二分类可视化分析目录
- 一、简述算法线性LDA、k-means和SVM算法
- 二、线性判别分析LDA
- 三、k-means聚类分析
- 四、SVM(支持向量机)算法
- 五、SVM算法的优缺点
一、简述算法线性LDA、k-means和SVM算法
| 算法 |
基本思想 |
| LDA |
LDA 是一种可作为特征抽取的技术,其目标是向最大化类间差异,最小化类内差异的方向投影,以利于分类等任务即将不同类的样本有效的分开。LDA 可以提高数据分析过程中的计算效率,对于未能正则化的模型,可以降低维度灾难带来的过拟合 |
| k-means |
在K-means算法中K是事先给定的,这个K值的选定是非常难以估计的;在K-means算法中,首先需要根据初始聚类中心来确定一个初始划分,然后对初始划分进行优化;从K-means算法框架可以看出,该算法需要不断地进行样本分类调整,不断地计算调整后的新的聚类中心,因此当数据量非常大时,算法的时间开销是非常大的。 |
| SVM |
SVM (支持向量机)是一种算法,它以以下方法做工,它是一种种非线性映射额,把原训练数据映射到较高的维上,在新的维上,它搜索最佳分离超平面。 |
二、线性判别分析LDA
1.鸢尾花数据集
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_classification
class LDA():
def Train(self, X, y):
"""X为训练数据集,y为训练label"""
X1 = np.array([X[i] for i in range(len(X)) if y[i] == 0])
X2 = np.array([X[i] for i in range(len(X)) if y[i] == 1])
# 求中心点
mju1 = np.mean(X1, axis=0) # mju1是ndrray类型
mju2 = np.mean(X2, axis=0)
# dot(a, b, out=None) 计算矩阵乘法
cov1 = np.dot((X1 - mju1).T, (X1 - mju1))
cov2 = np.dot((X2 - mju2).T, (X2 - mju2))
Sw = cov1 + cov2
# 计算w
w = np.dot(np.mat(Sw).I, (mju1 - mju2).reshape((len(mju1), 1)))
# 记录训练结果
self.mju1 = mju1 # 第1类的分类中心
self.cov1 = cov1
self.mju2 = mju2 # 第2类的分类中心
self.cov2 = cov2
self.Sw = Sw # 类内散度矩阵
self.w = w # 判别权重矩阵
def Test(self, X, y):
"""X为测试数据集,y为测试label"""
# 分类结果
y_new = np.dot((X), self.w)
# 计算fisher线性判别式
nums = len(y)
c1 = np.dot((self.mju1 - self.mju2).reshape(1, (len(self.mju1))), np.mat(self.Sw).I)
c2 = np.dot(c1, (self.mju1 + self.mju2).reshape((len(self.mju1), 1)))
c = 1/2 * c2 # 2个分类的中心
h = y_new - c
# 判别
y_hat = []
for i in range(nums):
if h[i] >= 0:
y_hat.append(0)
else:
y_hat.append(1)
# 计算分类精度
count = 0
for i in range(nums):
if y_hat[i] == y[i]:
count += 1
precise = count / nums
# 显示信息
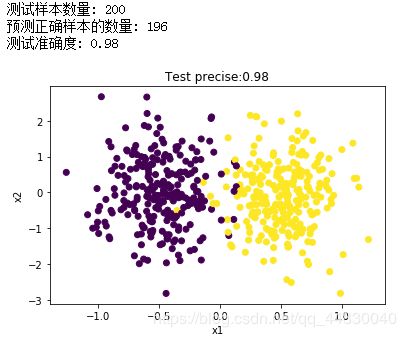
print("测试样本数量:", nums)
print("预测正确样本的数量:", count)
print("测试准确度:", precise)
return precise
if '__main__' == __name__:
# 产生分类数据
n_samples = 500
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=n_samples, n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_classes=2,n_informative=1, n_clusters_per_class=1, class_sep=0.5, random_state=10)
# LDA线性判别分析(二分类)
lda = LDA()
# 60% 用作训练,40%用作测试
Xtrain = X[:299, :]
Ytrain = y[:299]
Xtest = X[300:, :]
Ytest = y[300:]
lda.Train(Xtrain, Ytrain)
precise = lda.Test(Xtest, Ytest)
# 原始数据
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], marker='o', c=y)
plt.xlabel("x1")
plt.ylabel("x2")
plt.title("Test precise:" + str(precise))
plt.show()
2.月亮数据集
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
class LDA():
def Train(self, X, y):
"""X为训练数据集,y为训练label"""
X1 = np.array([X[i] for i in range(len(X)) if y[i] == 0])
X2 = np.array([X[i] for i in range(len(X)) if y[i] == 1])
# 求中心点
mju1 = np.mean(X1, axis=0) # mju1是ndrray类型
mju2 = np.mean(X2, axis=0)
# dot(a, b, out=None) 计算矩阵乘法
cov1 = np.dot((X1 - mju1).T, (X1 - mju1))
cov2 = np.dot((X2 - mju2).T, (X2 - mju2))
Sw = cov1 + cov2
# 计算w
w = np.dot(np.mat(Sw).I, (mju1 - mju2).reshape((len(mju1), 1)))
# 记录训练结果
self.mju1 = mju1 # 第1类的分类中心
self.cov1 = cov1
self.mju2 = mju2 # 第1类的分类中心
self.cov2 = cov2
self.Sw = Sw # 类内散度矩阵
self.w = w # 判别权重矩阵
def Test(self, X, y):
"""X为测试数据集,y为测试label"""
# 分类结果
y_new = np.dot((X), self.w)
# 计算fisher线性判别式
nums = len(y)
c1 = np.dot((self.mju1 - self.mju2).reshape(1, (len(self.mju1))), np.mat(self.Sw).I)
c2 = np.dot(c1, (self.mju1 + self.mju2).reshape((len(self.mju1), 1)))
c = 1/2 * c2 # 2个分类的中心
h = y_new - c
# 判别
y_hat = []
for i in range(nums):
if h[i] >= 0:
y_hat.append(0)
else:
y_hat.append(1)
# 计算分类精度
count = 0
for i in range(nums):
if y_hat[i] == y[i]:
count += 1
precise = count / (nums+0.000001)
# 显示信息
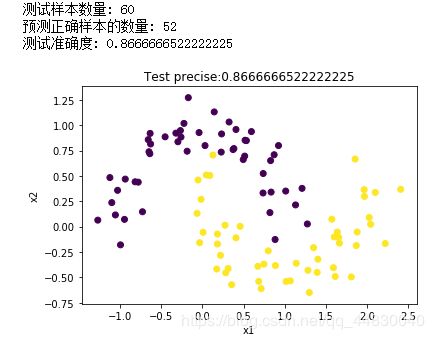
print("测试样本数量:", nums)
print("预测正确样本的数量:", count)
print("测试准确度:", precise)
return precise
if '__main__' == __name__:
# 产生分类数据
X, y = make_moons(n_samples=100, noise=0.15, random_state=42)
# LDA线性判别分析(二分类)
lda = LDA()
# 60% 用作训练,40%用作测试
Xtrain = X[:60, :]
Ytrain = y[:60]
Xtest = X[40:, :]
Ytest = y[40:]
lda.Train(Xtrain, Ytrain)
precise = lda.Test(Xtest, Ytest)
# 原始数据
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], marker='o', c=y)
plt.xlabel("x1")
plt.ylabel("x2")
plt.title("Test precise:" + str(precise))
plt.show()
三、k-means聚类分析
1.鸢尾花数据集
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
iris = load_iris()
X = iris.data[:] ##表示我们只取特征空间中的后两个维度
estimator = KMeans(n_clusters=5)#构造聚类器
estimator.fit(X)#聚类
label_pred = estimator.labels_ #获取聚类标签
#绘制k-means结果
x0 = X[label_pred == 0]
x1 = X[label_pred == 1]
x2 = X[label_pred == 2]
x3 = X[label_pred == 3]
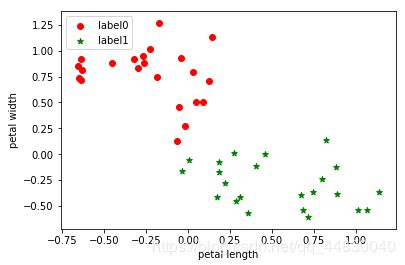
plt.scatter(x0[:, 0], x0[:, 1], c = "red", marker='o', label='label0')
plt.scatter(x1[:, 0], x1[:, 1], c = "green", marker='*', label='label1')
#plt.scatter(x2[:, 0], x2[:, 1], c = "blue", marker='+', label='label2')
#plt.scatter(x3[:, 0], x3[:, 1], c = "yellow", marker='o', label='label3')
plt.xlabel('petal length')
plt.ylabel('petal width')
plt.legend(loc=2)
plt.show()

2.月亮数据集
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
X, y = make_moons(n_samples=100, noise=0.15, random_state=42)
estimator = KMeans(n_clusters=5)#构造聚类器
estimator.fit(X)#聚类
label_pred = estimator.labels_ #获取聚类标签
#绘制k-means结果
x0 = X[label_pred == 0]
x1 = X[label_pred == 1]
x2 = X[label_pred == 2]
x3 = X[label_pred == 3]
plt.scatter(x0[:, 0], x0[:, 1], c = "red", marker='o', label='label0')
plt.scatter(x1[:, 0], x1[:, 1], c = "green", marker='*', label='label1')
#plt.scatter(x2[:, 0], x2[:, 1], c = "blue", marker='+', label='label2')
#plt.scatter(x3[:, 0], x3[:, 1], c = "yellow", marker='o', label='label3')
plt.xlabel('petal length')
plt.ylabel('petal width')
plt.legend(loc=2)
plt.show()
四、SVM(支持向量机)算法
1.鸢尾花数据集
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets, svm
import pandas as pd
from pylab import *
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
iris = datasets.load_iris()
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
X = X[y != 0, :2] # 选择X的前两个特性
y = y[y != 0]
n_sample = len(X)
np.random.seed(0)
order = np.random.permutation(n_sample) # 排列,置换
X = X[order]
y = y[order].astype(np.float)
X_train = X[:int(.9 * n_sample)]
y_train = y[:int(.9 * n_sample)]
X_test = X[int(.9 * n_sample):]
y_test = y[int(.9 * n_sample):]
#合适的模型
for fig_num, kernel in enumerate(('linear', 'rbf','poly')): # 径向基函数 (Radial Basis Function 简称 RBF),常用的是高斯基函数
clf = svm.SVC(kernel=kernel, gamma=10) # gamma是“rbf”、“poly”和“sigmoid”的核系数。
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
plt.figure(str(kernel))
plt.xlabel('x1')
plt.ylabel('x2')
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, zorder=10, cmap=plt.cm.Paired, edgecolor='k', s=20)
# zorder: z方向上排列顺序,数值越大,在上方显示
# paired两个色彩相近输出(paired)
# 圈出测试数据
plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], s=80, facecolors='none',zorder=10, edgecolor='k')
plt.axis('tight') #更改 x 和 y 轴限制,以便显示所有数据
x_min = X[:, 0].min()
x_max = X[:, 0].max()
y_min = X[:, 1].min()
y_max = X[:, 1].max()
XX, YY = np.mgrid[x_min:x_max:200j, y_min:y_max:200j]
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[XX.ravel(), YY.ravel()]) # 样本X到分离超平面的距离
Z = Z.reshape(XX.shape)
plt.contourf(XX,YY,Z>0,cmap=plt.cm.Paired)
plt.contour(XX, YY, Z, colors=['r', 'k', 'b'],
linestyles=['--', '-', '--'], levels=[-0.5, 0, 0.5]) # 范围
plt.title(kernel)
plt.show()



2.月亮数据集
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
# 为了显示中文
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = [u'SimHei']
mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
X, y = make_moons(n_samples=100, noise=0.15, random_state=42)
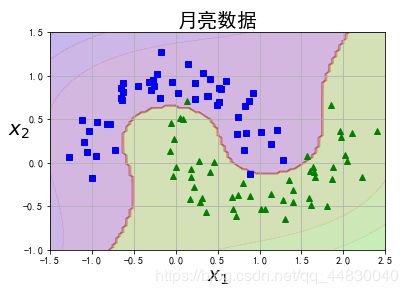
def plot_dataset(X, y, axes):
plt.plot(X[:, 0][y==0], X[:, 1][y==0], "bs")
plt.plot(X[:, 0][y==1], X[:, 1][y==1], "g^")
plt.axis(axes)
plt.grid(True, which='both')
plt.xlabel(r"$x_1$", fontsize=20)
plt.ylabel(r"$x_2$", fontsize=20, rotation=0)
plt.title("月亮数据",fontsize=20)
plot_dataset(X, y, [-1.5, 2.5, -1, 1.5])
plt.show()

polynomial_svm_clf = Pipeline([
# 将源数据 映射到 3阶多项式
("poly_features", PolynomialFeatures(degree=3)),
# 标准化
("scaler", StandardScaler()),
# SVC线性分类器
("svm_clf", LinearSVC(C=10, loss="hinge", random_state=42))
])
polynomial_svm_clf.fit(X, y)
def plot_predictions(clf, axes):
# 打表
x0s = np.linspace(axes[0], axes[1], 100)
x1s = np.linspace(axes[2], axes[3], 100)
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(x0s, x1s)
X = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
y_pred = clf.predict(X).reshape(x0.shape)
y_decision = clf.decision_function(X).reshape(x0.shape)
# print(y_pred)
# print(y_decision)
plt.contourf(x0, x1, y_pred, cmap=plt.cm.brg, alpha=0.2)
plt.contourf(x0, x1, y_decision, cmap=plt.cm.brg, alpha=0.1)
plot_predictions(polynomial_svm_clf, [-1.5, 2.5, -1, 1.5])
plot_dataset(X, y, [-1.5, 2.5, -1, 1.5])
plt.show()
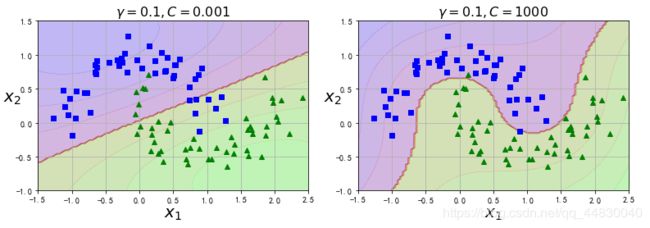
from sklearn.svm import SVC
gamma1, gamma2 = 0.1, 5
C1, C2 = 0.001, 1000
hyperparams = (gamma1, C1), (gamma1, C2)
svm_clfs = []
for gamma, C in hyperparams:
rbf_kernel_svm_clf = Pipeline([
("scaler", StandardScaler()),
("svm_clf", SVC(kernel="rbf", gamma=gamma, C=C))
])
rbf_kernel_svm_clf.fit(X, y)
svm_clfs.append(rbf_kernel_svm_clf)
plt.figure(figsize=(11, 7))
for i, svm_clf in enumerate(svm_clfs):
plt.subplot(221 + i)
plot_predictions(svm_clf, [-1.5, 2.5, -1, 1.5])
plot_dataset(X, y, [-1.5, 2.5, -1, 1.5])
gamma, C = hyperparams[i]
plt.title(r"$\gamma = {}, C = {}$".format(gamma, C), fontsize=16)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
五、SVM算法的优缺点
| 优点 |
①SVM算法既可以解决线性问题,又可以解决非线性问题②非线性映射是SVM方法的理论基础,SVM利用内积核函数代替向高维空间的非线性映射③对特征空间划分的最优超平面是SVM的目标,最大化分类边际的思想是SVM方法的核心④支持向量是SVM的训练结果,在SVM分类决策中起决定作用的是支持向量 |
| 优点 |
①对参数调节和核函数的选择敏感②不易处理多分类问题③对大规模训练样本难以实施④SVM的可解释性较差,无法给出决策树那样的规则 |
周志华《机器学习》LDA深入补充推导和python实现(二分类问题)









