(数据结构)图的应用,一个简单的学校地图.包含的内容:图的最短路径算法 和 图的深度优先遍历算法
数据结构,图的应用实例,一个简单的学校地图.
其中包含的内容:图的最短路径算法(迪杰斯特拉算法) 和 图的深度优先遍历算法
其中程序功能: 1.存储简单的学校地图并显示; 2.给出一个点,能够输出从此点到其他顶点的最短路径及最短距离; 3.给出两个顶点,能够输出次两点之间所有路径及距离 和 最短路径及距离
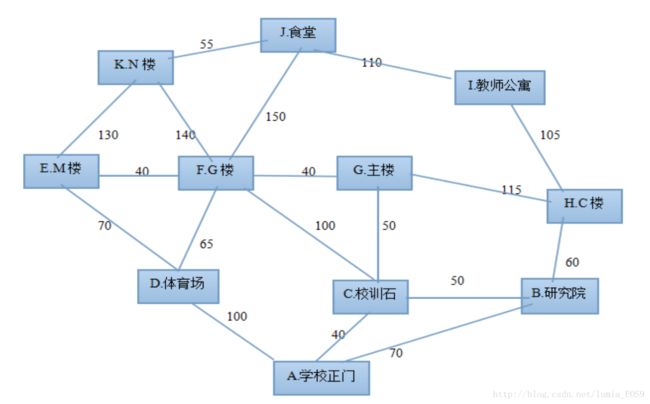
学校地图:(建立图的基础,看着这个图会容易理解一点)
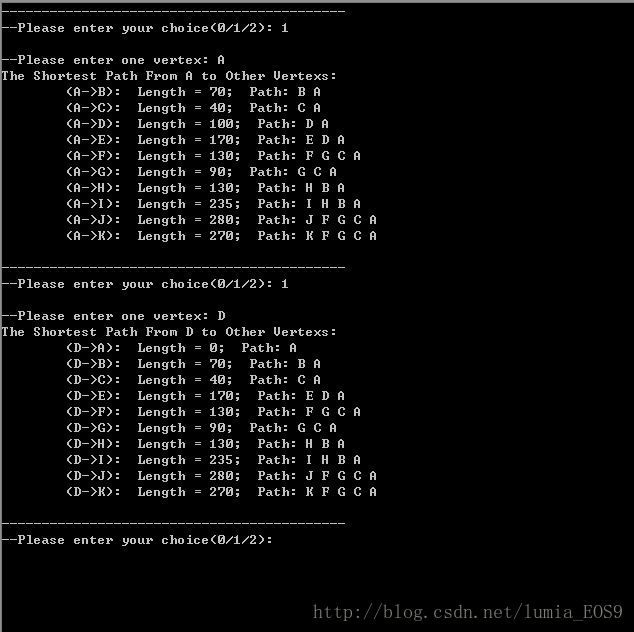
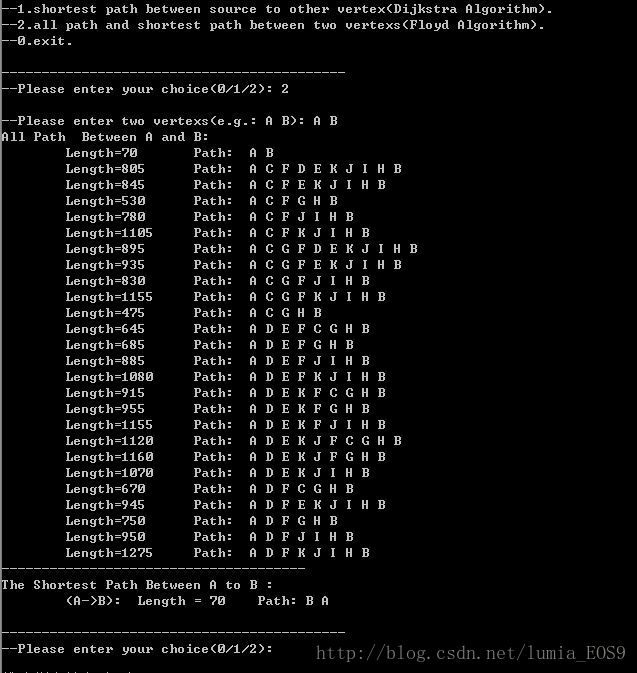
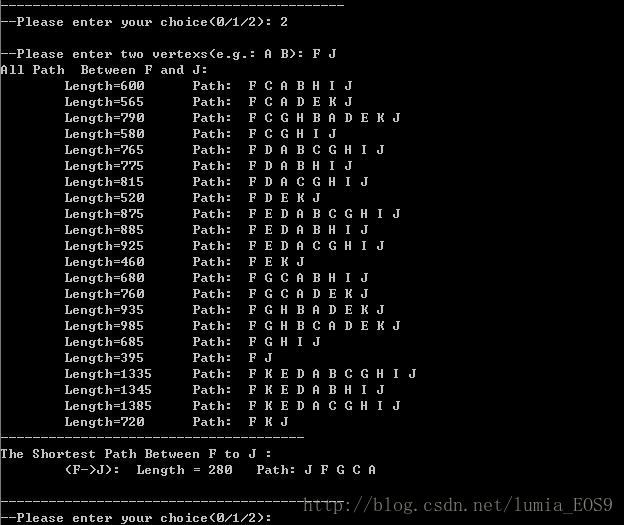
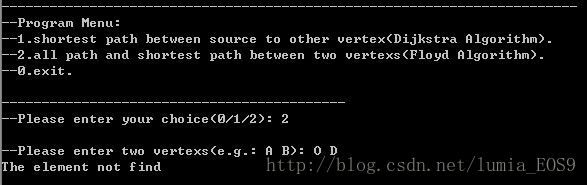
程序运行结果截图:
废话不说,直接上程序源码. 自己需要的地方可以看一下源码,找一下自己需要的地方
我写的代码是用C++干着面向过程的勾当...真心觉得自己能力不咋滴...贴出代码, 大家有需要的函数可以参考一下原理.
程序源码:
main.cpp
#include "GraphList.h"
int main()
{
GraphList graphList;//图
int choice;//存放用户的选择
char element_1, element_2;
int locate_1, locate_2;
int Path[MAX_VERTEX_NUM], Dest[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
bool DIJFlag = false;//标记是否进行过了DIJ算法
createGraph(graphList);
cout << "A.学校正门, B.研究院, C.校训石, D.体育场, E.M楼, F.G楼, G.主楼, H.C楼, I.教师公寓, J.食堂, K.N楼\n"
<< "\n--The output formate: (Source,Destination,Value)"
<< "\n------------------------------------------------------------------------"
<< "\n--The Graph have been created:";
printGraph(graphList);
cout << "\n------------------------------------------------------------------------"
<< "\n--Program Menu:"
<< "\n--1.shortest path between source to other vertex(Dijkstra Algorithm)."
<< "\n--2.all path and shortest path between two vertexs(Floyd Algorithm)."
<< "\n--0.exit."
<< "\n\n-------------------------------------------"
<< "\n--Please enter your choice(0/1/2): ";
cin >> choice;
while(choice != 0)
{
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
cout << "\n--Please enter one vertex: ";
cin >> element_1;
if((locate_1=findNode(graphList, element_1)) == -1) return 0;
if(!DIJFlag)//如果没有进行了DIJ算法查找最短路径
{
shortestPath_DIJ(graphList, locate_1, Path, Dest);
DIJFlag = true;
}
printShortestPath_DIJ(graphList, locate_1, Path, Dest);
break;
case 2:
cout << "\n--Please enter two vertexs(e.g.: A B): ";
cin >> element_1 >> element_2;
locate_1 = findNode(graphList, element_1);
locate_2 = findNode(graphList, element_2);
if((locate_1==-1) || (locate_2==-1)) return 0;
if(!DIJFlag)//如果没有进行了DIJ算法查找最短路径
{
shortestPath_DIJ(graphList, locate_1, Path, Dest);
DIJFlag = true;
}
cout << "All Path Between " << element_1 << " and " << element_2 << ":";
allPath_2Vexs(graphList, locate_1, locate_2);//输出所有路径
cout << "\n--------------------------------------";
printShortestPath_2Vexs(graphList, locate_1, locate_2, Path, Dest);
break;
default:
cout << "--Your input unavailable!\n";
return 0;
}
cout << "\n\n-------------------------------------------"
<< "\n--Please enter your choice(0/1/2): ";
cin >> choice;
}
deleteGraph(graphList);//删除图,防止内存泄露
return 0;
}GraphList.h
#ifndef GRAPHLIST_H_INCLUDED
#define GRAPHLIST_H_INCLUDED
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 11//最大支持的节点数
#define INFINITY 1000//表示无穷大
typedef int EdgeValueType;//定义边权重类型
typedef char VertexType;//定义顶点表顶点的内容类型
typedef struct EdgeNode//边表节点
{
int adjvexLocate;//该弧所指向的顶点在定点表中的位置
EdgeValueType value;//权重
EdgeNode *next;//指向下一个节点
} EdgeNode;
typedef struct VertexNode//顶点表
{
VertexType data;//顶点名称
EdgeNode *firstarc;//指向第一条依附顶点的指针
} VertexNode, VertexList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; //顶点节点,顶点表
typedef struct GraphList
{
VertexList vertexList;//建立顶点表
int vertexNum, edgeNum;//整个图中存放顶点、边的个数
} GraphList;
//函数声明
int findNode(GraphList &graphList, char element);
bool createGraph(GraphList &graphList);
bool printGraph(GraphList &graphList);
void shortestPath_DIJ(GraphList &graphList, int vex, int P[], int D[]);//单源最短路径算法
void printShortestPath_DIJ(GraphList &graphList, int vex, int Path[], int Dest[]);//打印出生成的单源最短路径
void printShortestPath_2Vexs(GraphList &graphList, int vex1, int vex2, int Path[], int Dest[]);//打印两点之间最短路径及距离
void allPath_2Vexs(GraphList &graphList, int startVex, int endVex);//任意两点之间的所有路径
void visit(GraphList &graphList, int vex, int endVex, bool status[], vector &pathStack, int length);
bool deleteGraph(GraphList &graphList);//销毁图,防止内存泄露
#endif // GRAPHLIST_H_INCLUDED
GraphList.cpp
#include "GraphList.h"
int findNode(GraphList &graphList, char element)//查找顶点,工具方法
{
int i;
for(i=0; i= graphList.vertexNum)
{
cout << "The element not find\n";
return -1;
}
return i;
}
bool createGraph(GraphList &graphList)//创建图,并执行初始化
{
//为了方便,所有顶点以及边都已经在程序内部定义好了
//初始化定点表
graphList.vertexNum = 0;//顶点数
graphList.edgeNum = 0;//边数
int value = 0;//暂时存放从邻接矩阵中读取的数值
char vexArray[MAX_VERTEX_NUM] = {'A','B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K'};
for(int v=0; vadjvexLocate = j;
Node->value = value;
Node->next = NULL;//生成节点
graphList.edgeNum++;
if(graphList.vertexList[i].firstarc == NULL)//第一个节点
{
graphList.vertexList[i].firstarc = Node;
temp = Node;
}
else
{
temp->next = Node;
temp = Node;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
bool printGraph(GraphList &graphList)//输出图
{
EdgeNode *temp = NULL;
//if(!&graphList) return false;
for(int i=0; iadjvexLocate].data << ","
<< temp->value << ") ";
temp = temp->next;
}
}
return true;
}
void shortestPath_DIJ(GraphList &graphList, int vex, int Path[], int Dest[])///单源最短路径算法
{
bool finalShortest[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
EdgeNode *temp = NULL;
int minValue = INFINITY;//用作寻找最小的路径权值
int v = 0;//记录每一次寻找的最小路径终点的位置
for(int i=0; iadjvexLocate] = temp->value;
Path[temp->adjvexLocate] = vex;//前驱
temp = temp->next;
}//初始化完成
for(int i=1; iadjvexLocate == j)
{
vValue = temp->value;
break;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
if(!finalShortest[j] && (minValue+vValue= INFINITY || i == vex) continue;
cout << "\n\t(" << graphList.vertexList[vex].data << "->" << graphList.vertexList[i].data
<< "): Length = " << Dest[i] << "; Path: " << graphList.vertexList[i].data;
pre = Path[i];
while(pre != -1)
{
cout << " " << graphList.vertexList[pre].data;
pre = Path[pre];
}
}
}
//打印两点之间最短路径及距离
void printShortestPath_2Vexs(GraphList &graphList, int vex1, int vex2, int Path[], int Dest[])
{
int pre = 0;
cout << "\nThe Shortest Path Between " << graphList.vertexList[vex1].data << " to "
<< graphList.vertexList[vex2].data << " :";
for(int i=0; i" << graphList.vertexList[vex2].data
<< "): Length = " << Dest[i] << "\tPath: " << graphList.vertexList[i].data;
pre = Path[i];
while(pre != -1)
{
cout << " " << graphList.vertexList[pre].data;
pre = Path[pre];
}
return;
}
}
}
bool deleteGraph(GraphList &graphList)//销毁图
{
if(graphList.vertexNum == 0) return false;
EdgeNode *temp = NULL;
for(int i=0; inext;
delete temp;
temp = graphList.vertexList[i].firstarc;
}
}
return true;
}
void allPath_2Vexs(GraphList &graphList, int startVex, int endVex)
{
if(startVex == endVex)
{
return;
}
bool status[MAX_VERTEX_NUM] = {false};//标记点被访问的状态
vector pathStack;//记录访问到节点的位置
int length = 0;
visit(graphList, startVex, endVex, status, pathStack, length);
}
//递归访问每个元素
void visit(GraphList &graphList, int vex, int endVex, bool status[], vector &pathStack, int length)//对vex点进行访问
{
if(vex == endVex)//找到了终点
{
//cout << "\n\tLength=" << pathStack.size()+1 << "\tPath: ";
cout << "\n\tLength=" << length << "\tPath: ";
for(unsigned int i=0; inext)
{
if(!status[current->adjvexLocate])
{
length += current->value;
visit(graphList, current->adjvexLocate, endVex, status, pathStack, length);
}
}
status[vex] = false;//修改标志
pathStack.pop_back();//回溯
}