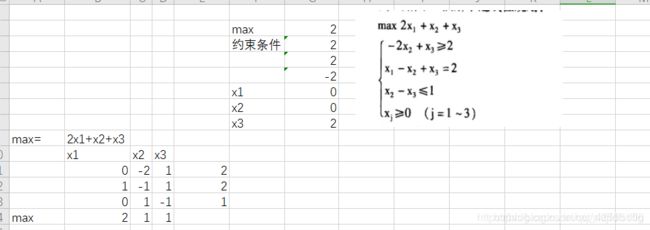
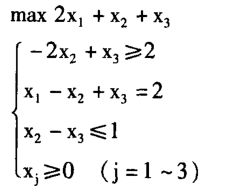大M法的python求解
大M法的python编程求解
- 一、大M法的python求解
- python求解
- 三、利用python包scipyd 优化包optimize
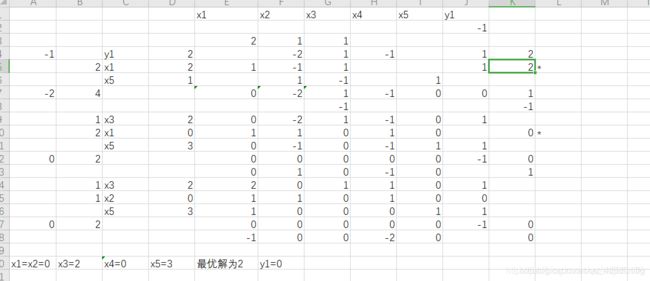
- 四、Excel求解
一、大M法的python求解
残差对应的是对偶问题可行条件,小于0表示对偶问题还不可行,需要继续探索。
接下来的问题是具体选择哪个基变量和哪个非基变量进行对换。我们用启发式原则,每次将负数残差(cTN−cTBB−1N)i(cNT−cBTB−1N)i (cT_N-cT_BB^{-1}N)_i(cNT−cBTB−1N)i最小(绝对值最大)的非基变量xixi x_ixi替换为基变量,同时将(B−1b(B−1N)i)j(B−1b(B−1N)i)j (\frac{B{-1}b}{(B{-1}N)_i})j((B−1N)iB−1b)j最小值对应的基变量xjxj x_jxj替换为非基变量。这个进基/出基的过程称为pivoting。
python求解
# encoding=utf-8
import numpy as np # python 矩阵操作lib
class Simplex():
def __init__(self):
self._A = "" # 系数矩阵
self._b = "" #数组
self._c = '' # 约束
self._B = '' # 基变量的下标集合
self.row = 0 # 约束个数
def solve(self):
# 读取文件内容,文件结构前两行分别为 变量数 和 约束条件个数
# 接下来是系数矩阵
# 然后是b数组
# 然后是约束条件c
# 假设线性规划形式是标准形式(都是等式)
A = []
b = []
c = []
self._A = np.array(A, dtype=float)
self._b = np.array(b, dtype=float)
self._c = np.array(c, dtype=float)
self._A = np.array([[0,2,-1],[0,1,-1]],dtype=float)
self._b = np.array([-2,1],dtype=float)
self._A = np.array([[1,-1,1]])# 等式约束系数self._A,3x1维列向量
self._b = np.array([2])# 等式约束系数self._b,1x1数值
self._c = np.array([2,1,1],dtype=float)
self._B = []
self.row = len(self._b)
self.var = len(self._c)
(x, obj) = self.Simplex(self._A, self._b, self._c)
self.pprint(x, obj, A)
def pprint(self, x, obj, A):
px = ['x_%d = %f' % (i + 1, x[i]) for i in range(len(x))]
print(','.join(px))
print('objective value is : %f' % obj)
print('------------------------------')
for i in range(len(A)):
print('%d-th line constraint value is : %f' % (i + 1, x.dot(A[i])))
def InitializeSimplex(self, A, b):
b_min, min_pos = (np.min(b), np.argmin(b)) # 得到最小bi
# 将bi全部转化成正数
if (b_min < 0):
for i in range(self.row):
if i != min_pos:
A[i] = A[i] - A[min_pos]
b[i] = b[i] - b[min_pos]
A[min_pos] = A[min_pos] * -1
b[min_pos] = b[min_pos] * -1
# 添加松弛变量
slacks = np.eye(self.row)
A = np.concatenate((A, slacks), axis=1)
c = np.concatenate((np.zeros(self.var), np.ones(self.row)), axis=0)
# 松弛变量全部加入基,初始解为b
new_B = [i + self.var for i in range(self.row)]
# 辅助方程的目标函数值
obj = np.sum(b)
c = c[new_B].reshape(1, -1).dot(A) - c
c = c[0]
# entering basis
e = np.argmax(c)
while c[e] > 0:
theta = []
for i in range(len(b)):
if A[i][e] > 0:
theta.append(b[i] / A[i][e])
else:
theta.append(float("inf"))
l = np.argmin(np.array(theta))
if theta[l] == float('inf'):
print('unbounded')
return False
(new_B, A, b, c, obj) = self._PIVOT(new_B, A, b, c, obj, l, e)
e = np.argmax(c)
# 如果此时人工变量仍在基中,用原变量去替换之
for mb in new_B:
if mb >= self.var:
row = mb - self.var
i = 0
while A[row][i] == 0 and i < self.var:
i += 1
(new_B, A, b, c, obj) = self._PIVOT(new_B, A, b, c, obj, new_B.index(mb), i)
return (new_B, A[:, 0:self.var], b)
# 算法入口
def Simplex(self, A, b, c):
B = ''
(B, A, b) = self.InitializeSimplex(A, b)
# 函数目标值
obj = np.dot(c[B], b)
c = np.dot(c[B].reshape(1, -1), A) - c
c = c[0]
# entering basis
e = np.argmax(c)
# 找到最大的检验数,如果大于0,则目标函数可以优化
while c[e] > 0:
theta = []
for i in range(len(b)):
if A[i][e] > 0:
theta.append(b[i] / A[i][e])
else:
theta.append(float("inf"))
l = np.argmin(np.array(theta))
if theta[l] == float('inf'):
print("unbounded")
return False
(B, A, b, c, obj) = self._PIVOT(B, A, b, c, obj, l, e)
e = np.argmax(c)
x = self._CalculateX(B, A, b, c)
return (x, obj)
# 得到完整解
def _CalculateX(self, B, A, b, c):
x = np.zeros(self.var, dtype=float)
x[B] = b
return x
# 基变换
def _PIVOT(self, B, A, b, c, z, l, e):
# main element is a_le
# l represents leaving basis
# e represents entering basis
main_elem = A[l][e]
# scaling the l-th line
A[l] = A[l] / main_elem
b[l] = b[l] / main_elem
# change e-th column to unit array
for i in range(self.row):
if i != l:
b[i] = b[i] - A[i][e] * b[l]
A[i] = A[i] - A[i][e] * A[l]
# update objective value
z -= b[l] * c[e]
c = c - c[e] * A[l]
# change the basis
B[l] = e
return (B, A, b, c, z)
s = Simplex()
s.solve()
x_1 = 0.000000,x_2 = 0.000000,x_3 = 2.000000
objective value is : 2.000000
------------------------------
三、利用python包scipyd 优化包optimize
import numpy as np
from scipy import optimize as op
# 给出变量取值范围
x1=(0,None)
x2=(0,None)
x3=(0,None)
#定义给出变量,确定c,A_ub,B_ub,A_eq,B_eq
c = np.array([2,1,1])# 目标函数系数,3x1列向量
A_ub = np.array([[0,2,-1],[0,1,-1]]) # 不等式约束系数A,2x3维矩阵
B_ub = np.array([-2,1])# 等式约束系数B, 2x1维列向量
A_eq = np.array([[1,-1,1]])# 等式约束系数Aeq,3x1维列向量
B_eq = np.array([2])# 等式约束系数beq,1x1数值
#调用函数求解
res=op.linprog(c,A_ub,B_ub,A_eq,B_eq,bounds=(x1,x2,x3))#调用函数进行求解
print(res)
con: array([3.41133788e-11])
fun: 1.9999999999762483
message: 'Optimization terminated successfully.'
nit: 4
slack: array([-3.94371202e-11, 3.00000000e+00])
status: 0
success: True
x: array([2.85788627e-13, 5.03802074e-12, 2.00000000e+00])