Android进程保活全攻略(上)
对于每个公司的APP来说,当然都希望自己APP的进程尽量的不被杀死,于是乎,就有了一些列进程保活的方法出现,网上也有很多关于这类的文章,但网上很多资料往往只告诉了思路,并未将实现代码展示,本次我的博客将分为上下两篇,阐述关于进程保活的所有方法,以及实现的方式,若有错漏之处,大家可以在博客进行留言。
**
1.进程保活-背景知识
**
(1)什么时候系统会去杀死进程?
Android系统会在内存不足的时候去将进程杀死,俗称Low Memory Killer,它是 基于linux内核的 OOM Killer(Out-Of-Memory killer)机制,内存不足时,优先杀oom_adj值高的进程。
既然知道了oom_adj值,那大家肯定想知道,如何去查看应用的oom_adj值呢?
系统进程oom值小于0,应用进程大于0,可以发现,系统的就是叼
我们可以通过 adb命令,去查看相应进程的oom_adj值,命令如下:
查看命令:adb shell ps | grep 进程名 | awk ‘{print $2}’ | xargs -i adb shell cat /proc/{}/oom_adj
这里我总结了各种类型进程的oom_adj值
![]()
(2)进程被杀的场景有哪些?
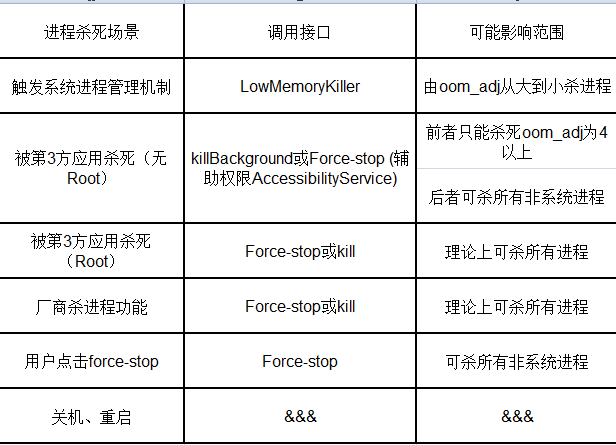
进程被杀死的场景很多,例如被第三方应用杀死(360管家等),关机等等,不同的场景调用的系统接口也是不同,同时杀死的oom_adj值范围也是不同的,于是我将这些场景总结成了一个表格,方便大家了解:
2.常见的保活拉起方式
了解进程被杀死的相关场景后,相信大家对进程保活已经有了初步的认识,接下来我将给大家介绍一下,现在市面上存在的各种常见的保活拉起方式,这些保活方式如下:
**a) 将Service设置为前台服务
b) 在service的onstart方法里返回 STATR_STICK
c) 添加Manifest文件属性值为android:persistent=“true”
d) 覆写Service的onDestroy方法
e) 监听一堆系统静态广播
f) 监听第三方应用的静态广播
g) AlarmManager唤醒
h) 账户同步,定时唤醒
i) 1像素悬浮层
j) GCM或其它3方推送
k) 应用间互相拉起
l) 心跳唤醒
m)Native进程拉起
n) 双进程守护**
1) 将Service设置为前台服务
思路:启用前台服务,主要是startForeground()
保活程度:一般情况下不被杀,部分定制ROM会在应用切到后台即杀
,会被 force stop 杀死
代码实现:
Notificationnotification = newNotification(R.drawable.queen2, "有消息来了"
, System.currentTimeMillis());
notification.setLatestEventInfo(this, "双11,上天猫!",
"一律5折", null);
//设置通知默认效果
notification.flags = Notification.FLAG_SHOW_LIGHTS;
startForeground(1, notification);
2) 在service的onstart方法里返回 STATR_STICK
思路:其实就是onStartCommand中返回STATR_STICK
保活程度:有次数和时间的限制
,会被 force stop 杀死
代码实现:
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return START_STICKY;
//return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
3) 添加Manifest文件属性值为android:persistent=“true”
代码实现(清单文件中配置):
保活程度:一般情况下不被杀,会被 force stop 杀死
"PhoneApp"
android:persistent="true"
android:label="@string/dialerIconLabel"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher_phone">
注意:该方法需要系统签名
4) 覆写Service的onDestroy方法
思路:在onDestroy中再次启动该服务
保活程度:很弱,只在两种情况下work:正在运行里杀服务、DDMS里stop进程
代码实现:
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Intent intent = new Intent(this, KeeLiveService.class);
startService(intent);
super.onDestroy();
}
5) 监听一堆系统静态广播
思路:在发生特定系统事件时,系统会发出响应的广播,通过在 AndroidManifest 中“静态”注册对应的广播监听器,即可在发生响应事件时拉活。
可以监听的系统静态广播列表如下:
![]()
保活强度:我们可以发现,这个方法都是监听系统的一些广播,所以我们需要在我们的应用中注册静态广播,但是静态广播又会出现问题,那就是在4.0版本以上,没有启动过的应用或Force-Stop后收不到静态广播,也就是说4.0以后,如果我们应用从未启动过,或者被Force-Stop杀死过,是无法接收到静态广播的。
如果是两个应用相互拉起,那么在一个应用内可发送带FLAG_INCLUDE_STOPPED_PACKAGES的Intent,那即使另一个应用也是以上两种情况,也可以接收到系统的广播
应用1的代码实现:
//应用1,发送拉起服务的广播
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction("com.action.keepLive");
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_INCLUDE_STOPPED_PACKAGES);
this.sendBroadcast(intent);
应用2的代码实现:
<receiver android:name="com.yzy.supercleanmaster.receiver.KeepLiveReceiver">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.action.keepLive" />
intent-filter>
receiver>
public class KeepLiveReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver{
//应用2中,接受应用1发送的广播,进行服务的拉起
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Intent i = new Intent(context, KeeLiveService.class);
context.startService(i);
}
}
6) 监听第三方应用的静态广播
思路:通过反编译第三方 Top 应用,如:手机QQ、微信、支付宝、UC浏览器等,以及友盟、信鸽、个推等 SDK,找出它们外发的广播,在应用中进行监听,这样当这些应用发出广播时,就会将我们的应用拉活。
保活强度:
该方案的局限性除与系统广播一样的因素外,主要受如下因素限制:
1) 反编译分析过的第三方应用的多少
2) 第三方应用的广播属于应用私有,当前版本中有效的广播,在后续版本随时就可能被移除或被改为不外发,这些因素都影响了拉活的效果。
7) AlarmManager唤醒
思路:通过AlarmManager设置一个定时器,定时的唤醒服务
**保活强度:**killBackgroundProcess下,大部分情况work,
不敌force-stop,闹钟会被清除。
代码实现:
public void startKeepLiveService(Context context, int timeMillis,String action) {
//获取AlarmManager系统服务
AlarmManager alarmManager = (AlarmManager) context.getSystemService(Context.ALARM_SERVICE);
//包装Intent
Intent intent = newIntent(context,KeepLiveServie.class);
intent.setAction(action);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getService(context,0,intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
//添加到AlarmManager
alarmManager.setRepeating(AlarmManager.RTC_WAKEUP,System.currentTimeMillis(),timeMillis,pendingIntent);
}
8) 账户同步,定时唤醒
**思路:**android系统里有一个账户系统,系统定期唤醒账号更新服务,同步的事件间隔是有限制的,最短1分钟。
难点:需要手动设置账户,你如何骗你的用户给你手动设置账户完了之后不卸载你,必须联网
代码实现:
① 建立数据同步系统(ContentProvider)
通过一个ContentProvider用来作数据同步,由于并没有实际数据同步,所以此处就直接建立一个空的ContentProvider即可
public class XXAccountProvider extends ContentProvider {
public static final String AUTHORITY = "包名.provider";
public static final String CONTENT_URI_BASE = "content://" + AUTHORITY;
public static final String TABLE_NAME = "data";
public static final Uri CONTENT_URI = Uri.parse(CONTENT_URI_BASE + "/" + TABLE_NAME);
@Override
public boolean onCreate() {
return true;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection,
String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder) {
return null;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public String getType(Uri uri) {
return new String();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) {
return null;
}
@Override
public int delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
return 0;
}
}
然后再Manifest中声明
<provider
android:name="**.XXAccountProvider"
android:authorities="@string/account_auth_provider"
android:exported="false"
android:syncable="true"/>
② 建立Sync系统 (SyncAdapter)
通过实现SyncAdapter这个系统服务后, 利用系统的定时器对程序数据ContentProvider进行更新,具体步骤为:
- 创建Sync服务
public class XXSyncService extends Service {
private static final Object sSyncAdapterLock = new Object();
private static XXSyncAdapter sSyncAdapter = null;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
synchronized (sSyncAdapterLock) {
if (sSyncAdapter == null) {
sSyncAdapter = new XXSyncAdapter(getApplicationContext(), true);
}
}
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return sSyncAdapter.getSyncAdapterBinder();
}
static class XXSyncAdapter extends AbstractThreadedSyncAdapter {
public XXSyncAdapter(Context context, boolean autoInitialize) {
super(context, autoInitialize);
}
@Override
public void onPerformSync(Account account, Bundle extras, String authority, ContentProviderClient provider, SyncResult syncResult) {
getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(XXAccountProvider.CONTENT_URI, null, false);
}
}
}
- 声明Sync服务
<service
android:name="**.XXSyncService"
android:exported="true"
android:process=":core">
<intent-filter>
<action
android:name="android.content.SyncAdapter"/>
intent-filter>
<meta-data
android:name="android.content.SyncAdapter"
android:resource="@xml/sync_adapter"/>
service>
其中sync_adapter为:
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:accountType="@string/account_auth_type"
android:allowParallelSyncs="false"
android:contentAuthority="@string/account_auth_provide"
android:isAlwaysSyncable="true"
android:supportsUploading="false"
android:userVisible="true"/>
参数说明:
android:contentAuthority 指定要同步的ContentProvider在其AndroidManifest.xml文件中有个android:authorities属性。
android:accountType 表示进行同步的账号的类型。
android:userVisible 设置是否在“设置”中显示
android:supportsUploading 设置是否必须notifyChange通知才能同步
android:allowParallelSyncs 是否支持多账号同时同步
android:isAlwaysSyncable 设置所有账号的isSyncable为1
android:syncAdapterSettingsAction 指定一个可以设置同步的activity的Action。
- 账户调用Sync服务
首先配置好Account(第三步),然后再通过ContentProvider实现
手动更新
public void triggerRefresh() {
Bundle b = new Bundle();
b.putBoolean(ContentResolver.SYNC_EXTRAS_MANUAL, true);
b.putBoolean(ContentResolver.SYNC_EXTRAS_EXPEDITED, true);
ContentResolver.requestSync(
account,
CONTENT_AUTHORITY,
b);
}
添加账号
Account account = AccountService.GetAccount();
AccountManager accountManager = (AccountManager) context.getSystemService(Context.ACCOUNT_SERVICE);
accountManager.addAccountExplicitly(...)
``
同步周期设置
ContentResolver.setIsSyncable(account, CONTENT_AUTHORITY, 1);
ContentResolver.setSyncAutomatically(account, CONTENT_AUTHORITY, true);
ContentResolver.addPeriodicSync(account, CONTENT_AUTHORITY, new Bundle(), SYNC_FREQUENCY);
“
③ 建立账号系统 (Account Authenticator)
通过建立Account账号,并关联SyncAdapter服务实现同步
- 创建Account服务
public class XXAuthService extends Service {
private XXAuthenticator mAuthenticator;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
mAuthenticator = new XXAuthenticator(this);
}
private XXAuthenticator getAuthenticator() {
if (mAuthenticator == null)
mAuthenticator = new XXAuthenticator(this);
return mAuthenticator;
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return getAuthenticator().getIBinder();
}
class XXAuthenticator extends AbstractAccountAuthenticator {
private final Context context;
private AccountManager accountManager;
public XXAuthenticator(Context context) {
super(context);
this.context = context;
accountManager = AccountManager.get(context);
}
@Override
public Bundle addAccount(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, String accountType, String authTokenType, String[] requiredFeatures, Bundle options)
throws NetworkErrorException {
// 添加账号 示例代码
final Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
final Intent intent = new Intent(context, AuthActivity.class);
intent.putExtra(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_AUTHENTICATOR_RESPONSE, response);
bundle.putParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT, intent);
return bundle;
}
@Override
public Bundle getAuthToken(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, Account account, String authTokenType, Bundle options)
throws NetworkErrorException {
// 认证 示例代码
String authToken = accountManager.peekAuthToken(account, getString(R.string.account_token_type));
//if not, might be expired, register again
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(authToken)) {
final String password = accountManager.getPassword(account);
if (password != null) {
//get new token
authToken = account.name + password;
}
}
//without password, need to sign again
final Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(authToken)) {
bundle.putString(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_NAME, account.name);
bundle.putString(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_TYPE, account.type);
bundle.putString(AccountManager.KEY_AUTHTOKEN, authToken);
return bundle;
}
//no account data at all, need to do a sign
final Intent intent = new Intent(context, AuthActivity.class);
intent.putExtra(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_AUTHENTICATOR_RESPONSE, response);
intent.putExtra(AuthActivity.ARG_ACCOUNT_NAME, account.name);
bundle.putParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT, intent);
return bundle;
}
@Override
public String getAuthTokenLabel(String authTokenType) {
// throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
return null;
}
@Override
public Bundle editProperties(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, String accountType) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Bundle confirmCredentials(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, Account account, Bundle options)
throws NetworkErrorException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Bundle updateCredentials(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, Account account, String authTokenType, Bundle options)
throws NetworkErrorException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Bundle hasFeatures(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, Account account, String[] features)
throws NetworkErrorException {
return null;
}
}
- 声明Account服务
<service
android:name="**.XXAuthService"
android:exported="true"
android:process=":core">
<intent-filter>
<action
android:name="android.accounts.AccountAuthenticator"/>
intent-filter>
<meta-data
android:name="android.accounts.AccountAuthenticator"
android:resource="@xml/authenticator"/>
service>
其中authenticator为:
<account-authenticator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:accountType="@string/account_auth_type"
android:icon="@drawable/icon"
android:smallIcon="@drawable/icon"
android:label="@string/app_name"
/>
- 使用Account服务
同SyncAdapter,通过AccountManager使用
- 申请Token主要是通过 [AccountManager.getAuthToken]系列方法
- 添加账号则通过 [AccountManager.addAccount]
- 查看是否存在账号通过 [AccountManager.getAccountsByType]
保活强度:
该方案适用于所有的 Android 版本,包括被 forestop 掉的进程也可以进行拉活。最新 Android 版本(Android N)中系统好像对账户同步这里做了变动,该方法不再有效。
本篇介绍了进程保活的一些方法,由于篇幅原因,1像素悬浮层、应用间互相拉起、心跳唤醒等方法将在下一篇进行介绍。