int getFirst(){
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,没有数据可取");
}
return arr[front+1];
}
}
- 问题分析并优化
- 目前数组使用一次就不能用,没有达到复用的效果
- 将这个数组使用算法,改进成一个环形的队列 取模:%
4、数组模拟环形队列
对前面的数组模拟队列的优化,充分利用数组.因此将数组看做是一个环形的。(通过取模的方式来实现即可)
- 分析说明:
- 代码实现
package com.sukang.queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @description: 环形数据队列
* @author: sukang
* @date: 2019-12-27 16:02
*/
public class CircleArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个队列
CircleArrayQueue queue = new CircleArrayQueue(3);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
char key = ' ';
boolean loop = true;
while (loop) {
System.out.println("s(show):显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit):退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add):添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get):从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head):查看队列头的数据");
System.out.println("z(size):查看队列有效数字个数");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (key) {
case 's':
queue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("请数据一个数字");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g':
try {
int data = queue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("从队列中取出的值为:%d\n", data);
} catch ( Exception e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
case 'h':
try {
int data = queue.showHead();
System.out.printf("查看队列头的数据为:%d\n", data);
} catch ( Exception e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
case 'z':
int size = queue.size();
System.out.printf("查看队列有效数字个数为:%d\n", size);
break;
case 'e':
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("退出程序!");
}
}
//环形数组队列
class CircleArrayQueue{
private int maxSize; //数据最大空间
private int front = 0; //数组头指向的位置,默认为数组的第一个位置
/* 在学习循环队列这一个知识点时候,我遇到了一些问题所以这也算是我的一些个人心得吧,
我在学习这个知识点时候,喜欢生动形象的来解释原理,首先循环队列,我采用数组来存储,
举个列子a[5]吧,一共有5个存储空间,其次,再来说一下循环队列有那些特征,首先循环循环,
那必定是一个环,转呀转的,就当成一个操场一样,大家可以脑海里想象一下,
其次,还有两个指针变量rear和front,刚开始,他俩都是在a[0]这个位置,因为现在没有元素,
好了,此时突然有一个元素进来了,rear这变量就需要挪一下位置,移动到下一个空的位置,
以方便,下次插入新的元素时候,有空的地方给新元素,好如此进行,终于rear到了a[4]这个位置,
a[4]这个位置首先肯定是空的,因为rear就是为了告诉系统我有空位置,有新的元素要插入,
你就到我这儿来吧,系统一听好的,你空啦,那我来了,那rear又要挪动位置给新的元素,
他得去下一个空的位置,哎,rear突然发现,哦,你是循环队列啊,
那下一个不就又回到了a【0】这个位置吗,可是啊,里面不是有元素了吗,
rear一想我的任务是去找空的位置给新元素啊,这下咋办,凉凉了,哎,
我真后悔应该在a[4]这个位置的时候就提前告诉系统,你别放新元素进来了,已经满了,放不下了,
好了,那我下次就这么做,当我在最后一个空的位置时候,我就告诉系统,
所以这也就是为什么循环队列存的元素个数总是比他占用的存储空间少一个的原因。*/
private int rear = 0; //数组尾指向的位置,默认为数组最后一个位置的后一位置,因为希望空出一个空间作为约定
int[] arr = {}; //声明一个数组来模拟队列
public CircleArrayQueue(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.arr = new int[maxSize];
}
/**
* @description: 判断数组队列是否为空
* @param
* @return: boolean
* @author: sukang
* @date: 2019/12/27 14:37
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){
return front == rear;
}
/**
* @description: 判断数据队列是否塞满
* @param
* @return: boolean
* @author: sukang
* @date: 2019/12/27 14:38
*/
public boolean isFull(){
return (rear + 1) % maxSize == front;
}
/**
* @description: 往队列里面添加一个数据
* @param data
* @return: void
* @author: sukang
* @date: 2019/12/27 14:39
*/
public void addQueue(int data){
if(isFull()){
System.out.println("队列已经满,无法进行添加");
return;
}
arr[rear] = data;
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
System.out.println("添加成功!");
}
/**
* @description: 从队列中取出一个数据
* @param
* @return: void
* @author: sukang
* @date: 2019/12/27 14:44
*/
public int getQueue(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空!无法取数据");
}
int value = arr[front];
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
return value;
}
/**
* @description: 遍历队列
* @param
* @return: void
* @author: sukang
* @date: 2019/12/27 14:47
*/
public void showQueue(){
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列为空!无法遍历");
return;
}
for (int i = front; i < front + size(); i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d] = %d\n", i % maxSize, arr[i % maxSize]);
}
}
/**
* @description: 显示头结点
* @param
* @return: void
* @author: sukang
* @date: 2019/12/27 14:51
*/
public int showHead(){
if(isEmpty()){
new RuntimeException("队列为空!没有数据");
}
return arr[front];
}
/**
* @description: 当前队列有效数据个数
* @param
* @return: int
* @author: sukang
* @date: 2019/12/27 16:14
*/
public int size(){
return (rear - front + maxSize) % maxSize;
}
}