Sensor系列之Sensor HAL层数据获取,基于Qualcomm平台
前面我们分析了Android Sensor HAL层源码分析(基于Qualcomm平台),该篇博文主要讲解了Sensor HAL的初始化,以及hal层是怎样获取所有sensor列表的。今天我们来进一步了解下sensor hal层的数据获取流程。
我们知道Native层SensorService启动后,会进入我们的treadLoop方法:
bool SensorService::threadLoop()
{
ALOGD("nuSensorService thread starting...");
// each virtual sensor could generate an event per "real" event, that's why we need
// to size numEventMax much smaller than MAX_RECEIVE_BUFFER_EVENT_COUNT.
// in practice, this is too aggressive, but guaranteed to be enough.
const size_t minBufferSize = SensorEventQueue::MAX_RECEIVE_BUFFER_EVENT_COUNT;
const size_t numEventMax = minBufferSize / (1 + mVirtualSensorList.size());
SensorDevice& device(SensorDevice::getInstance());
const size_t vcount = mVirtualSensorList.size();
const int halVersion = device.getHalDeviceVersion();
do {
ssize_t count = device.poll(mSensorEventBuffer, numEventMax);
if (count < 0) {
ALOGE("sensor poll failed (%s)", strerror(-count));
break;
}
// Reset sensors_event_t.flags to zero for all events in the buffer.
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
mSensorEventBuffer[i].flags = 0;
}
// Make a copy of the connection vector as some connections may be removed during the
// course of this loop (especially when one-shot sensor events are present in the
// sensor_event buffer). Promote all connections to StrongPointers before the lock is
// acquired. If the destructor of the sp gets called when the lock is acquired, it may
// result in a deadlock as ~SensorEventConnection() needs to acquire mLock again for
// cleanup. So copy all the strongPointers to a vector before the lock is acquired.
SortedVector< sp > activeConnections;
populateActiveConnections(&activeConnections);
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
// Poll has returned. Hold a wakelock if one of the events is from a wake up sensor. The
// rest of this loop is under a critical section protected by mLock. Acquiring a wakeLock,
// sending events to clients (incrementing SensorEventConnection::mWakeLockRefCount) should
// not be interleaved with decrementing SensorEventConnection::mWakeLockRefCount and
// releasing the wakelock.
bool bufferHasWakeUpEvent = false;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (isWakeUpSensorEvent(mSensorEventBuffer[i])) {
bufferHasWakeUpEvent = true;
break;
}
}
if (bufferHasWakeUpEvent && !mWakeLockAcquired) {
setWakeLockAcquiredLocked(true);
}
recordLastValueLocked(mSensorEventBuffer, count);
// handle virtual sensors
if (count && vcount) {
sensors_event_t const * const event = mSensorEventBuffer;
const size_t activeVirtualSensorCount = mActiveVirtualSensors.size();
if (activeVirtualSensorCount) {
size_t k = 0;
SensorFusion& fusion(SensorFusion::getInstance());
if (fusion.isEnabled()) {
for (size_t i=0 ; i= minBufferSize) {
ALOGE("buffer too small to hold all events: "
"count=%zd, k=%zu, size=%zu",
count, k, minBufferSize);
break;
}
sensors_event_t out;
SensorInterface* si = mActiveVirtualSensors.valueAt(j);
if (si->process(&out, event[i])) {
mSensorEventBuffer[count + k] = out;
k++;
}
}
}
if (k) {
// record the last synthesized values
recordLastValueLocked(&mSensorEventBuffer[count], k);
count += k;
// sort the buffer by time-stamps
sortEventBuffer(mSensorEventBuffer, count);
}
}
}
// handle backward compatibility for RotationVector sensor
if (halVersion < SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_0) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (mSensorEventBuffer[i].type == SENSOR_TYPE_ROTATION_VECTOR) {
// All the 4 components of the quaternion should be available
// No heading accuracy. Set it to -1
mSensorEventBuffer[i].data[4] = -1;
}
}
}
// Map flush_complete_events in the buffer to SensorEventConnections which called
// flush on the hardware sensor. mapFlushEventsToConnections[i] will be the
// SensorEventConnection mapped to the corresponding flush_complete_event in
// mSensorEventBuffer[i] if such a mapping exists (NULL otherwise).
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
mMapFlushEventsToConnections[i] = NULL;
if (mSensorEventBuffer[i].type == SENSOR_TYPE_META_DATA) {
const int sensor_handle = mSensorEventBuffer[i].meta_data.sensor;
SensorRecord* rec = mActiveSensors.valueFor(sensor_handle);
if (rec != NULL) {
mMapFlushEventsToConnections[i] = rec->getFirstPendingFlushConnection();
rec->removeFirstPendingFlushConnection();
}
}
}
// Send our events to clients. Check the state of wake lock for each client and release the
// lock if none of the clients need it.
bool needsWakeLock = false;
size_t numConnections = activeConnections.size();
for (size_t i=0 ; i < numConnections; ++i) {
if (activeConnections[i] != 0) {
activeConnections[i]->sendEvents(mSensorEventBuffer, count, mSensorEventScratch,
mMapFlushEventsToConnections);
needsWakeLock |= activeConnections[i]->needsWakeLock();
// If the connection has one-shot sensors, it may be cleaned up after first trigger.
// Early check for one-shot sensors.
if (activeConnections[i]->hasOneShotSensors()) {
cleanupAutoDisabledSensorLocked(activeConnections[i], mSensorEventBuffer,
count);
}
}
}
if (mWakeLockAcquired && !needsWakeLock) {
setWakeLockAcquiredLocked(false);
}
} while (!Thread::exitPending());
ALOGW("Exiting SensorService::threadLoop => aborting...");
abort();
return false;
} 其中在do…while循环体中通过device->poll方法进行去hal层读取sensor上报的数据。device的类型为sensors_poll_device_1_t结构体,在sensors_open方法中我们已经将其中的方法进行了初始化:
static int sensors_open(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* id,
struct hw_device_t** device)
{
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(id);
int ret = -EINVAL;
SensorsContext *dev = SensorsContext::getInstance();
memset(&dev->device, 0, sizeof(sensors_poll_device_1_t));
dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
dev->device.common.version = SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_3;
dev->device.common.module = const_cast(module);
dev->device.common.close = sensors_close;
dev->device.activate = sensors_activate;
dev->device.setDelay = sensors_set_delay;
dev->device.poll = sensors_poll;
dev->device.batch = sensors_batch;
dev->device.flush = sensors_flush;
*device = &dev->device.common;
ret = 0;
return ret;
} 所以device->poll方法最终会调用到hal层的sensors_poll,因此我们跟进sensors_poll方法:
static int sensors_poll(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
sensors_event_t* data, int count)
{
SensorsContext *ctx = (SensorsContext *)dev;
return ctx->poll(data, count);
}继而调用我们之前介绍过的SensorsContext对象的poll方法,其中数据将会填充到由类型为sensors_event_t* data的数据结构中。这个结构体定义在hal层,其结构体如下:
typedef struct sensors_event_t {
/* must be sizeof(struct sensors_event_t) */
int32_t version; // sensors版本
/* sensor identifier */
int32_t sensor; // sensor id
/* sensor type */
int32_t type; // sensor type
/* reserved */
int32_t reserved0;
/* time is in nanosecond */
int64_t timestamp;
union {
union {
float data[16];
/* acceleration values are in meter per second per second (m/s^2) */
sensors_vec_t acceleration;
/* magnetic vector values are in micro-Tesla (uT) */
sensors_vec_t magnetic;
/* orientation values are in degrees */
sensors_vec_t orientation;
/* gyroscope values are in rad/s */
sensors_vec_t gyro;
/* temperature is in degrees centigrade (Celsius) */
float temperature;
/* distance in centimeters */
float distance;
/* light in SI lux units */
float light;
/* pressure in hectopascal (hPa) */
float pressure;
/* relative humidity in percent */
float relative_humidity;
/* uncalibrated gyroscope values are in rad/s */
uncalibrated_event_t uncalibrated_gyro;
/* uncalibrated magnetometer values are in micro-Teslas */
uncalibrated_event_t uncalibrated_magnetic;
/* heart rate data containing value in bpm and status */
heart_rate_event_t heart_rate;
/* this is a special event. see SENSOR_TYPE_META_DATA above.
* sensors_meta_data_event_t events are all reported with a type of
* SENSOR_TYPE_META_DATA. The handle is ignored and must be zero.
*/
meta_data_event_t meta_data;
};
union {
uint64_t data[8];
/* step-counter */
uint64_t step_counter;
} u64;
};
/* Reserved flags for internal use. Set to zero. */
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t reserved1[3];
} sensors_event_t;联合体会根据具体的sensor 类型来决定其数据该怎样封装到对应的vec结构体中。
我们继续跟进SensorsContext类的poll方法中去。
int SensorsContext::poll(sensors_event_t* data, int count)
{
int i = 0;
int err;
bool wakeup_event_being_processed = false;
int sensorFlag = -1;
HAL_LOG_DEBUG("%s: count: %d", __FUNCTION__, count );
pthread_mutex_lock(&data_cb->data_mutex);
while(i < count) {
/* check if any responses have been buffered */
if(!Utility::removeFromQueue(&data[i])) {
break;
}
if (data[i].type == SENSOR_TYPE_META_DATA) {
sensorFlag = mSensors[data[i].meta_data.sensor]->getFlags();
}
else {
sensorFlag = mSensors[data[i].sensor]->getFlags();
}
if (sensorFlag & SENSOR_FLAG_WAKE_UP) {
wakeup_event_being_processed = true;
Utility::decrement_wake_events_in_queue_count(data_cb);
}
i++;
}
/* Release wakelock if held */
pthread_mutex_lock(&data_cb->wakelock_mutex);
if (wakeup_event_being_processed == false &&
data_cb->wake_events_in_queue == 0 &&
data_cb->sensors_wakelock_held == true ) {
/*
* We purposely don't call release_sensor_wake_lock() here as we've already
* decremented the wake events in the queue counter.
*/
data_cb->sensors_wakelock_held = false;
release_wake_lock( SENSORS_WAKE_LOCK );
HAL_LOG_DEBUG("%s: released wakelock %s", __FUNCTION__, SENSORS_WAKE_LOCK);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&data_cb->wakelock_mutex);
while(i == 0) {
data_cb->is_ind_arrived = false;
/* wait for notify cb - wait indefinitely */
err = Utility::waitForResponse(0, &data_cb->data_mutex,
&data_cb->data_cond,
&data_cb->is_ind_arrived);
if(err == false) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&data_cb->data_mutex);
return -ETIMEDOUT;
}
/* Data received */
while(i < count && Utility::removeFromQueue(&data[i])) {
if (data[i].type == SENSOR_TYPE_META_DATA) {
sensorFlag = mSensors[data[i].meta_data.sensor]->getFlags();
}
else {
sensorFlag = mSensors[data[i].sensor]->getFlags();
}
if (sensorFlag & SENSOR_FLAG_WAKE_UP) {
Utility::decrement_wake_events_in_queue_count(data_cb);
}
i++;
}
}
/* latency mesaure */
if (Latency::isLatencyMeasureEnabled()) {
struct timespec current_time;
uint64_t curr_timestamp = android::elapsedRealtimeNano();
Latency::latencyMeasure(curr_timestamp, data, i);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&data_cb->data_mutex);
HAL_LOG_DEBUG("%s:polldata:%d, sensor:%d, type:%d, x:%f y:%f z:%f",
__FUNCTION__, i,
data[0].sensor, data[0].type,
data[0].acceleration.x,
data[0].acceleration.y,
data[0].acceleration.z);
return i;
}在while循环中,首先会通过Utility工具类的removeFromQueue方法去队列里尝试取数据,并将数据存储到data位置,如果有数据将会返回true,最后该数据也就达到了上层,反之返回false。
从这里我们也可以看出,sensor的数据是存放在一个队列里面的,所以肯定有另外一个地方往这个队列里存数据,然后我们的app通过SensorService的线程循环去这个队列里取到并返回给app。
bool Utility::removeFromQueue(sensors_event_t* data_ptr)
{
hal_sensor_dataq_t* q_ptr;
bool rv = false;
if (NULL != q_head_ptr) {
/* copy the data from head */
q_ptr = q_head_ptr;
*data_ptr = q_head_ptr->data;
/* update the pointers */
if (q_head_ptr == q_tail_ptr) {
/* queue has only one element */
q_tail_ptr = NULL;
}
q_head_ptr = q_head_ptr->next;
free(q_ptr);
rv = true;
}
return rv;
}hal_sensor_dataq_t* Utility::q_head_ptr = NULL;
/* sensor event data buffer node */
typedef struct hal_sensor_dataq_t {
sensors_event_t data; /* sensor event data that will report to framework */
struct hal_sensor_dataq_t* next; /* pointer to the next sensor event data */
} hal_sensor_dataq_t;如果没有数据,poll方法会通过waitForResponse等待indication消息notify返回,继续通过removeFromQueue取队列里的消息,然回返回。
如下的log展示了一个step counter的消息上报过程:
06-04 19:58:57.384 V/qti_sensors_hal: SAMSensor_sensor1_cb: msg_type 2, Sn 37, msg Id 5, txn Id 0
06-04 19:58:57.384 I/qti_sensors_hal: processInd: handle:49
06-04 19:58:57.384 D/qti_sensors_hal: processInd: SNS_SAM_PED_REPORT_IND_V01
06-04 19:58:57.384 D/qti_sensors_hal: processInd: handle 49, count=1
06-04 19:58:57.384 V/qti_sensors_hal: processInd:sensor android.sensor.step_counter
06-04 19:58:57.384 V/qti_sensors_hal: processInd: STEP COUNTER: steps 1, running_total 0 SAM TS: 22393870 HAL TS:679857437028 elapsedRealtimeNano:680554179479
06-04 19:58:57.385 D/qti_sensors_hal: poll:polldata:1, sensor:49, type:19, x:0.000000 y:0.000000 z:-0.000000我们跟进stepCounter的hal包装层去取看看他是怎样将数据放入队列里的。
最后我们在stepCounter.cpp中,其processInd方法将驱动层上报的数据放入了队列里:
void StepCounter::processInd(sensor1_msg_header_s *msg_hdr, void *msg_ptr)
{
hal_sam_sample_t *sample_list = NULL;
hal_sam_sample_t *curr_sample = NULL;
sensors_event_t la_sample;
uint32_t i = 0;
uint32_t count = 0;
uint64_t steps = 0;
HAL_LOG_INFO("%s: handle:%d", __FUNCTION__, handle);
if (SNS_SAM_PED_REPORT_IND_V01 == msg_hdr->msg_id) {
HAL_LOG_DEBUG("%s: SNS_SAM_PED_REPORT_IND_V01", __FUNCTION__);
if( batching ) {
/* Switch from Async state to batching mode*/
sendBatchReq();
}
sns_sam_ped_report_ind_msg_v01* sam_ind =
(sns_sam_ped_report_ind_msg_v01*)msg_ptr;
sample_list = (hal_sam_sample_t *)malloc(sizeof(hal_sam_sample_t));
if (NULL == sample_list) {
HAL_LOG_ERROR( "%s: Malloc error", __FUNCTION__ );
} else {
count = 1;
sample_list->data[0] = sam_ind->report_data.step_count;
sample_list->data[1] = sam_ind->report_data.step_rate;
sample_list->data[2] = sam_ind->report_data.step_confidence;
sample_list->data[3] = sam_ind->report_data.step_event;
sample_list->data[4] = sam_ind->report_data.step_count_error;
sample_list->accuracy = 0;
sample_list->timestamp = sam_ind->timestamp;
}
}
else if (SNS_SAM_PED_GET_REPORT_RESP_V01 == msg_hdr->msg_id) {
HAL_LOG_DEBUG("%s: SNS_SAM_PED_GET_REPORT_RESP_V01", __FUNCTION__);
sns_sam_ped_get_report_resp_msg_v01 *sam_ind =
(sns_sam_ped_get_report_resp_msg_v01 *)msg_ptr;
if (sam_ind->timestamp_valid && sam_ind->report_data_valid) {
sample_list = (hal_sam_sample_t *)malloc( sizeof(hal_sam_sample_t) );
if (NULL == sample_list) {
HAL_LOG_ERROR( "%s: Malloc error", __FUNCTION__ );
} else {
count = 1;
sample_list->data[0] = sam_ind->report_data.step_count;
sample_list->data[1] = sam_ind->report_data.step_rate;
sample_list->data[2] = sam_ind->report_data.step_confidence;
sample_list->data[3] = 0; /* We don't want to generate extra step detector events */
sample_list->data[4] = sam_ind->report_data.step_count_error;
sample_list->accuracy = 0;
sample_list->timestamp = sam_ind->timestamp;
}
}
else {
HAL_LOG_WARN("%s: Received report with invalid data", __FUNCTION__);
}
}
else if(SNS_SAM_PED_BATCH_IND_V01 == msg_hdr->msg_id) {
HAL_LOG_DEBUG("%s: SNS_SAM_PED_BATCH_IND_V01", __FUNCTION__);
sns_sam_ped_batch_ind_msg_v01* sam_ind =
(sns_sam_ped_batch_ind_msg_v01*)msg_ptr;
sample_list = (hal_sam_sample_t *)malloc(sam_ind->items_len * sizeof(hal_sam_sample_t));
if (NULL == sample_list) {
HAL_LOG_ERROR( "%s: Malloc error", __FUNCTION__ );
}
else {
curr_sample = sample_list;
clock_gettime( CLOCK_BOOTTIME, &ts_event );
ts_poll.tv_sec = ts_event.tv_sec;
for(i = 0; i < sam_ind->items_len; i++) {
curr_sample->data[0] = sam_ind->items[ i ].report.step_count;
curr_sample->data[1] = sam_ind->items[ i ].report.step_rate;
curr_sample->data[2] = sam_ind->items[ i ].report.step_confidence;
curr_sample->data[3] = sam_ind->items[ i ].report.step_event;
curr_sample->data[4] = sam_ind->items[ i ].report.step_count_error;
curr_sample->accuracy = 0;
curr_sample->timestamp = sam_ind->items[ i ].timestamp;
}
/* Report only last event*/
count = 1;
curr_sample++;
}
}
else {
HAL_LOG_ERROR("%s: Unknown message ID = %d", __FUNCTION__, msg_hdr->msg_id);
}
if(count == 0) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&data_cb->data_mutex);
/* Release wakelock if held */
if (getFlags() & SENSOR_FLAG_WAKE_UP) {
Utility::release_sensor_wake_lock(data_cb, __FUNCTION__);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&data_cb->data_mutex);
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
HAL_LOG_DEBUG("%s: handle %d, count=%d", __FUNCTION__, handle, count);
curr_sample = &sample_list[i];
/* As we update all sensors associated with an algo when SAM sends a response,
* step counter needs a special handling to avoid spurious events generated
* from step detector or pedometer when either of them are registered/de-registered.
*/
if ((step_counter_running_total == 0) ||
(step_counter_current_instance != sample_list->data[0])) {
step_counter_current_instance = curr_sample->data[0]; // 取出传感器传回的距离值
steps = step_counter_running_total + step_counter_current_instance; // 计算当前的总步数
step_counter_running_instance = steps;
la_sample.type = SENSOR_TYPE_STEP_COUNTER;
if(bWakeUp == false) {
la_sample.sensor = HANDLE_SAM_STEP_COUNTER;
HAL_LOG_VERBOSE("%s:sensor %s ",__FUNCTION__,
Utility::SensorTypeToSensorString(getType()));
} else {
la_sample.sensor = HANDLE_SAM_STEP_COUNTER_WAKE_UP;
HAL_LOG_VERBOSE("%s:sensor %s (wake_up)",__FUNCTION__,
Utility::SensorTypeToSensorString(getType()));
}
la_sample.u64.step_counter = steps;
la_sample.version = sizeof(sensors_event_t);
if( step_counter_current_instance == 0) {
/* Step count didn't change.
* Use present time to make sure timestamp is larger than previous event timestamp. */
la_sample.timestamp = android::elapsedRealtimeNano();
} else {
la_sample.timestamp = time_service->timestampCalc((uint64_t)curr_sample->timestamp, la_sample.sensor);
}
HAL_LOG_VERBOSE("%s: STEP COUNTER: steps %" PRIu64", running_total %" PRIu64" SAM TS: %u HAL TS:%lld elapsedRealtimeNano:%lld",
__FUNCTION__, steps, step_counter_running_total, curr_sample->timestamp, la_sample.timestamp,
android::elapsedRealtimeNano());
pthread_mutex_lock(&data_cb->data_mutex);
if (Utility::insertQueue(&la_sample)) { // 将数据插入到队列中
Utility::signalInd(data_cb); // 告知有数据达到,另一边等待的waitReponse返回,poll方法便可通过removeQueue方法取到数据了,即我们当前行走的总步数
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&data_cb->data_mutex);
}
}
free(sample_list);
}遍历下insertQueue的地方,我们发现基本上所有具体的sensor实现文件的processInd方法中都会调用这个方法,根据自身数据的特点,对其数据结构做指定封装。也就是所谓的工厂模式,是不是很神奇。。。
./libhalsensors/src/MultiShake.cpp:198: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/GeoMagneticRotationVector.cpp:377: if (Utility::insertQueue(&la_sample)) {
./libhalsensors/src/FaceNShake.cpp:195: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/MagneticCalibration.cpp:246: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/Gravity.cpp:522: if (Utility::insertQueue(&la_sample)) {
./libhalsensors/src/SignificantMotionDetector.cpp:230: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/Sensor.cpp:97: if (Utility::insertQueue(&flush_evt)){
./libhalsensors/src/LinearAcceleration.cpp:524: if (Utility::insertQueue(&la_sample)) {
./libhalsensors/src/Orientation.cpp:507: if (Utility::insertQueue(&la_sample)) {
./libhalsensors/src/SpeedPulse.cpp:174: if (Utility::insertQueue(&la_sample)) {
./libhalsensors/src/Tilt.cpp:200: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/QHeart.cpp:357: if (Utility::insertQueue(&la_sample)) {
./libhalsensors/src/BringToEar.cpp:195: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/StepDetector.cpp:362: if (Utility::insertQueue(&la_sample)) {
./libhalsensors/src/IOD.cpp:272: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/MagneticUncalibratedSAM.cpp:248: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/AbsoluteMotionDetector.cpp:200: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/GameRotationVector.cpp:363: if (Utility::insertQueue(&la_sample)) {
./libhalsensors/src/Pedometer.cpp:248: if (Utility::insertQueue(&la_sample)) {
./libhalsensors/src/PedestrianActivityMonitor.cpp:215: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/TiltDetector.cpp:307: if (Utility::insertQueue(&la_sample)) {
./libhalsensors/src/Facing.cpp:194: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/VehicleMotionDetector.cpp:202: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/Thresh.cpp:354: if (Utility::insertQueue(&la_sample)) {
./libhalsensors/src/RelativeMotionDetector.cpp:203: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/GyroTap.cpp:202: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/PickUpGesture.cpp:235: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/FastAbsoluteMotionDetector.cpp:196: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/SMGRSensor.cpp:849: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/StepCounter.cpp:526: if (Utility::insertQueue(&la_sample)) {
./libhalsensors/src/CoarseMotionClassifier.cpp:196: if (Utility::insertQueue(&sensor_data)) {
./libhalsensors/src/Utility.cpp:322: FUNCTION: insertQueue
./libhalsensors/src/Utility.cpp:325:bool Utility::insertQueue(sensors_event_t const *data_ptr)数据拿到的过程已经清楚了,那么processInd又是怎样被调用的呢?
在Android Sensor HAL层源码分析(基于Qualcomm平台)一文中,我们讲到通过addSensor的时候会实例化我们的sensor hal层对象,我们在回过头复习下Step Counter的构造过程,先看下其初始化的部分log:
06-04 19:48:04.423 D/qti_sensors_hal: addSensor: STEP COUNTER enabled handle:49
06-04 19:48:04.423 D/libsensor1: sensor1_init
06-04 19:48:04.423 V/libsensor1: libsensor_add_client Adding client index 7 (62)
06-04 19:48:04.423 D/libsensor1: libsensor_add_client: waking up rx thread 51 52
06-04 19:48:04.423 D/libsensor1: libsensor_rx_thread: waking on wakeup pipe 51
06-04 19:48:04.424 I/qti_sensors_hal: SAMSensor: sensor() is_attrib_ok=1
06-04 19:48:04.424 D/libsensor1: libsensor_rx_thread: waiting on fd 55
06-04 19:48:04.424 I/qti_sensors_hal: StepCounter: handle:49
06-04 19:48:04.424 I/qti_sensors_hal: sendAlgoAttribReq:sensor(android.sensor.step_counter) svc no:37 handle:49
06-04 19:48:04.424 D/libsensor1: libsensor_rx_thread: waiting on fd 56
06-04 19:48:04.424 D/libsensor1: libsensor_rx_thread: waiting on fd 57
06-04 19:48:04.424 I/libsensor1: libsensor_log_ctl_write_pkt: fd 62; svc 37; msg 36; txn 0; cmd WRITE_QMI
06-04 19:48:04.424 D/qti_sensors_hal: waitForResponse: timeout=1000
06-04 19:48:04.426 D/libsensor1: libsensor_rx_thread: waking on fd 62
06-04 19:48:04.426 I/libsensor1: libsensor_log_read_pkt: fd 62; svc 37; msg 36; txn 0; type RESP; cmd WRITE_QMI
06-04 19:48:04.426 V/qti_sensors_hal: SAMSensor_sensor1_cb: msg_type 1, Sn 37, msg Id 36, txn Id 0
06-04 19:48:04.426 D/libsensor1: libsensor_rx_thread: waiting on fd 57
06-04 19:48:04.426 I/qti_sensors_hal: processResp: handle:49
06-04 19:48:04.426 D/libsensor1: libsensor_rx_thread: waiting on fd 59
06-04 19:48:04.426 D/qti_sensors_hal: processResp: Received SNS_SAM_PED_GET_ATTRIBUTES_RESP_V01
06-04 19:48:04.426 D/libsensor1: libsensor_rx_thread: waiting on fd 60
06-04 19:48:04.426 D/libsensor1: libsensor_rx_thread: waiting on fd 61
06-04 19:48:04.426 I/qti_sensors_hal: processAlgoAttribResp:sensor(android.sensor.step_counter) Received response 0 for svc_num 37 handle 49
06-04 19:48:04.426 D/libsensor1: libsensor_rx_thread: waiting on fd 62
06-04 19:48:04.426 D/libsensor1: libsensor_rx_thread: waiting on fd 51
06-04 19:48:04.426 I/qti_sensors_hal: processAlgoAttribResp:sensor(android.sensor.step_counter) sensor1 Version:1 Power:11796 MaxFreq:65536 MinFreq:18 MaxSampleFreq:3276800 MinSampleFreq:3276800 case HANDLE_SAM_STEP_COUNTER:
case HANDLE_SAM_STEP_COUNTER_WAKE_UP:
property_get( HAL_PROP_STEP_COUNTER, add_sensor, "true" );
if (!strncmp("true", add_sensor, 4)) {
HAL_LOG_DEBUG("%s: STEP COUNTER enabled handle:%d",
__FUNCTION__, handle);
mSensors[handle] = new StepCounter(handle);
} else {
HAL_LOG_DEBUG("%s: STEP COUNTER disabled!", __FUNCTION__);
}
break;class StepCounter : public SAMSensor {
uint64_t step_counter_running_total;
uint64_t step_counter_running_instance;
uint64_t step_counter_current_instance;
bool step_counter_is_timer_created;
struct timespec ts_event, ts_poll;
uint64_t prev_stepcount;
bool asyncmode;
timer_t sc_timer;
/*===========================================================================
FUNCTION: sendGetReportReq
Get the last report data after enabling the sensor.
===========================================================================*/
int sendGetReportReq(bool bRespRequired);
public:
StepCounter(int handle);
~StepCounter();
int enable(int en);
/*===========================================================================
FUNCTION: processResp
Process the response to the sensor1 SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_RESP
Parameters
@msg_hdr : sensor1 message header
@msg_ptr : sensor1 message data
===========================================================================*/
void processResp(sensor1_msg_header_s *msg_hdr, void *msg_ptr);
/*===========================================================================
FUNCTION: processInd
Process the response to the sensor1 SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_IND
Parameters
@msg_hdr : sensor1 message header
@msg_ptr : sensor1 message data
===========================================================================*/
void processInd(sensor1_msg_header_s *msg_hdr, void *msg_ptr);
/*===========================================================================
FUNCTION: setSensorInfo
Fill the sensor specific information.
===========================================================================*/
void setSensorInfo();
/*===========================================================================
FUNCTION: sendBatchReq
Send request to receive stepcounter info at periodic intervals
===========================================================================*/
int sendBatchReq();
/*===========================================================================
FUNCTION: manageBatch
Timer handler which allows switching to async mode when activity stopped
===========================================================================*/
static void manageBatch( sigval_t );
/*===========================================================================
FUNCTION: initTimer
Setup timer handler
===========================================================================*/
int initTimer(void);
};可以看到stepCounter继承自SAMSensor,因此在构建StepCounter实例的时候,也会创建我们的SAMSensor,
StepCounter有几个成员变量,这里解释下:
step_counter_running_total保存之前步行的总数;
step_counter_current_instance保存当前sensor检测到的行走步数;
step_counter_running_instance则为本次行走探测完毕后的总步数;
即step_counter_running_instance=step_counter_running_total(之前的步数) + step_counter_current_instance(当前行走步数);
我们在前面StepCounter的processInd方法中看到,得到的mSteps就是这二者之和,最终会将此值返回到app层,即我们在app的如下地方打印的值event.values[0]:
public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) {
mSteps = event.values[0];
Log.i(TAG,"Detected step changes:"+event.values[0]);
tv.setText("您今天走了"+String.valueOf((int)mSteps)+"步");
} 在SAMSensor的构造方法中,会通过Sensor1_open打开一条客户端连接,传入回调函数SAMSensor_sensor1_cb。
/* open sensor1 connection for SAM Sensor */
err = sensor1_open(&sensor1_cb->sensor1_handle, &SAMSensor_sensor1_cb, (intptr_t)this);
if (SENSOR1_SUCCESS != err) {
HAL_LOG_ERROR("%s: sensor1 open failed for %s!", __FUNCTION__,
Utility::SensorTypeToSensorString(getType()));
setAttribOK(false);
} else {
setAttribOK(true);
report_rate = (int)lroundf(calcSampleRate(0));
}
HAL_LOG_INFO("%s: sensor(%s) is_attrib_ok=%d", __FUNCTION__,
Utility::SensorTypeToSensorString(getType()), getAttribOK());所以最后得到的step数据都会通过注册的SAMSensor_sensor1_cb方法返回(这里不明白的请戳上一篇文章复习),这对应于上面贴出的log,这里再贴一遍。
06-04 19:58:57.384 V/qti_sensors_hal: SAMSensor_sensor1_cb: msg_type 2, Sn 37, msg Id 5, txn Id 0
06-04 19:58:57.384 I/qti_sensors_hal: processInd: handle:49
06-04 19:58:57.384 D/qti_sensors_hal: processInd: SNS_SAM_PED_REPORT_IND_V01
06-04 19:58:57.384 D/qti_sensors_hal: processInd: handle 49, count=1
06-04 19:58:57.384 V/qti_sensors_hal: processInd:sensor android.sensor.step_counter
06-04 19:58:57.384 V/qti_sensors_hal: processInd: STEP COUNTER: steps 1, running_total 0 SAM TS: 22393870 HAL TS:679857437028 elapsedRealtimeNano:680554179479
06-04 19:58:57.385 D/qti_sensors_hal: poll:polldata:1, sensor:49, type:19, x:0.000000 y:0.000000 z:-0.000000我们接着看SAMSensor_sensor1_cb方法得具体处理:
void SAMSensor_sensor1_cb (intptr_t cb_data,
sensor1_msg_header_s *msg_hdr,
sensor1_msg_type_e msg_type,
void *msg_ptr)
{
SAMSensor *sam = (SAMSensor *)cb_data;
hal_sensor1_cb_t *sensor1_cb = sam->getSensor1Cb();
hal_data_cb_t *data_cb = Utility::getDataCb();
if (msg_hdr != NULL) {
HAL_LOG_VERBOSE("%s: msg_type %d, Sn %d, msg Id %d, txn Id %d", __FUNCTION__,
msg_type, msg_hdr->service_number, msg_hdr->msg_id, msg_hdr->txn_id );
}
else {
if (msg_type != SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_BROKEN_PIPE &&
msg_type != SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_REQ &&
msg_type != SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_RETRY_OPEN ) {
HAL_LOG_ERROR("%s: Error - invalid msg type with NULL msg_hdr: %u",
__FUNCTION__, msg_type);
return;
}
else {
HAL_LOG_VERBOSE("%s: msg_type %d", __FUNCTION__, msg_type);
}
}
switch(msg_type) {
case SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_RESP_INT_ERR:
pthread_mutex_lock(&sensor1_cb->cb_mutex);
Utility::signalResponse(true, sensor1_cb);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&sensor1_cb->cb_mutex);
break;
case SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_RESP:
sam->processResp(msg_hdr, msg_ptr);
break;
case SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_IND:
pthread_mutex_lock(&data_cb->data_mutex);
/* acquire wakelock to make sure system doesn't go into suspend
* till data/indication is received by Android */
if (sam->getFlags() & SENSOR_FLAG_WAKE_UP) {
Utility::acquire_sensor_wake_lock(data_cb, __FUNCTION__);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&data_cb->data_mutex);
sam->processInd(msg_hdr, msg_ptr);
break;
case SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_BROKEN_PIPE:
HAL_LOG_WARN("%s: SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_BROKEN_PIPE", __FUNCTION__);
if (sensor1_cb != NULL) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&sensor1_cb->cb_mutex);
Recovery::handleBrokenPipe(sensor1_cb, &SAMSensor_sensor1_cb, cb_data);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&sensor1_cb->cb_mutex);
if (sam->getAttribOK()) {
if (sam->getEnabled()) {
/* Before enable the sensor, it is better to disable the
sensor to reset the enabled variable */
sam->enable(0);
/* Re-enable the sensor */
sam->enable(1);
}
}
} else {
HAL_LOG_ERROR("%s: sensor1_cb is NULL!", __FUNCTION__);
return;
}
break;
case SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_RETRY_OPEN:
HAL_LOG_WARN("%s: SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_RETRY_OPEN", __FUNCTION__);
if (sensor1_cb != NULL) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&sensor1_cb->cb_mutex);
Recovery::reInit(sensor1_cb, &SAMSensor_sensor1_cb, cb_data);
pthread_mutex_unlock( &sensor1_cb->cb_mutex );
} else {
HAL_LOG_ERROR("%s: sensor1_cb is NULL!", __FUNCTION__);
return;
}
break;
case SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_REQ:
default:
HAL_LOG_ERROR("%s: Error - invalid msg type in cb: %u", __FUNCTION__, msg_type);
break;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&sensor1_cb->cb_mutex);
if (NULL != msg_ptr && sensor1_cb->sensor1_handle) {
sensor1_free_msg_buf(sensor1_cb->sensor1_handle, msg_ptr);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&sensor1_cb->cb_mutex);
return;
}参数cb_data里面保存了我们的sensor上报的数据。
由于底层上报的数据msg_type为,即我们的SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_IND,主动上报的,因此会进入该分支继续处理。
消息类型定义如下:
/**
* Defines the types of response messages
*/
typedef enum sensor1_msg_type_e {
SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_REQ, /**< Request */
SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_RESP, /**< Response to a request */
SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_IND, /**< Asynchronous indication */
SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_RESP_INT_ERR, /**< Error response due to internal error.
Request failed. The associated msg data is
not a valid response. The msg header should
be used to identify the failed REQ. */
SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_BROKEN_PIPE = 250,
/**< This "message type" indicates that the
message pipe to the sensors has been broken,
and the associated client handle is no longer
usable. The client should call sensor1_close()
to free the client handle. */
SENSOR1_MSG_TYPE_RETRY_OPEN = 251
/**< This "message type" will be used if sensor1_open returns
SENSOR1_WOULDBLOCK. This indicates that the sensor client may now retry
calling sensor1_open to get a valid client handle. */
} sensor1_msg_type_e;最后直接call其processInd方法进一步处理上报的数据,该方法在SAMSensor中未虚方法,因此需要对应的子类具体实现,我们现在上报的是StepCounter类的数据,因此,会进入到StepCounter类中的processInd方法中处理,而这里处理了数据后会将数据通过Utility::insertQueue(&la_sample)方法将数据插入到我们的全局变量hal_sensor_dataq_t* Utility::q_head_ptr = NULL;队列里面去,以供poll方法可以从中读取并返回给上层使用。这样就和我们之前的逻辑推导吻合了。
我们看看hal层step counter的数据封装:
/** Indication Message; Output report from the pedometer algorithm. */
typedef struct {
/* Mandatory */
uint8_t instance_id;
/**< Identifies the algorithm instance. */
/* Mandatory */
uint32_t timestamp;
/**< Timestamp of the input with which the latest step was detected; in SSC
ticks. */
/* Mandatory */
sns_sam_ped_report_data_s_v01 report_data;
/**< Pedometer algorithm output report. */
}sns_sam_ped_report_ind_msg_v01; /* Message */typedef struct {
uint8_t step_event;
/**< Indicates whether a step has been detected since the last client-initiated
reset. If this flag is FALSE, all other output fields are to be ignored.
*/
uint8_t step_confidence;
/**< Confidence with which the latest step was detected, scaled to a percentage
(0 to 100).
*/
uint32_t step_count;
/**< Count of the steps detected since the last client-initiated reset.
*/
int32_t step_count_error;
/**< Error metric associated with the reported step count, in steps.
*/
float step_rate;
/**< Rate in Hz at which steps are detected since the last client report or
reset (whichever is latest).
*/
}sns_sam_ped_report_data_s_v01; /* Type */这里提醒一下,每一个sensor的processInd都会有具体的实现,每个sensor的数据都有自己独有的数据结构,最终都会封装转换成sensors_event_t结构体插入到queue队列中去。
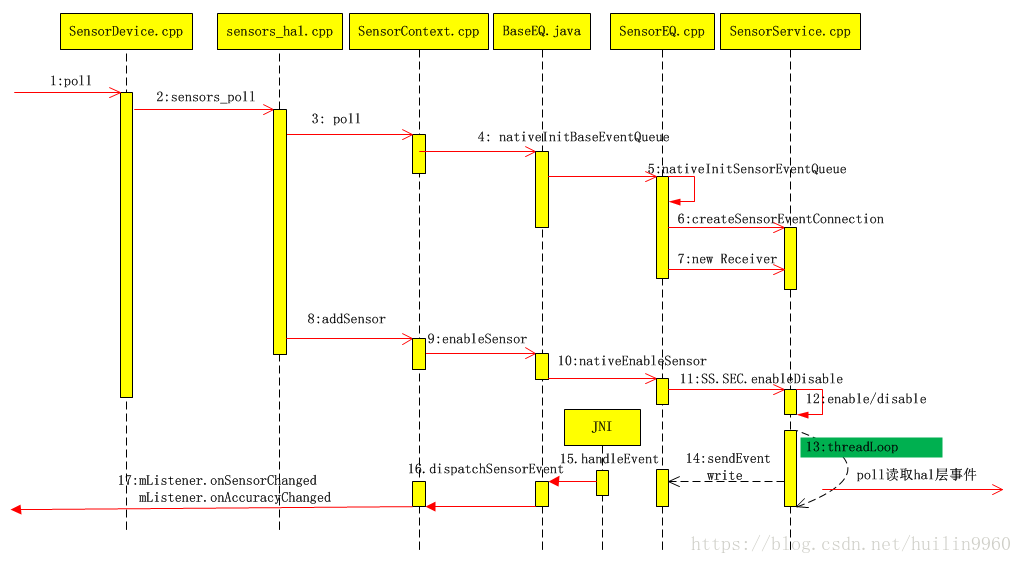
下图反映了该过程的一部分流程,关于hal层部分,我会后面补上,记得关注我哦。
到这里,hal层的数据驱动基本上就分析完,接下来我们会继续跟进hal层的数据来源,这就会涉及到SensorDaemon以及高通的aDsp芯片了,欢迎关注。