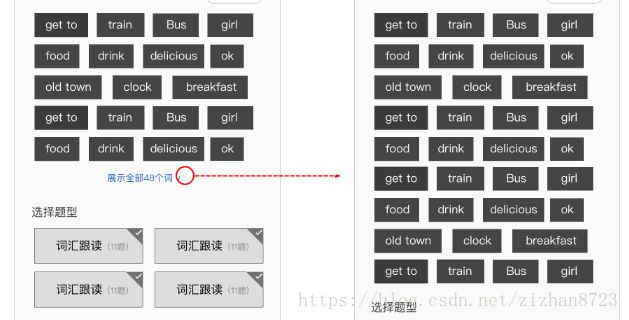
流式布局FlowLayout及行数限制
动态添加childView并实现自动换行操作,这个比较简单,重写ViewGroup的onMesure()方法,遍历动态计算每个View的宽高,宽度累加,当超过ViewGroup宽度,则换行显示,负责设置子控件的测量模式和大小 根据所有子控件设置自己的宽和高 。然后重写onLayout()方法,完成对所有childView的位置以及大小的指定。
网上有鸿洋大神写的工具类,但是不能做到动态的控制行数限制,所以我进行了改动。鸿洋大神此文章的地址:https://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/38352503
如果有和我相同需求的人,请继续往下看
1.对外暴露几个参数
首先加了几个对外暴露的变量,默认显示的行数,是否有行数限制,这个是根据自身去求动态设置的,另外一个参数isOverFlow 是否溢出,因为接口返回的数据数量是不确定的,可能不会超过行限制,也可能超过行限制,如果超过,则显示点击显示全部按钮,所以这个参数是起到这个作用的。
private int limitLineCount = 5; //显示行数
private boolean isLimitLine; //是否有行限制
private boolean isOverFlow; //是否溢出
public boolean isOverFlow() {
return isOverFlow;
}
public void setOverFlow(boolean overFlow) {
isOverFlow = overFlow;
}
public void setIsLimitLine(boolean isLimitLine) {
this.isLimitLine = isLimitLine;
this.requestLayout();
this.invalidate();
}
2.在测量时做行数限制
如果超过,则不继续测量高度
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 获得它的父容器为它设置的测量模式和大小
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
// 如果是warp_content情况下,记录宽和高
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
/**
* 记录每一行的宽度,width不断取最大宽度
*/
int lineWidth = 0;
/**
* 每一行的高度,累加至height
*/
int lineHeight = 0;
int lineCount = 1;
isOverFlow = false;
int cCount = getChildCount();
// 遍历每个子元素
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 测量每一个child的宽和高
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 得到child的lp
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
// 当前子空间实际占据的宽度
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin
+ lp.rightMargin;
// 当前子空间实际占据的高度
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin
+ lp.bottomMargin;
/**
* 如果加入当前child,则超出最大宽度,则的到目前最大宽度给width,累加height 然后开启新行
*/
if (lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth) {
if(isLimitLine) {
if(lineCount == this.limitLineCount + 1) {
setOverFlow(true);
break;
}
}
width = Math.max(lineWidth, childWidth);// 取最大的
lineWidth = childWidth; // 重新开启新行,开始记录
// 叠加当前高度,
height += lineHeight;
// 开启记录下一行的高度
lineHeight = childHeight;
lineCount ++;
} else
// 否则累加值lineWidth,lineHeight取最大高度
{
lineWidth += childWidth;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
}
// 如果是最后一个,则将当前记录的最大宽度和当前lineWidth做比较
if (i == cCount - 1) {
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth);
height += lineHeight;
}
}
setMeasuredDimension((modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeWidth
: width, (modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeHeight
: height);
YrLogger.d("CMM", "measure flowLayout width = "
+ ((modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeWidth : width)
+ ",height = "
+ ((modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeHeight : height));
}
#可以看到,我自己定义了参数 int lineCount;用来记录行数,核心代码
if (lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth) {
if(isLimitLine) {
if(lineCount == this.limitLineCount + 1) {//这里必须加一,如果超过限制则break;
setOverFlow(true);
break;
}
}
.
.
.
3.放置位置的时候进行限制
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
mAllViews.clear();
mLineHeight.clear();
int width = getWidth();
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
// 存储每一行所有的childView
List lineViews = new ArrayList();
int cCount = getChildCount();
int lineCount = 1;
// 遍历所有的孩子
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 如果已经需要换行
if (childWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + lineWidth > width) {
if(isLimitLine) {
if(lineCount == this.limitLineCount + 1) {
break;
}
}
// 记录这一行所有的View以及最大高度
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
// 将当前行的childView保存,然后开启新的ArrayList保存下一行的childView
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
lineWidth = 0;// 重置行宽
lineViews = new ArrayList();
lineCount ++;
}
/**
* 如果不需要换行,则累加
*/
lineWidth += childWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight + lp.topMargin
+ lp.bottomMargin);
lineViews.add(child);
}
// 记录最后一行
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
int left = 0;
int top = 0;
// 得到总行数
int lineNums = mAllViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lineNums; i++) {
// 每一行的所有的views
lineViews = mAllViews.get(i);
// 当前行的最大高度
lineHeight = mLineHeight.get(i);
// 遍历当前行所有的View
for (int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j++) {
View child = lineViews.get(j);
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
continue;
}
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
// 计算childView的left,top,right,bottom
int lc = left + lp.leftMargin;
int tc = top + lp.topMargin;
int rc = lc + child.getMeasuredWidth();
int bc = tc + child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 修正rc margin
if (rc + lp.rightMargin > getWidth()) {
rc = getWidth() - lp.rightMargin;
// 单行textView,设置为FocusInTouch mode,
// 第一次点击是获取focus,第二次点击执行onClick事件。
// if (lineViews.size() == 1 && lineViews.get(0) instanceof
// TextView) {
// ((TextView)
// lineViews.get(0)).setFocusableInTouchMode(true);
// }
}
child.layout(lc, tc, rc, bc);
left += child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.rightMargin
+ lp.leftMargin;
}
left = 0;
top += lineHeight;
}
}
依旧是添加了个变量用于记录行数,当超过是,不去放置子view
// 如果已经需要换行
if (childWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + lineWidth > width) {
if(isLimitLine) {
if(lineCount == this.limitLineCount + 1) {
break;
}
}
// 记录这一行所有的View以及最大高度
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
// 将当前行的childView保存,然后开启新的ArrayList保存下一行的childView
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
lineWidth = 0;// 重置行宽
lineViews = new ArrayList();
lineCount ++;
}
到这里其实已经差不多了,下面说一下怎么动态添加数据的吧
4.添加数据
this.mFlowLayout.addView(textView,params);// params是textView的布局样式,如果不需要则不要这个参数
5.最后一个问题
当添加完数据之后,按理说我们应该知道开头那个变量判断是否溢出,从而动态显示点击显示更多样式,难点来了,怎么判断view绘制完成呢?查了一波view流程,发现有个方法dispatchDraw()很适合
FlowLayout中重新dispatchDraw方法
@Override
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.dispatchDraw(canvas);
if(isLimitLine) {
...这里写一个回调,activity中收到后判断isOverFlow,如果溢出,则显示点击更多样式,否则不显示。
}
}
如果有不懂得地方欢迎私信我,稍后有时间我会写个demo整理到github上