数据结构与算法——栈和队列
栈
定义
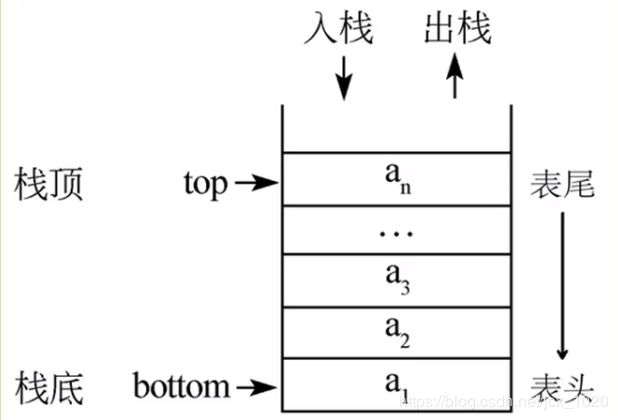
栈是一种只允许在一端进行插入和删除的线性表,它是一种操作受限的线性表。
表中只允许进行插入和删除的一端称为栈顶(top),另一端称为栈低(bottom)。
栈的插入操作称为进栈(push),栈的删除操作称为出栈(pop)。
特点:先进后出。
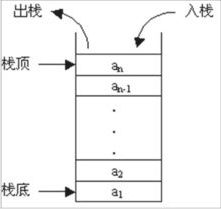
栈的顺序存储结构
public class SeqStack<T> {
//存储栈数据元素的数组
private Object element[];
//栈顶元素下标
private int top;
//构造容量为size的栈
public SeqStack(int size) {
this.element = new Object[Math.abs(size)];
this.top = -1;
}
//设置默认容量的栈
public SeqStack() {
this(64);
}
}
进栈:
public void push(T x) {
if (x == null) {
return;
}
//若栈满,扩容
if (this.top == element.length - 1) {
Object[] temp = this.element;
this.element = new Object[temp.length * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {
this.element[i] = temp[i];
}
}
this.top++;
this.element[this.top] = x;
}
弹栈:
public T pop() {
return this.top == -1 ? null : (T) this.element[this.top--];
}
栈的链式存储结构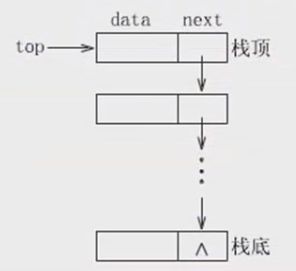
链式栈的定义:
public class LinkedStack<T> {
//栈顶点结点(声明见《数据结构与算法——线性表》)
private Node<T> top;
//构造空栈
public LinkedStack() {
this.top = null;
}
}
进栈:
public void push(T x) {
if (x != null) {
this.top = new Node(x, this.top);
}
}
弹栈:
public T pop() {
if (this.top == null) {
return null;
}
T temp = this.top.data;
this.top = this.top.next;
return temp;
}
源码
Stack的源码:
public
class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {
/**
* Creates an empty Stack.
*/
public Stack() {
}
/**
* Pushes an item onto the top of this stack. This has exactly
* the same effect as:
*
* addElement(item)
*
* @param item the item to be pushed onto this stack.
* @return the item argument.
* @see java.util.Vector#addElement
*/
public E push(E item) {
addElement(item);
return item;
}
/**
* Removes the object at the top of this stack and returns that
* object as the value of this function.
*
* @return The object at the top of this stack (the last item
* of the Vector object).
* @throws EmptyStackException if this stack is empty.
*/
public synchronized E pop() {
E obj;
int len = size();
obj = peek();
removeElementAt(len - 1);
return obj;
}
/**
* Looks at the object at the top of this stack without removing it
* from the stack.
*
* @return the object at the top of this stack (the last item
* of the Vector object).
* @throws EmptyStackException if this stack is empty.
*/
public synchronized E peek() {
int len = size();
if (len == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
return elementAt(len - 1);
}
/**
* Tests if this stack is empty.
*
* @return true if and only if this stack contains
* no items; false otherwise.
*/
public boolean empty() {
return size() == 0;
}
/**
* Returns the 1-based position where an object is on this stack.
* If the object o occurs as an item in this stack, this
* method returns the distance from the top of the stack of the
* occurrence nearest the top of the stack; the topmost item on the
* stack is considered to be at distance 1. The equals
* method is used to compare o to the
* items in this stack.
*
* @param o the desired object.
* @return the 1-based position from the top of the stack where
* the object is located; the return value -1
* indicates that the object is not on the stack.
*/
public synchronized int search(Object o) {
int i = lastIndexOf(o);
if (i >= 0) {
return size() - i;
}
return -1;
}
/** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1224463164541339165L;
}
练习题:逆波兰表达式
https://github.com/jcx-1020/Algorithm/blob/master/src/com/jcx/algorithm_stack_queue/ReversePolishNotation.java
队列
定义
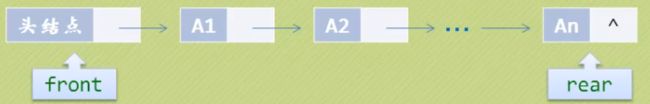
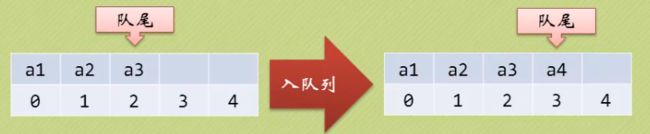
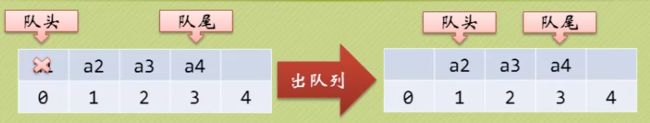
只允许在一端进行插入操作,而在另一端进行删除操作的线性表。
特点:先进先出。

队列的链式存储结构
public class LinkedQueue<T> {
//队头、队尾结点(声明见《数据结构与算法——线性表》)
private Node<T> front, rear;
//构造空队列
public LinkedQueue() {
this.front = this.rear = null;
}
}
入队列(采用c语言描述):
p -> data = x;
p -> next = null;
q -> rear -> next = p;
q -> rear = p;
出队列(采用c语言描述):
p = q -> front -> next;
*x = p -> data;
q -> front -> next = p -> next;
队列的顺序存储结构
循环队列
将队列的数据区看成头尾相接的循环结构,即规定最后一个单元的后继为第一个单元,这样整个数据区就像一个环,称之为循环队列。
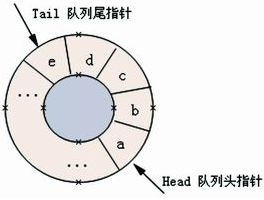
初始化循环队列(采用c语言描述):
q -> front = q -> rear = 0;
入队列(采用c语言描述):
q -> rear = (q -> rear + 1) % MAXSIZE;
q -> data[q -> rear] = x;
出队列(采用c语言描述):
q -> front = (q -> front + 1) % MAXSIZE;
*x = q -> data[q -> front];
源码
Queue的源码:
public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> {
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this queue if it is possible to do so
* immediately without violating capacity restrictions, returning
* {@code true} upon success and throwing an {@code IllegalStateException}
* if no space is currently available.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @throws IllegalStateException if the element cannot be added at this
* time due to capacity restrictions
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this queue
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and
* this queue does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of this element
* prevents it from being added to this queue
*/
boolean add(E e);
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this queue if it is possible to do
* so immediately without violating capacity restrictions.
* When using a capacity-restricted queue, this method is generally
* preferable to {@link #add}, which can fail to insert an element only
* by throwing an exception.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} if the element was added to this queue, else
* {@code false}
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this queue
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and
* this queue does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of this element
* prevents it from being added to this queue
*/
boolean offer(E e);
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head of this queue. This method differs
* from {@link #poll poll} only in that it throws an exception if this
* queue is empty.
*
* @return the head of this queue
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty
*/
E remove();
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head of this queue,
* or returns {@code null} if this queue is empty.
*
* @return the head of this queue, or {@code null} if this queue is empty
*/
E poll();
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue. This method
* differs from {@link #peek peek} only in that it throws an exception
* if this queue is empty.
*
* @return the head of this queue
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty
*/
E element();
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue,
* or returns {@code null} if this queue is empty.
*
* @return the head of this queue, or {@code null} if this queue is empty
*/
E peek();
}
ArrayQueue的源码:
public class ArrayQueue<T> extends AbstractList<T> {
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity + 1;
this.queue = newArray(capacity + 1);
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
}
public void resize(int newcapacity) {
int size = size();
if (newcapacity < size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Resizing would lose data");
newcapacity++;
if (newcapacity == this.capacity)
return;
T[] newqueue = newArray(newcapacity);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
newqueue[i] = get(i);
this.capacity = newcapacity;
this.queue = newqueue;
this.head = 0;
this.tail = size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private T[] newArray(int size) {
return (T[]) new Object[size];
}
public boolean add(T o) {
queue[tail] = o;
int newtail = (tail + 1) % capacity;
if (newtail == head)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue full");
tail = newtail;
return true; // we did add something
}
public T remove(int i) {
if (i != 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can only remove head of queue");
if (head == tail)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue empty");
T removed = queue[head];
queue[head] = null;
head = (head + 1) % capacity;
return removed;
}
public T get(int i) {
int size = size();
if (i < 0 || i >= size) {
final String msg = "Index " + i + ", queue size " + size;
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(msg);
}
int index = (head + i) % capacity;
return queue[index];
}
public int size() {
// Can't use % here because it's not mod: -3 % 2 is -1, not +1.
int diff = tail - head;
if (diff < 0)
diff += capacity;
return diff;
}
private int capacity;
private T[] queue;
private int head;
private int tail;
}
练习题:逆波兰计算器
https://github.com/jcx-1020/Algorithm/blob/master/src/com/jcx/algorithm_stack_queue/ReversePolishNotationCalculate.java