在前一篇文章 HotSpot的二分模型 中已经讲过,HotSpot采用了OOP-Klass模型描述Java的类和对象。Klass模型采用Klass类及相关子类来表示具体的Java类,可以理解这些类为Java类在C++ 中的对等体。一般 JVM 在加载 Class 文件时,会在方法区创建 Klass ,表示类的元数据,包括常量池、字段、方法等。
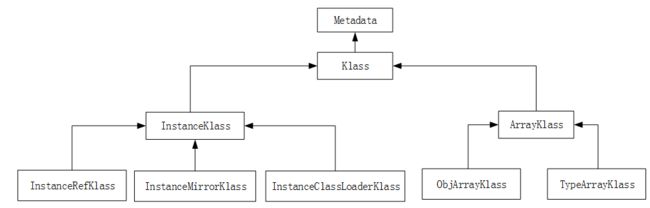
相关类的继承体系如下图所示。
Metadata是元数据类的基础类型,除了Klass会直接继承外,表示方法的Method与表示常量池的ConstantPool也会继承,这里只讨论Klass继承体系中涉及到的相关类。
整个Klass模型中涉及到的类主要提供了2个功能:
(1)提供C++层面的Java类(包括Java类和Java数组)表示
(2)方法分派
这一篇文章重点介绍一下Klass这个基础类型。
一个Klass对象(注意是Klass对象表示Java类的元数据,所以不同的Java类就用不同的Klass对象)代表一个Java类的元数据(相当于java.lang.Class对象)。所以Klass中要有描述Java类中常量池、字段、方法的能力,也就是能保存这些信息,同时还能提供一些方法供HotSpot的开发者操作这些信息。
Klass类及重要属性的定义如下:
class Klass : public Metadata {
...
protected:
// note: put frequently-used fields together at start of klass structure
// for better cache behavior (may not make much of a difference but sure won't hurt)
enum { _primary_super_limit = 8 };
// The "layout helper" is a combined descriptor of object layout.
// For klasses which are neither instance nor array, the value is zero.
//
// For instances, layout helper is a positive number, the instance size.
// This size is already passed through align_object_size and scaled to bytes.
// The low order bit is set if instances of this class cannot be
// allocated using the fastpath.
//
// For arrays, layout helper is a negative number, containing four
// distinct bytes, as follows:
// MSB:[tag, hsz, ebt, log2(esz)]:LSB
// where:
// tag is 0x80 if the elements are oops, 0xC0 if non-oops
// hsz is array header size in bytes (i.e., offset of first element)
// ebt is the BasicType of the elements
// esz is the element size in bytes
// This packed word is arranged so as to be quickly unpacked by the
// various fast paths that use the various subfields.
//
// The esz bits can be used directly by a SLL instruction, without masking.
//
// Note that the array-kind tag looks like 0x00 for instance klasses,
// since their length in bytes is always less than 24Mb.
//
// Final note: This comes first, immediately after C++ vtable,
// because it is frequently queried.
jint _layout_helper;
// The fields _super_check_offset, _secondary_super_cache, _secondary_supers
// and _primary_supers all help make fast subtype checks. See big discussion
// in doc/server_compiler/checktype.txt
//
// Where to look to observe a supertype (it is &_secondary_super_cache for
// secondary supers, else is &_primary_supers[depth()].
juint _super_check_offset;
// Class name. Instance classes: java/lang/String, etc. Array classes: [I,
// [Ljava/lang/String;, etc. Set to zero for all other kinds of classes.
Symbol* _name;
// Cache of last observed secondary supertype
Klass* _secondary_super_cache;
// Array of all secondary supertypes
Array* _secondary_supers;
// Ordered list of all primary supertypes
Klass* _primary_supers[_primary_super_limit];
// java/lang/Class instance mirroring this class
oop _java_mirror;
// Superclass
Klass* _super;
// First subclass (NULL if none); _subklass->next_sibling() is next one
Klass* _subklass;
// Sibling link (or NULL); links all subklasses of a klass
Klass* _next_sibling;
// All klasses loaded by a class loader are chained through these links
Klass* _next_link;
// The VM's representation of the ClassLoader used to load this class.
// Provide access the corresponding instance java.lang.ClassLoader.
ClassLoaderData* _class_loader_data;
AccessFlags _access_flags; // Access flags. The class/interface distinction is stored here.
markOop _prototype_header; // Used when biased locking is both enabled and disabled for this type
...
}
下表对各个属性进行了简单的介绍。
| 字段名 | 作用 |
| _layout_helper | 对象布局的综合描述符。如果不是InstanceKlass或ArrayKlass,值为0。如果是InstantceKlass或 ArrayKlass时,这个值是个组合数字。 对InstanceKlass而言,组合数字中包含有表示对象的以字节为单位的内存占用大小,也就是说 InstanceKlass表示Java类,由这个Java类创建的对象所需要的大小。 对ArrayKlass而言,该值是一个组合数字,包含4部分,具体怎么组合和解析由子类实现:
|
| _name | 类名,如java/lang/String,[Ljava/lang/String |
| _primary_supers | Klass指针数组,大小固定为8。_primary_supers代表了这个类的父类。例如IOException,是Exception的子类, 而Exception又是Throwable的子类。所以IOException的 _primary_supers是这样的: [Throwable, Exception, IOException]。如果继承链过长,也就是当前类加上继承的类多于8个(默认值,可通过命令更改)时, 会将多出来的类存储到secondary_supers数组中。 |
| _super_check_offset | 快速查找supertype的一个偏移量,这个偏移量是相对于Klass对象起始地址的偏移量。如果当前类是IOException, 那么这个属性就指向_primary_supers数组中存储IOException的位置。当存储的类多于8个时,值与secondary_super_cache 相等。 |
| _secondary_supers | Klass指针数组,一般存储类实现的接口,偶尔还会存储类 |
| _secondary_super_cache | Klass指针,保存上一次查询父类的结果 |
| _java_mirror | oopDesc指针,此类对应的java/lang/Class对象,可以据此访问类的静态属性 |
| _super | Klass指针,父类 |
| _subklass | Klass指针,子类 |
| _next_sibling | Klass指针,该类的下一个子类,也就是通过_subklass->next_sibling()来获取_subklass的兄弟子类 |
| _next_link | Klass指针,ClassLoader加载的下一个Klass |
| _class_loader_data | ClassLoaderData指针,加载该类的ClassLoader |
| _access_flags | 获取类的修饰符,如private、final、static、abstract 、native等 |
| _prototype_header | 在锁的实现过程中非常重要,后续在介绍锁时会介绍 |
可以看到,能够通过Klass类中的相关属性保存Java类定义的一些信息,如_name保存Java类的名称、_super保存Java类实现的类型等。Klass类是Klass模型中定义的类的基类,所以只保存了Java类的一些必要信息,其它如常量池、方法、字段等会通过具体子类的属性来保存。
类的属性比较多,我们在后面解释类的过程中可以看到对相关属性的赋值操作。下面来看一个对属性赋值相对复杂一点的方法,如initialize_supers()方法,实现如下:
源代码位置:hotspot/src/share/vm/oops/klass.cpp
void Klass::initialize_supers(Klass* k, TRAPS) {
// 当前类的父类k可能为NULL,例如Object的父类为NULL
if (k == NULL) {
set_super(NULL);
_primary_supers[0] = this;
} else if (k != super() || k == SystemDictionary::Object_klass()) {
set_super(k); // 设置Klass的_super属性
Klass* sup = k;
int sup_depth = sup->super_depth();
juint my_depth = MIN2(sup_depth + 1, (int)primary_super_limit()); // primary_super_limit()方法得到的值一般默认为8
// 当父类的的继承链长度大于等于primary_super_limit()时,当前的深度只能是primary_super_limit(),也就是8,因为_primary_supers中只存储8个类
if (!can_be_primary_super_slow()){
my_depth = primary_super_limit(); // 8
}
for (juint i = 0; i < my_depth; i++) { // my_depth默认的值为8
_primary_supers[i] = sup->_primary_supers[i];
}
Klass* *super_check_cell;
if (my_depth < primary_super_limit()) { // primary_super_limit()的默认为8
_primary_supers[my_depth] = this;
super_check_cell = &_primary_supers[my_depth];
} else {
// Overflow of the primary_supers array forces me to be secondary.
super_check_cell = &_secondary_super_cache;
}
// 通过_super_check_offset这个偏移量可以快速定义到当前在_primary_supers中的位置
juint _super_check_offset = (address)super_check_cell - (address) this;
set_super_check_offset( _super_check_offset ); // 设置Klass中的_super_check_offset属性
}
// 第2部分代码在下面
}
在设置当前类的父类时通常都会调用initialize_supers方法,同时也会设置_primary_supers、super_check_offset,如果继承链过长,还有可能设置secondary_supers、secondary_super_cache等值。这此属性中存储继承链中涉及到的类以方便快速的进行类关系之间的判断,例如父子关系的判断。
方法的第2部分代码实现如下:
if (secondary_supers() == NULL) {
KlassHandle this_kh (THREAD, this);
// Now compute the list of secondary supertypes.
// Secondaries can occasionally be on the super chain,
// if the inline "_primary_supers" array overflows.
int extras = 0;
Klass* p;
for (p = super();
// 当p不为NULL并且p已经存储在了_secondary_supers数组中时,条件为true
// 也就是当前类的父类多于8个,将多出来的存储到了_secondary_supers数组中了
!(p == NULL || p->can_be_primary_super());
p = p->super()) {
++extras;
}
// 计算secondaries需要的大小,因为secondaries数组中还需要存储当前类的所有实现接口(包括直接和间接实现的接口)
// Compute the "real" non-extra secondaries.
GrowableArray* secondaries = compute_secondary_supers(extras);
if (secondaries == NULL) { // extras为0时直接返回,不需要额外的处理
// secondary_supers set by compute_secondary_supers
return;
}
GrowableArray* primaries = new GrowableArray(extras);
for ( p = this_kh->super();
!(p == NULL || p->can_be_primary_super());
p = p->super()
){
primaries->push(p);
}
// Combine the two arrays into a metadata object to pack the array.
// The primaries are added in the reverse order, then the secondaries.
int new_length = primaries->length() + secondaries->length();
Array* s2 = MetadataFactory::new_array(class_loader_data(), new_length, CHECK);
int fill_p = primaries->length();
for (int j = 0; j < fill_p; j++) {
s2->at_put(j, primaries->pop()); // add primaries in reverse order.也就是父类永远在数组前,子类永远在数组后
}
for( int j = 0; j < secondaries->length(); j++ ) {
s2->at_put(j+fill_p, secondaries->at(j)); // add secondaries on the end.
}
this_kh->set_secondary_supers(s2); // 设置_secondary_supers属性
}
可以看到,会将父亲继承链中多于8个的父类存储到secondary_supers数组中,不过因为继承链一般都不会多于8个,所以设置了默认值为8。
下面举个例子,看一下是如何应用这几个属性的,例如is_subtype_of()方法,实现如下:
// subtype check: true if is_subclass_of, or if k is interface and receiver implements it
bool is_subtype_of(Klass* k) const { // 判断当前类是否为k的子类
juint off = k->super_check_offset();
Klass* sup = *(Klass**)( (address)this + off );
const juint secondary_offset = in_bytes(secondary_super_cache_offset());
if (sup == k) {
return true;
} else if (off != secondary_offset) { // ??没弄明白这个逻辑,有大神可以给指点下
return false;
} else {
return search_secondary_supers(k);
}
}
当通过_super_check_offset获取到的类与k相同时,那么k存在于当前类的继承链上,肯定有父子关系。
如果k存在于_primary_supers数组中,那么通过_super_check_offset就可快速判断,如果k存在于_secondary_supers中,那么需要调用search_secondary_supers()来判断。
调用的search_secondary_supers()方法的实现如下:
bool Klass::search_secondary_supers(Klass* k) const {
// Put some extra logic here out-of-line, before the search proper.
// This cuts down the size of the inline method.
// This is necessary, since I am never in my own secondary_super list.
if (this == k){
return true;
}
// Scan the array-of-objects for a match
int cnt = secondary_supers()->length();
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
if (secondary_supers()->at(i) == k) {
((Klass*)this)->set_secondary_super_cache(k); // 设置_secondary_super_cache属性,保存这次查询的结果
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
可以看到,属性_secondary_super_cache保存了这一次父类查询的结果。查询的逻辑很简单,遍历_secondary_supers数组中的值并比较即可。
另外还能调用Klass::append_to_sibling_list()函数设置_next_sibling与_subklass的值,方法的实现如下:
void Klass::append_to_sibling_list() {
// add ourselves to superklass' subklass list
InstanceKlass* super = superklass(); // 获取到_super属性的值
if (super == NULL)
return; // special case: class Object
Klass* prev_first_subklass = super->subklass_oop(); // 获取_subklass属性的值
if (prev_first_subklass != NULL) {
// set our sibling to be the superklass' previous first subklass
set_next_sibling(prev_first_subklass); // 设置_next_sibling属性的值
}
// make ourselves the superklass' first subklass
super->set_subklass(this); // 设置_subklass属性的值
}
方法的实现逻辑很简单,这里不过多介绍。
还有对_layout_helper属性的设置相对复杂,在讲解InstanceKlass或ArrayKlass时介绍。
相关文章的链接如下:
1、在Ubuntu 16.04上编译OpenJDK8的源代码
2、调试HotSpot源代码
3、HotSpot项目结构
4、HotSpot的启动过程
5、HotSpot二分模型 (1)
6、HotSpot的类模型(2)
关注个人博客www.classloading.com或公众号,有HotSpot源码剖析系列文章!
![]()