双数组字典树(DATrie)详解及实现
1.背景
Trie树本质是一个确定的有限状态自动机(DFA),核心思想是空间换时间,利用字符串的公共前缀来降低查询时间的开销以达到提高效率的目的。但由于Trie树的稀疏现象严重,空间利用率较低为了让Trie树实现占用较少的空间,同时还要保证查询的效率,最后提出了用2个线性数组来进行Trie树的表示,即双数组Trie(Double Array Trie).
2.算法及公式解析
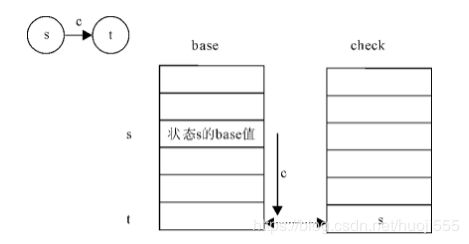
base[s] + c = t
check[t] = s
往往读到这里,大家都是一头雾水,不知所云,我们首先了解下base和check代表的意义及作用
base数组的每个元素表示一个
Trie节点,即一个状态(分为空闲状态和占用状态)
check数组的每个元素表示某个状态的前驱状态
现在我们分析一下以上出现的公式
base树组中的
s代表当前状态的下标,t代表转移状态的下标,c代表输入字符的数值base[s] + c = t //表示一次状态转移
由于转移后状态下标为
t,且父子关系是唯一的,所以可通过检验当前元素的前驱状态确定转移是否成功check[t] = s //检验状态转移是否成功
那么这种算法相对于传统的Trie树的优点是,只需要一个加法一次比较即可完成一次状态转移,只花费了常数时间,下面给出了双数组Trie树的原理图(注意观察状态转移的过程)
4.状态冲突及解决方案(划重点)
说的简单一点,状态冲突的意思就是,进行状态转移时,发现转换的位置base[t]已经被人占了(状态冲突),那你怎么办呢,重新改变c值(改变父节点的转移基数),让它放在base数组中未被占用的位置
解决方案,用while函数由发生冲突的位置向前遍历,一旦发现有空位置便占用并更新转移基数(也就是c值),可以把这个过程看作为公交车上从后往前占座的过程
构造字典时,如果有新词加入,若新词的首字未出现,写入时有冲突的情况下,导致根节点的转移基数改变,会导致重构整个树的情况(否则不能进行正确的状态转移),所以构建树时建议先构建每个词的首字,再构建各个词的子节点,这样产生冲突的情况下,可以将冲突局限在单个父节点和子节点之间,不至于大范围的节点重构
5.叶子节点的构造与处理
下面介绍几种处理叶子节点的处理方案:
- 将每个词的词尾设置为特殊字符(/0),因为最后一个字已经不需要状态转移,所以可以这样构造,但是增加了节点的数量,构建字典时会造成消耗
- 将每个词的词尾设置为转移基数的负数(只有词尾为负值),这样能够节省构建时间,不过进行转移时要将状态转移函数改为
|base[s]|+code(字符)
我们的实现中采用后一种构建方案
6.双字典树结构
private final int ARRAY_SIZE = 655350; //数组大小
private final int BASE_ROOT = 1; //base根节点状态
private final int BASE_NULL = 0; //base空闲状态
private final int CHECK_ROOT = -1; //check根节点状态
private final int CHECK_NULL = -2; //check空闲状态
private TrieNode base[];
private int check[];
/**
* @author: Ragty
* @Date: 2020/3/5 16:05
* @Description: DATrie节点
*/
public class TrieNode {
private int transferRatio; //转移基数
private boolean isLeaf = false; //是否为叶子节点
private Character label = null; //节点标识即插入的字符本身
private int value = -1; //当该节点为叶子节点时关联的字典表中对应词条的索引号
public int getTransferRatio() {
return transferRatio;
}
public void setTransferRatio(int transferRatio) {
this.transferRatio = transferRatio;
}
public boolean isLeaf() {
return isLeaf;
}
public void setLeaf(boolean leaf) {
isLeaf = leaf;
}
public Character getLabel() {
return label;
}
public void setLabel(Character label) {
this.label = label;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
7.双字典树的构建
这里说一句,构建的准则是,先构建每个词的首字,后构建每个词的剩余节点
/**
* @author: Ragty
* @Date: 2020/3/10 19:37
* @Description: 构造DATrie
*/
public void build(List<String> words) {
init();
boolean shut = false;
for (int idx = 0; idx < words.size(); idx++)
{
int startState = 0;
char chars[] = words.get(idx).toCharArray();
if (shut == false) {
TrieNode node = insert(startState, getCode(chars[0]), (chars.length == 1), idx);
node.setLabel(chars[0]);
} else {
for (int j=1; j<chars.length; j++) {
startState = transfer(startState, getCode(chars[j-1]));
TrieNode node = insert(startState, getCode(chars[j]), (chars.length == j+1), idx);
node.setLabel(chars[j]);
}
}
if (idx == words.size()-1 && shut == false) {
idx = -1; //因为开始的时候还有一个加的过程
shut = true;
}
}
}
/**
* @author: Ragty
* @Date: 2020/3/5 16:06
* @Description: 初始化DATrie(base,check数组全部初始化)
*/
private void init() {
base = new TrieNode[ARRAY_SIZE];
check = new int[ARRAY_SIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++) {
TrieNode node = new TrieNode();
node.setTransferRatio(BASE_NULL);
base[i] = node;
check[i] = CHECK_NULL;
}
TrieNode root = new TrieNode();
root.setTransferRatio(BASE_ROOT);
base[0] = root;
check[0] = CHECK_ROOT;
}
8.双数组字典树的插入
插入时,有冲突需要解决冲突,无冲突再检查是否为叶子节点,最后进行状态转移
/**
* @author: Ragty
* @Date: 2020/3/5 18:49
* @Description: 根据起始状态和转移技术插入新节点并返回插入的节点
* @param startState 起始状态
* @param offset 状态偏移量
* @param isLeaf 是否为叶子节点
* @param idx 当前节点在词典中的索引号
*/
private TrieNode insert(int startState, int offset, boolean isLeaf, int idx) {
int endState = transfer(startState, offset); //状态转移
if (base[endState].getTransferRatio() != BASE_NULL && check[endState] != startState) { //已被占用
do {
endState += 1;
} while (base[endState].getTransferRatio() != BASE_NULL);
base[startState].setTransferRatio(endState - offset); //改变父节点转移基数
}
if (isLeaf) {
base[endState].setTransferRatio(Math.abs(base[startState].getTransferRatio())*-1); //叶子节点转移基数标识为父节点转移基数的相反数
base[endState].setLeaf(true);
base[endState].setValue(idx); //为叶子节点时需要记录下该词在字典中的索引号
} else {
if (base[endState].getTransferRatio() == BASE_NULL) { //未有节点经过
base[endState].setTransferRatio(Math.abs(base[startState].getTransferRatio())); //非叶子节点的转移基数一定为正
}
}
check[endState] = startState;//check中记录当前状态的父状态
return base[endState];
}
9.双数组字典树的查询
这里我写的比较简单,用正向匹配做的,这里比较关键的一句是这个
base[endState].getTransferRatio() != BASE_NULL && check[endState] == startState
可以检测出节点是否在树上
/**
* @author: Ragty
* @Date: 2020/3/5 18:54
* @Description: 查询匹配项(正向匹配)
*/
public List<Integer> match(String keyWord) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int startState, endState;
char chars[] = keyWord.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
startState = 0;
for (int j = i; j < chars.length; j++) {
endState = transfer(startState, getCode(chars[j]));
if (base[endState].getTransferRatio() != BASE_NULL && check[endState] == startState) { //节点存在于 Trie 树上
if (base[endState].isLeaf()) {
if (!result.contains(base[endState].getValue())) {
result.add(base[endState].getValue());
}
}
startState = endState;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
10.双数组字典树测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> words = new ArrayList<String>();
words.add("清华");
words.add("清华大学");
words.add("清新");
words.add("中华");
words.add("中华人民");
words.add("华人");
words.add("学生");
words.add("大学生");
words.add("wo");
words.add("shi");
words.add("human");
words.add("this");
words.add("is");
words.add("ragty");
words.add("pump");
words.add("it");
words.add("up");
words.add("中国");
words.add("人名");
words.add("中国人民");
words.add("人民");
words.add("java");
words.add("java学习");
//构建 Trie 树
DATrie daTrie = new DATrie();
daTrie.build(words);
daTrie.printTrie();
String keyWord = "清华大学生都是华人";
List<Integer> result = daTrie.match(keyWord);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("输入语句为:"+keyWord);
//打印匹配结果
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("Match: {");
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
if (i == 0) {
System.out.printf("%s", words.get(result.get(i)));
} else {
System.out.printf(", %s", words.get(result.get(i)));
}
}
System.out.printf("}");
System.out.println();
}
11.测试结果
idx 0 98 99 100 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 20014 20099 20155 20156 20157 20158 21327 21328 21329 21518 22272 22824 22825 23399 23400 23401 23433 26034 27666 27668 27669 28166 29984 29986
char null a a a g h i j h i h m o p n r s t u u w i s t u m t p y p v s a 中 习 人 人 人 人 华 华 华 名 国 大 大 学 学 学 学 新 民 民 民 清 生 生
base 1 1 4 12 7 2 10 3 4 -4 16 2 -1 7 -4 1 4 6 15 2 1 16 -7 7 16 17 -10 -15 -7 -17 35 -16 -35 3 -35 1 -2 3 4 2 -2 -3 -1 4 3 2 1 -2 3 35 -2 -1 -3 -4 2 -1 -3
check -1 115 111 107 98 0 0 0 116 108 117 119 120 0 99 0 0 0 0 105 0 110 106 104 113 124 106 118 123 125 100 121 130 0 23433 0 21327 21329 22272 0 28166 20014 20155 20014 0 21328 0 22825 22824 132 28166 20155 20157 20158 0 23399 23401
leaf 否 否 否 否 否 否 否 否 否 是 否 否 是 否 是 否 否 否 否 否 否 否 是 否 否 否 是 是 是 是 否 是 是 否 是 否 是 否 否 否 是 是 是 是 否 否 否 是 否 否 是 是 是 是 否 是 是
idx -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 9 -1 -1 8 -1 10 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 12 -1 -1 -1 15 16 13 14 -1 11 21 -1 22 -1 5 -1 -1 -1 0 3 18 17 -1 -1 -1 1 -1 -1 2 20 4 19 -1 6 7
[0, 1, 7, 6, 5]
输入语句为:清华大学生都是华人
Match: {清华, 清华大学, 大学生, 学生, 华人}
12.总结
我刚开始写的时候没有任何头绪,看到那两个公式一头雾水,查了很多博客也写得一知半解,而且没有公式解析和实现代码。经过查阅文献以及自己的思考,有了这篇文章,希望能帮到更多想了解
DATrie的人。任何事情你清楚他要解决的问题和实现原理后,会发现它很简单。就像
DATrie,它的难点在于核心公式的理解以及对于冲突的解决方案。只要理解了这个,实现是很简单的一件事。
13.完整代码(可直接运行)
package Dictionary;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
public class DATrie {
private final int ARRAY_SIZE = 655350; //数组大小
private final int BASE_ROOT = 1; //base根节点状态
private final int BASE_NULL = 0; //base空闲状态
private final int CHECK_ROOT = -1; //check根节点状态
private final int CHECK_NULL = -2; //check空闲状态
private TrieNode base[];
private int check[];
/**
* @author: Ragty
* @Date: 2020/3/5 16:05
* @Description: DATrie节点
*/
public class TrieNode {
private int transferRatio; //转移基数
private boolean isLeaf = false; //是否为叶子节点
private Character label = null; //节点标识即插入的字符本身
private int value = -1; //当该节点为叶子节点时关联的字典表中对应词条的索引号
public int getTransferRatio() {
return transferRatio;
}
public void setTransferRatio(int transferRatio) {
this.transferRatio = transferRatio;
}
public boolean isLeaf() {
return isLeaf;
}
public void setLeaf(boolean leaf) {
isLeaf = leaf;
}
public Character getLabel() {
return label;
}
public void setLabel(Character label) {
this.label = label;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
/**
* @author: Ragty
* @Date: 2020/3/10 19:37
* @Description: 构造DATrie
*/
public void build(List<String> words) {
init();
boolean shut = false;
for (int idx = 0; idx < words.size(); idx++)
{
int startState = 0;
char chars[] = words.get(idx).toCharArray();
if (shut == false) {
TrieNode node = insert(startState, getCode(chars[0]), (chars.length == 1), idx);
node.setLabel(chars[0]);
} else {
for (int j=1; j<chars.length; j++) {
startState = transfer(startState, getCode(chars[j-1]));
TrieNode node = insert(startState, getCode(chars[j]), (chars.length == j+1), idx);
node.setLabel(chars[j]);
}
}
if (idx == words.size()-1 && shut == false) {
idx = -1; //因为开始的时候还有一个加的过程
shut = true;
}
}
}
/**
* @author: Ragty
* @Date: 2020/3/5 18:54
* @Description: 查询匹配项(正向匹配)
*/
public List<Integer> match(String keyWord) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int startState, endState;
char chars[] = keyWord.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
startState = 0;
for (int j = i; j < chars.length; j++) {
endState = transfer(startState, getCode(chars[j]));
if (base[endState].getTransferRatio() != BASE_NULL && check[endState] == startState) { //节点存在于 Trie 树上
if (base[endState].isLeaf()) {
if (!result.contains(base[endState].getValue())) {
result.add(base[endState].getValue());
}
}
startState = endState;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* @author: Ragty
* @Date: 2020/3/5 19:00
* @Description: 打印DATrie
*/
public void printTrie() {
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("%5s", "idx");
for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++) {
if (base[i].getTransferRatio() != BASE_NULL) {
System.out.printf("%7d\t", i);
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("%5s", "char");
for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++) {
if (base[i].getTransferRatio() != BASE_NULL) {
System.out.printf("%7c\t", base[i].getLabel());
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("%5s", "base");
for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++) {
if (base[i].getTransferRatio() != BASE_NULL) {
System.out.printf("%7d\t", base[i].getTransferRatio());
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("%5s", "check");
for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++) {
if (base[i].getTransferRatio() != BASE_NULL) {
System.out.printf("%7d\t", check[i]);
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("%5s", "leaf");
for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++) {
if (base[i].getTransferRatio() != BASE_NULL) {
System.out.printf("%7s\t", base[i].isLeaf() ? "是" : "否");
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("%5s", "idx");
for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++) {
if (base[i].getTransferRatio() != BASE_NULL) {
System.out.printf("%7d\t", base[i].getValue());
}
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* @author: Ragty
* @Date: 2020/3/5 18:49
* @Description: 根据起始状态和转移技术插入新节点并返回插入的节点
* @param startState 起始状态
* @param offset 状态偏移量
* @param isLeaf 是否为叶子节点
* @param idx 当前节点在词典中的索引号
*/
private TrieNode insert(int startState, int offset, boolean isLeaf, int idx) {
int endState = transfer(startState, offset); //状态转移
if (base[endState].getTransferRatio() != BASE_NULL && check[endState] != startState) { //已被占用
do {
endState += 1;
} while (base[endState].getTransferRatio() != BASE_NULL);
base[startState].setTransferRatio(endState - offset); //改变父节点转移基数
}
if (isLeaf) {
base[endState].setTransferRatio(Math.abs(base[startState].getTransferRatio())*-1); //叶子节点转移基数标识为父节点转移基数的相反数
base[endState].setLeaf(true);
base[endState].setValue(idx); //为叶子节点时需要记录下该词在字典中的索引号
} else {
if (base[endState].getTransferRatio() == BASE_NULL) { //未有节点经过
base[endState].setTransferRatio(Math.abs(base[startState].getTransferRatio())); //非叶子节点的转移基数一定为正
}
}
check[endState] = startState;//check中记录当前状态的父状态
return base[endState];
}
/**
* @author: Ragty
* @Date: 2020/3/5 18:53
* @Description: 根据起始状态和转移基数返回结束状态
*/
private int transfer(int startState, int offset) {
return Math.abs(base[startState].getTransferRatio())+offset; //状态转移
}
/**
* @author: Ragty
* @Date: 2020/3/5 19:13
* @Description: 获取base数组的下标
*/
private int getCode(char c) {
return (int)c;//这里必须大于0
}
/**
* @author: Ragty
* @Date: 2020/3/5 16:06
* @Description: 初始化DATrie(base,check数组全部初始化)
*/
private void init() {
base = new TrieNode[ARRAY_SIZE];
check = new int[ARRAY_SIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++) {
TrieNode node = new TrieNode();
node.setTransferRatio(BASE_NULL);
base[i] = node;
check[i] = CHECK_NULL;
}
TrieNode root = new TrieNode();
root.setTransferRatio(BASE_ROOT);
base[0] = root;
check[0] = CHECK_ROOT;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> words = new ArrayList<String>();
words.add("清华");
words.add("清华大学");
words.add("清新");
words.add("中华");
words.add("中华人民");
words.add("华人");
words.add("学生");
words.add("大学生");
words.add("wo");
words.add("shi");
words.add("human");
words.add("this");
words.add("is");
words.add("ragty");
words.add("pump");
words.add("it");
words.add("up");
words.add("中国");
words.add("人名");
words.add("中国人民");
words.add("人民");
words.add("java");
words.add("java学习");
//构建 Trie 树
DATrie daTrie = new DATrie();
daTrie.build(words);
daTrie.printTrie();
String keyWord = "清华大学生都是华人";
List<Integer> result = daTrie.match(keyWord);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("输入语句为:"+keyWord);
//打印匹配结果
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("Match: {");
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
if (i == 0) {
System.out.printf("%s", words.get(result.get(i)));
} else {
System.out.printf(", %s", words.get(result.get(i)));
}
}
System.out.printf("}");
System.out.println();
}
}
参考文献
1.小白详解Trie树
2.《基于双数组Trie树算法的字典改进和实现》
3.Theppitak Karoonboonyanan, An Implementation of Double-Array Trie.