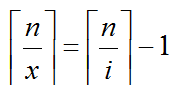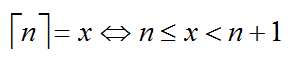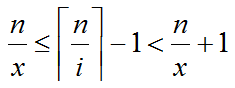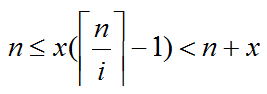PDF
A.Assigning Workstations && BZOJ 4425
佩内洛普是新建立的超级计算机的管理员中的一员。 她的工作是分配工作站给到这里来运行他们的计算研究任务的研究人员。
佩内洛普非常懒惰,不喜欢为到达的研究者们解锁机器。 她可以从在她的办公桌远程解锁这些机器,但她并不觉得这卑贱的任务配得上她,所以她决定忽略安全指南偷偷懒。她可以直接地要求,研究者在他们离开时不用锁定自己的工作站,然后把未在使用且还在未锁定状态的工作站分配给新来的研究人员。 这样,她只需要为每一个工作站第一次被使用所属的研究员解锁工作站,这对佩内洛普的工作来说是一个巨大的改善。
不幸的是,如果一个工作站在未锁定且没被使用的状态下超过m分钟,会自动锁定自己,佩内洛普必须为使用它的下一个研究员再次打开它。 鉴于抵达和离开的研究人员的确切时间表,你可以告诉佩内洛普,要求研究者在离开时不锁定工作站最多可以使她节约多少次的解锁工作。你可以认为这儿总是有足够的可用工作站。
Input
一行两个整数n (1≤n≤300000) 研究员的数量n,以及 m (1≤m≤100000000) 工作站在未锁定且没被使用的状态下超过m分钟会自动锁定。
下面的n行,每一行两个整数a与s (1≤a,s≤100000000) 表示一个研究员在第a分钟时到达以及待了s分钟后离开。
Output
输出研究者在离开时不锁定工作站最多可以使她节约多少次解锁工作。
二分+贪心
这个题我一开始按照右端点排了个序,然后遍历左端点,每次二分找到大于等于左端点-m的第一个,贪心的去用,结果wa了,想想肯定不对,但是 反例不太好找...
正解:
最后发现好像根据左端点更好处理一些,我先把所有点根据左端点排序,按先来后到安排位置,还是枚举左端点二分右端点,贪心的找到可以用的离开的最早的那个就可以了.
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 3e5 + 10;
multisetst;
multiset::iterator it;
int n,m;
struct node
{
int s;
int e;
bool operator < (const node &w) const
{
return s < w.s;
}
}q[maxn];
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d %d",&n,&m))
{
int a,s;
st.clear();
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&a,&s);
q[i].s = a;
q[i].e = a + s;
}
sort(q + 1,q + 1 + n);
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
int tmp = q[i].s - m;
//if(tmp <= 0)
//tmp = 1;
//cout< q[i].s)
{
ans++;
st.insert(q[i].e);
//vt.push_back(q[i].e);
}
else
{
st.erase(it);
st.insert(q[i].e);
//vt.push_back(q[i].e);
}
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",n - ans);
}
return 0;
}
/*
3 5
1 5
7 20
1 10
3 5
1 5
6 3
14 6
3 5
1 10
2 9
3 8
3 5
1 10
2 3
4 6
4 10000
1 1
3 2
4 6
6 2
*/
C Cleaning Pipes 待补
D Debugging && BZOJ 4428
你看中的调试器将不会在这件事上帮助你。有代码可以通过多种方式在调试与正式发布的间隙发生不同的行为,当出现这种情况,我们可能不得不求助于更原始的调试方式。
所以,你和你的printf现在在寻求一行导致该发布版本崩溃的代码。幸运的是:增加printf语句到程序里,既不会制造bug(仍然崩溃在同一原始的代码行),也没有影响执行时间(至少不显著)。 因此,即使在每行前加一个printf语句,运行程序,直到它崩溃,并检查最后打印行。
然而,它需要一些时间来添加每个printf语句到代码,并且该程序可以具有很多行。
因此,把一个printf语句在程序的中间或许是一个更好的计划,让它运行,观察它是否在加入行前崩溃,然后继续在代码的前一或后一半寻找。
不过话又说回来,运行程序可能需要很多时间,所以时效最优的策略可能是介于两者之间。
编写计算最坏情况下的最小时间来寻找崩溃行(无论它在哪里),认为你选择最优的加printf语句策略。
我们在5小时内发布新的版本,所以这个问题十分严重,需要尽快解决。
Input
输入包括一行三个整数:
n(1≤n≤10^6),代码行的数目;
r(1≤r≤10^9),编译和运行程序直到它崩溃的时间量;
p(1≤p≤10^9),增加单个的printf行所花费的时间。
您已经运行一次程序,因此已经知道它崩溃的地方。
Output
思路:
一开始我把这个题目和我做过类似的找最优的 扔鸡蛋的那个题目 UVA 的. 给混了,我觉得很像.都是具有单调性啥的.这类问题应该都比较经典.
显然,最坏的情况指的是出错地方一直处在最长的区间当中,为了使时间最少,我们每次都要尽可能的去等分区间.
设dp[n] 表示在最坏的情况下debug n行代码所需要的最少的时间.那么有:
dp[n] = min((i-1)*p+dp[ceil(n/i)])+r;
表示的是 : n行代码 分成i 块处理所需要的最少的时间.然后对均分之后区间最长的那个进行递归处理即可.
(i-1)p 是加 i-1行printf的时间.
这样的话复杂度应该是足够过这个题了,复杂度不是很好算啊 = =.
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 1e6 +10;
const ll inf = 1e18;
ll dp[maxn];
ll r,p;
ll ceil(int a,int b)
{
return (a + b - 1)/b;
}
ll dfs(int n)
{
if(n <= 1)
return 0;
if(dp[n])
return dp[n];
ll res = inf;
for(int i = 2;i <= n;i++)
{
res = min(res,dfs(ceil(n,i)) + (ll)(i - 1) * p + r);
}
return dp[n] = res ;
}
int main()
{
int n;
memset(dp,0,sizeof dp);
while(~scanf("%d %lld %lld",&n,&r,&p))
{
printf("%lld\n",dfs(n));
}
return 0;
}
优化:
因为我们发现 ceil(n/i) 有很多重复的.而且取值相同的i都在连续的一段内,那么为了花费最小,我们肯定是取最小i
以下来自转载
我们就要推导下标啦。
总之就是要解这个方程
x、i、n为非负整数,已知n、i,求最小的x
ps : 下面这个式子是因为你随着分的块越多,i越大,那么这个i就是当前块, 最长区间为ceil(n/i) 。因为我们要跳过重复的,
所以要直接找到下一个块数 x.他们两个区间长度差1
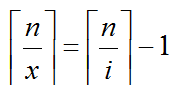
有两种方法
第一种:看Claris博客,得到x = (n - 1) / ((n - 1) / i) + 1(这里的除均为整除)
第二种:
首先要知道
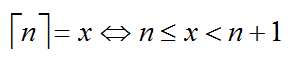
(具体数学里面有)
带入,得到
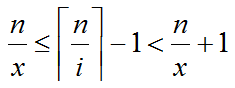
同乘上x
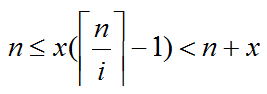
因为我们要求x的最小值,所以我们只看左边的不等式
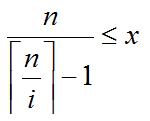
因为x为非负整数,左边不一定是整数,那么x的最小值应该是
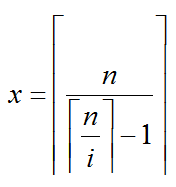
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 1e6 +10;
const ll inf = 1e18;
ll dp[maxn];
ll r,p;
ll ceil(int a,int b)
{
return (a + b - 1)/b;
}
ll dfs(int n)
{
if(n <= 1)
return 0;
if(dp[n])
return dp[n];
ll res = (ll)(n - 1) * p + r;
for(int i = 2;i < n;i = ceil(n,(ceil(n,i) - 1)))
{
res = min(res,dfs(ceil(n,i)) + (ll)(i - 1) * p + r);
}
return dp[n] = res ;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(~scanf("%d %lld %lld",&n,&r,&p))
{
memset(dp,0,sizeof dp);
printf("%lld\n",dfs(n));
}
return 0;
}
E Elementary Math
题意很简单, 给你n对数,每个数可以有+ - * 三中操作,现在要求这n对数计算过后的结果任意两个不一样,问你是否有可能
.可能输出任意一种方案,否则输出impossible
考虑这个题目 每一对数只有可能是三种结果. 可以把这n对数抽象成n个点,每个点对应右边三个点右边.然后就是最后看
能否找到一个二分图,跑遍匈牙利就好了.
很多细节,见代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
G Guessing Camels && BZOJ 4430 BIT求偏序对 OR cdq分治+BIT
aap,Jan和Thijs在摩洛哥参加完ACMICPC2015全球总决赛后去沙漠进行了一次旅行。旅行包括了骑骆驼。
在骑完回来之后,他们的向导邀请他们在晚上去看一场盛大的骆驼赛跑。他们骑的骆驼也会参加,而赌比赛的结果是
一个习惯。其中一个最有趣的赌涉及猜测完成比赛的骆驼的完整名单。这个赌可以为你赢得最多的钱,因为它也是最
难猜对的。
Jaap,Jan和Thijs已经下了注,但比赛要在一个小时后才开始,所以他们觉得很无聊。他们开始想知道有多少对骆驼
他们赌了同样的顺序。如果在他们三人的猜测名单中,骆驼c在骆驼d前,就意味着c和d在他们的名单中有相同的顺序
。你能帮他们计算有多少对骆驼是这样的吗?
思路:
考虑容斥:
答案 = 总对数 - 不满足条件的对数.
现在就是考虑怎么求不满足的对数.这里巧妙的利用了BIT
我们可以发现不满足偏序性质的这一对,一定是在某两个排列里位置是相同的,只有一个和他们的位置不相同,那么我们可以对每两个排列求一次不满足题意的偏序对的个数.但是这样算的话 对于那个排列里位置不同的数对,在另两个排列被算了两次,所以把最后的答案除以2就是最终的结果了.
求偏序对的话就是对于两个排列x,y. 先预处理处理x 中每一个x[i]的位置i,然后从后往前遍历 y[i].
那么关于一个点对x,y,若它们在两个排列中
____y__u______x____k
_______x___________y
这样从后向前扫第二个排列,扫到y的时候在第一个排列y的位置+1,然后扫到x的时候查询第一个排列x位置的前缀和,前缀和即为不满足条件的对数
所以就对扫到的每一个数都这样做就行了
即
将第二个排列中所有偏序对的位置固定下来作为一个标准,那么从后往前遍历第二个排列时,假设遍历到第i个,那么第i个后面所有的数都在他的后面了,由于我们把i后面的数都在第一个排列中的对应位置+1,那么现在我们求一下第二个排列中的第i个数在第一个排列中对应位置前面有多少个数,就可以求出不满足的偏序对个数了,好好体会..
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
I Identifying Map Tiles
签到题
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 32;
ll fac[maxn] = {1, 2};
char str[maxn];
int main(void)
{
for(int i = 2; i < maxn; i++)
fac[i] = fac[i-1]*2;
while(cin >> str)
{
ll len = strlen(str);
ll x = 0, y = 0, p = fac[len-1];
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if(str[i] == '0') ;
else if(str[i] == '1') y += p;
else if(str[i] == '2') x += p;
else x += p, y += p;
p /= 2;
}
// cout << x << ' ' << y << ' ' << p << endl;
printf("%I64d %I64d %I64d\n", len, y, x);
}
return 0;
}
J Jumbled Communication
给你 x^(x<<1) 的结果 让你求x,观察到x最大255 所以反过来逆推打个表就好
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
int a[maxn], ans[maxn];
void init()
{
for(int i = 0; i <= 255; i++)
a[i] = (i^(i<<1))%256, ans[a[i]] = i;
}
int main()
{
int n;
init();
while(~scanf("%d", &n))
{
int x;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("%d%c", ans[x], i == n ? '\n' : ' ');
}
}
return 0;
}
K -Kitchen Combinatorics 细节题
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include