关于外部表----external_table_clause
官方文档地址:http://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/server.102/b14200/statements_7002.htm#i2159541
(external_data_properties::=)
external_data_properties::=
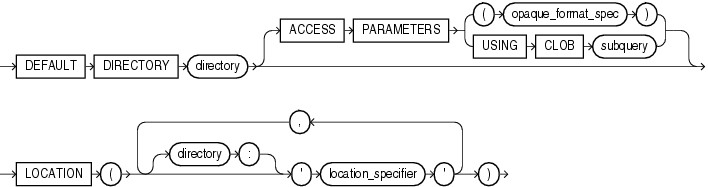
Description of the illustrationexternal_data_properties.gif
(opaque_format_spec: SeeOracleDatabase Utilities for information on how to specifyvalues for the opaque_format_spec.)--从语法图可以看出,ACCESSPARAMETERS子句可以省略(中间一根长线),直接到LOCATION。
例子:
01 CREATE TABLE INVOICES_EXTERNAL
02 ( INVOICE_ID CHAR(3),
03 INVOICE_DATE CHAR(9),
04 ACCOUNT_NUMBER CHAR(13)
05 )
06 ORGANIZATION EXTERNAL
07 (TYPE ORACLE_LOADER
08 DEFAULT DIRECTORY INVOICE_FILES
09 ACCESS PARAMETERS
10 (RECORDS DELIMITED BY NEWLINE
11 SKIP 2
12 FIELDS (INVOICE_ID CHAR(3),
13 INVOICE_DATE CHAR(9),
14 ACCOUNT_NUMBER CHAR(13))
15 )
16 LOCATION ('INVOICE_DATA.TXT')
17 );
57.
external_table_clause
Use the external_table_clause to createan external table, which is a read-only table whose metadata isstored in the database but whose data in stored outside thedatabase. Among other capabilities, external tables let you querydata without first loading it into the database.
See Also:
OracleData Warehousing Guide, OracleDatabase Administrator's Guide, and Oracle Database Utilities for information on the usesfor external tablesBecause external tables have no data in the database, you definethem with a small subset of the clauses normally available whencreating tables.
-
Within the
relational_propertiesclause,you can specify onlycolumnanddatatype. -
Within the
physical_properties_clause, youcan specify only the organization of the table(ORGANIZATIONEXTERNALexternal_table_clause). -
Within the
table_propertiesclause, you canspecify only theparallel_clause. Theparallel_clauselets youparallelize subsequent queries on the external data and subsequentoperations that populate the external table. -
You can populate the external table at create time by using the
ASsubqueryclause.
No other clauses are permitted in the same CREATETABLE statement.
See Also:
-
"External Table Example"
-
ALTER TABLE... "PROJECT COLUMN Clause" for information on the effect ofchanging the default property of the column projection
Restrictions onExternal Tables Externaltables are subject to the following restrictions:
-
An external table cannot be a temporary table.
-
You cannot specify constraints on an external table.
-
An external table cannot have object type, varray, or
LONGcolumns. However, you can populate LOB columns ofan external table with varray orLONGdata from aninternal database table.
TYPE TYPEaccess_driver_type indicates theaccess driver of the external table. The access driveris the API that interprets the external data for the database.Oracle Database provides two access drivers:ORACLE_LOADER and ORACLE_DATAPUMP.If you do not specify TYPE, thenthe database uses ORACLE_LOADER as the default accessdriver. You must specify the ORACLE_DATAPUMPaccess driver if you specify the ASsubqueryclause to unload data from one Oracle Database and reload it intothe same or a different Oracle Database.
See Also:
Oracle Database Utilities for information about theORACLE_LOADER and
ORACLE_DATAPUMP access drivers
DEFAULTDIRECTORY DEFAULTDIRECTORY lets you specify a default directory objectcorresponding to a directory on the file system where the externaldata sources may reside. The default directory can also be used bythe access driver to store auxiliary files such as error logs.
ACCESSPARAMETERS The optional ACCESS PARAMETERSclause lets you assign values to the parameters of the specificaccess driver for this external table.
-
The
opaque_format_speclets you listthe parameters and their values. Please refer to OracleDatabase Utilities for information on how to specifyvalues for theopaque_format_spec.Field names specified in the
opaque_format_specmust matchcolumns in the table definition. Oracle Database ignores any fieldin theopaque_format_specthat is notmatched by a column in the table definition. -
USINGCLOBsubquerylets you derive theparameters and their values through a subquery. The subquery cannotcontain any set operators or anORDERBYclause. It must return one row containing a single item of datatypeCLOB.
Whether you specify the parameters in an opaque_format_spec or derivethem using a subquery, the database does not interpret anything inthis clause. It is up to the access driver to interpret thisinformation in the context of the external data.
LOCATION TheLOCATION clause lets you specify one or more externaldata sources. Usually the location_specifier is a file,but it need not be. Oracle Database does not interpret this clause.It is up to the access driver to interpret this information in thecontext of the external data. You cannot use wildcards in thelocation_specifier to specifymultiple files.
REJECTLIMIT The REJECTLIMIT clause lets you specify how many conversionerrors can occur during a query of the external data before anOracle Database error is returned and the query is aborted. Thedefault value is 0.
CLUSTER Clause
The CLUSTER clause indicates that the table is tobe part of cluster. The columns listed inthis clause are the table columns that correspond to the clustercolumns. Generally, the cluster columns of a table are the columnor columns that make up its primary key or a portion of its primarykey. Please refer to CREATE CLUSTER for more information.
Specify one column from the table for each column in the clusterkey. The columns are matched by position, not by name.
A cluster table uses the space allocation of the cluster.Therefore, do not use the PCTFREE,PCTUSED, or INITRANS parameters, theTABLESPACE clause, or the storage_clause with theCLUSTER clause.
Restrictions onCluster Tables Cluster tables are subjectto the following restrictions:
-
Object tables and tables containing LOB columns cannot be partof a cluster.
-
You cannot specify
CLUSTERwith eitherROWDEPENDENCIESorNOROWDEPENDENCIESunless the cluster has been created with the sameROWDEPENDENCIESorNOROWDEPENDENCIESsetting.