文章将会被同步至微信公众号:Android部落格
概述
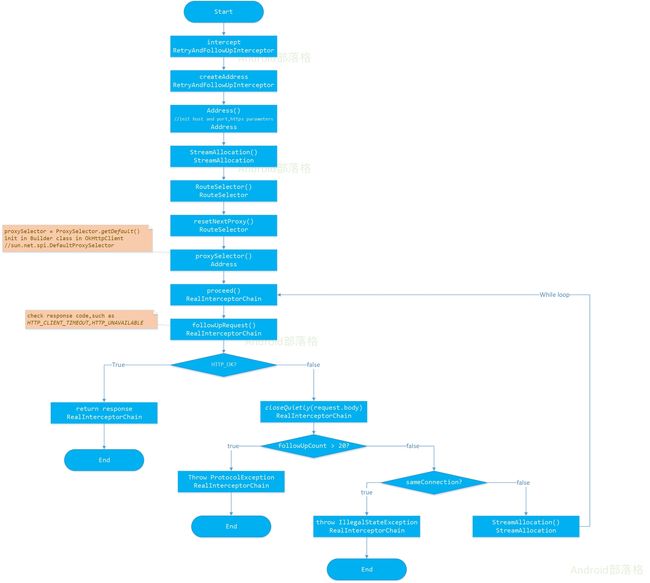
失败重试以及重定向
流程图如下:
(1)StreamAllocation
在RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor的intercept方法中初始化了一个StreamAllocation对象。
StreamAllocation streamAllocation = new StreamAllocation(client.connectionPool(),
createAddress(request.url()), call, eventListener, callStackTrace);
createAddress
方法创建了Address对象,如下:
return new Address(url.host(), url.port(), client.dns(), client.socketFactory(),
sslSocketFactory, hostnameVerifier, certificatePinner, client.proxyAuthenticator(),
client.proxy(), client.protocols(), client.connectionSpecs(), client.proxySelector());
其中proxySelector的默认初始化在OKHttpClient的内部类Builder中:
proxySelector = ProxySelector.getDefault();
public static ProxySelector getDefault() {
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.GET_PROXYSELECTOR_PERMISSION);
}
return theProxySelector;
}
StreamAllocation构造函数
public StreamAllocation(ConnectionPool connectionPool, Address address, Call call,
EventListener eventListener, Object callStackTrace) {
this.connectionPool = connectionPool;
this.address = address;
this.call = call;
this.eventListener = eventListener;
this.routeSelector = new RouteSelector(address, routeDatabase(), call, eventListener);
this.callStackTrace = callStackTrace;
}
可以看到最终路由选择是在RouteSelector类中,
/** Prepares the proxy servers to try. */
private void resetNextProxy(HttpUrl url, Proxy proxy) {
if (proxy != null) {
// If the user specifies a proxy, try that and only that.
proxies = Collections.singletonList(proxy);
} else {
// Try each of the ProxySelector choices until one connection succeeds.
List proxiesOrNull = address.proxySelector().select(url.uri());
proxies = proxiesOrNull != null && !proxiesOrNull.isEmpty()
? Util.immutableList(proxiesOrNull)
: Util.immutableList(Proxy.NO_PROXY);
}
nextProxyIndex = 0;
}
默认是系统的路由策略,也可以自己继承ProxySelector虚拟类自定义路由策略。
(2) while循环
在while循环中不断的判断其余拦截器的返回,如果请求失败则尝试重试连接。
针对请求返回的Response在followUpRequest方法中重新构建Request并返回请求。
重点看看followUpRequest方法,在该方法中差异化处理状态码Response.code,并根据不同的code对请求Header做了处理。Http状态码列表如下(https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/HTTP/Status/):
| 状态码 | 状态码英文名称 | 中文描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | Continue | 继续。客户端应继续其请求 |
| 101 | Switching Protocols | 切换协议。服务器根据客户端的请求切换协议。只能切换到更高级的协议,例如,切换到HTTP的新版本协议 |
| 200 | OK | 请求成功。一般用于GET与POST请求 |
| 201 | Created | 已创建。成功请求并创建了新的资源 |
| 202 | Accepted | 已接受。已经接受请求,但未处理完成 |
| 203 | Non-Authoritative Information | 非授权信息。请求成功。但返回的meta信息不在原始的服务器,而是一个副本 |
| 204 | No Content | 无内容。服务器成功处理,但未返回内容。在未更新网页的情况下,可确保浏览器继续显示当前文档 |
| 205 | Reset Content | 重置内容。服务器处理成功,用户终端(例如:浏览器)应重置文档视图。可通过此返回码清除浏览器的表单域 |
| 206 | Partial Content | 部分内容。服务器成功处理了部分GET请求 |
| 300 | Multiple Choices | 多种选择。请求的资源可包括多个位置,相应可返回一个资源特征与地址的列表用于用户终端(例如:浏览器)选择 |
| 301 | Moved Permanently | 永久移动。请求的资源已被永久的移动到新URI,返回信息会包括新的URI,浏览器会自动定向到新URI。今后任何新的请求都应使用新的URI代替 |
| 302 | Found | 临时移动。与301类似。但资源只是临时被移动。客户端应继续使用原有URI |
| 303 | See Other | 查看其它地址。与301类似。使用GET和POST请求查看 |
| 304 | Not Modified | 未修改。所请求的资源未修改,服务器返回此状态码时,不会返回任何资源。客户端通常会缓存访问过的资源,通过提供一个头信息指出客户端希望只返回在指定日期之后修改的资源 |
| 305 | Use Proxy | 使用代理。所请求的资源必须通过代理访问 |
| 306 | Unused | 已经被废弃的HTTP状态码 |
| 307 | Temporary Redirect | 临时重定向。与302类似。使用GET请求重定向 |
| 308 | Permanent Redirect | 永久重定向)是表示重定向的响应状态码,说明请求的资源已经被永久的移动到了由 Location 首部指定的 URL 上。浏览器会进行重定向,同时搜索引擎也会更新其链接 |
| 400 | Bad Request | 客户端请求的语法错误,服务器无法理解 |
| 401 | Unauthorized | 请求要求用户的身份认证 |
| 402 | Payment Required | 保留,将来使用 |
| 403 | Forbidden | 服务器理解请求客户端的请求,但是拒绝执行此请求 |
| 404 | Not Found | 服务器无法根据客户端的请求找到资源(网页)。通过此代码,网站设计人员可设置"您所请求的资源无法找到"的个性页面 |
| 405 | Method Not Allowed | 客户端请求中的方法被禁止 |
| 406 | Not Acceptable | 服务器无法根据客户端请求的内容特性完成请求 |
| 407 | Proxy Authentication Required | 请求要求代理的身份认证,与401类似,但请求者应当使用代理进行授权 |
| 408 | Request Time-out | 服务器等待客户端发送的请求时间过长,超时 |
| 409 | Conflict | 服务器完成客户端的PUT请求是可能返回此代码,服务器处理请求时发生了冲突 |
| 410 | Gone | 客户端请求的资源已经不存在。410不同于404,如果资源以前有现在被永久删除了可使用410代码,网站设计人员可通过301代码指定资源的新位置 |
| 411 | Length Required | 服务器无法处理客户端发送的不带Content-Length的请求信息 |
| 412 | Precondition Failed | 客户端请求信息的先决条件错误 |
| 413 | Request Entity Too Large | 由于请求的实体过大,服务器无法处理,因此拒绝请求。为防止客户端的连续请求,服务器可能会关闭连接。如果只是服务器暂时无法处理,则会包含一个Retry-After的响应信息 |
| 414 | Request-URI Too Large | 请求的URI过长(URI通常为网址),服务器无法处理 |
| 415 | Unsupported Media Type | 服务器无法处理请求附带的媒体格式 |
| 416 | Requested range not satisfiable | 客户端请求的范围无效 |
| 417 | Expectation Failed | 服务器无法满足Expect的请求头信息 |
| 500 | Internal Server Error | 服务器内部错误,无法完成请求 |
| 501 | Not Implemented | 服务器不支持请求的功能,无法完成请求 |
| 502 | Bad Gateway | 作为网关或者代理工作的服务器尝试执行请求时,从远程服务器接收到了一个无效的响应 |
| 503 | Service Unavailable | 由于超载或系统维护,服务器暂时的无法处理客户端的请求。延时的长度可包含在服务器的Retry-After头信息中 |
| 504 | Gateway Time-out | 充当网关或代理的服务器,未及时从远端服务器获取请求 |
| 505 | HTTP Version not supported | 服务器不支持请求的HTTP协议的版本,无法完成处理 |
此处处理的状态码有:
- HTTP_PROXY_AUTH(407)需要代理身份认证,在请求之初如果不做认证处理的话,默认为
Authenticator.NONE,如果要做认证处理,需要实现Authenticator接口,并实现authenticate方法,并返回携带认证信息的Request。
client.proxyAuthenticator().authenticate(route, userResponse)
public interface Authenticator {
/** An authenticator that knows no credentials and makes no attempt to authenticate. */
Authenticator NONE = new Authenticator() {
@Override public Request authenticate(Route route, Response response) {
return null;
}
};
/**
* Returns a request that includes a credential to satisfy an authentication challenge in {@code
* response}. Returns null if the challenge cannot be satisfied.
*/
@Nullable Request authenticate(Route route, Response response) throws IOException;
}
- HTTP_PROXY_AUTH(401) 要求用户身份认证,跟407不一样的是,这个状态码不是代理身份认证,处理方式是:
client.authenticator().authenticate(route, userResponse)
- HTTP_PERM_REDIRECT or HTTP_TEMP_REDIRECT(308/307)
永久重定向或临时重定向,
if (!method.equals("GET") && !method.equals("HEAD")) {
return null;
}
对于非GET和HEAD请求方法,不能再去修改请求方法做重定向。307 或308状态码可以确保请求方法和消息主体不会发生变化。
- HTTP_MULT_CHOICE or HTTP_MOVED_PERM or HTTP_MOVED_TEMP or HTTP_SEE_OTHER (300/301/302/303)
请求的资源被移到了新的URI,需要用新的URI重新发起请求。按照源码的思路,重新获取Response的request,对于可以携带request body的方法,则填写body,否则置空。同时如果不携带body的请求,将请求头的以下三个信息去掉然后重新返回组织过的Request:
// Most redirects don't include a request body.
Request.Builder requestBuilder = userResponse.request().newBuilder();
if (HttpMethod.permitsRequestBody(method)) {
final boolean maintainBody = HttpMethod.redirectsWithBody(method);
if (HttpMethod.redirectsToGet(method)) {
requestBuilder.method("GET", null);
} else {
RequestBody requestBody = maintainBody ? userResponse.request().body() : null;
requestBuilder.method(method, requestBody);
}
if (!maintainBody) {
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Transfer-Encoding");
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Content-Length");
requestBuilder.removeHeader("Content-Type");
}
}
- HTTP_CLIENT_TIMEOUT(408)
服务器等待客户端发送的请求时间过长,导致超时,此时如果Response中的头部Retry-After返回的重试时间大于0,则不会重试直接返回null,否则返回Response.request重试。
if (retryAfter(userResponse, 0) > 0) {
return null;
}
private int retryAfter(Response userResponse, int defaultDelay) {
String header = userResponse.header("Retry-After");
if (header == null) {
return defaultDelay;
}
// https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.1.3
// currently ignores a HTTP-date, and assumes any non int 0 is a delay
if (header.matches("\\d+")) {
return Integer.valueOf(header);
}
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
- HTTP_UNAVAILABLE(503)503 Service Unavailable 是一种HTTP协议的服务器端错误状态代码,它表示服务器尚未处于可以接受请求的状态。通常造成这种情况的原因是由于服务器停机维护或者已超载。注意在发送该响应的时候,应该同时发送一个对用户友好的页面来解释问题发生的原因。该种响应应该用于临时状况下,与之同时,在可行的情况下,应该在 Retry-After 首部字段中包含服务恢复的预期时间。缓存相关的首部在与该响应一同发送时应该小心使用,因为503状态码通常应用于临时状况下,而此类响应一般不应该进行缓存。
按照源码的意思,除非Response的Retry-After值为0,否则不会返回Request重试。
if (retryAfter(userResponse, Integer.MAX_VALUE) == 0) {
// specifically received an instruction to retry without delay
return userResponse.request();
}
(3)开始重试
对返回码处理完毕之后,有一些情况会重新构造Request方法返回用于重试,并且有20次的限制:
if (++followUpCount > MAX_FOLLOW_UPS) {
streamAllocation.release();
throw new ProtocolException("Too many follow-up requests: " + followUpCount);
}
同时,对于返回的Request与之前的相比,不相同的话,会重新构造StreamAllocation并请求:
if (!sameConnection(response, followUp.url())) {
streamAllocation.release();
streamAllocation = new StreamAllocation(client.connectionPool(),
createAddress(followUp.url()), call, eventListener, callStackTrace);
this.streamAllocation = streamAllocation;
} else if (streamAllocation.codec() != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Closing the body of " + response
+ " didn't close its backing stream. Bad interceptor?");
}
对于是否是同一个连接的判断依据是sameConnection方法:
private boolean sameConnection(Response response, HttpUrl followUp) {
HttpUrl url = response.request().url();
return url.host().equals(followUp.host())
&& url.port() == followUp.port()
&& url.scheme().equals(followUp.scheme());
}
判断依据是host,port和scheme(http/https).
最后利用重新创建的Request开始新一轮的连接,如果构建用于重试的Request为null的话,直接返回Response。
微信公众号: