本文是基于TensorRT 5.0.2基础上,关于其内部的yolov3_onnx例子的分析和介绍。
本例子展示一个完整的ONNX的pipline,在tensorrt 5.0的ONNX-TensorRT基础上,基于Yolov3-608网络进行inference,包含预处理和后处理。
- 首先,从作者网站下载yolov3,然后将其转换成onnx形式,接着基于onnx的graph生成一个tensorrt engine;
- 然后,在样本图片上进行预处理,并将结果作为engine的输入;
- 在inference之后,开始关于包含bounding-box聚类的后处理,然后最终得到一个新的图像文件,并将其存放在磁盘上,以便后续肉眼观察。
1 引言
假设当前路径为:
TensorRT-5.0.2.6/samples
其对应当前例子文件目录树为:
# tree python
python
├── common.py
└── yolov3_onnx
├── coco_labels.txt
├── data_processing.py
├── onnx_to_tensorrt.py
├── README.md
├── requirements.txt
├── yolov3.cfg
├── yolov3.weights
├── dog.jpg
└── yolov3_to_onnx.py
其中:
- yolov3_to_onnx.py:将原始yolov3模型转换成onnx结构。该脚本会自动下载所需要依赖文件;
- onnx_to_tensorrt.py:将onnx的yolov3转换成engine然后进行inference。
2 darknet转onnx
首先运行:
python yolov3_to_onnx.py
就会自动从作者网站下载yolo3的所需依赖
from __future__ import print_function
from collections import OrderedDict
import hashlib
import os.path
import wget
import onnx
from onnx import helper
from onnx import TensorProto
import numpy as np
import sys
‘’‘main第二步:解析yolov3.cfg ‘’’
class DarkNetParser(object):
“”“定义一个基于DarkNet YOLOv3-608的解析器.”""
def __init__(self, supported_layers):
"""初始化DarkNetParser对象.
Keyword argument:
supported_layers -- 一个list,其中每个元素为字符串,表示支持的层,以DarkNet的命名习惯,
"""
self.layer_configs = OrderedDict()
self.supported_layers = supported_layers
self.layer_counter = 0
def parse_cfg_file(self, cfg_file_path):
"""逐层解析yolov3.cfg文件,以字典形式追加每层的参数到layer_configs
Keyword argument:
cfg_file_path -- yolov3.cfg文件的路径
"""
with open(cfg_file_path, 'rb') as cfg_file:
remainder = cfg_file.read()
remainder = remainder.decode('utf-8')
while remainder:
layer_dict, layer_name, remainder = self._next_layer(remainder)
if layer_dict:
self.layer_configs[layer_name] = layer_dict
return self.layer_configs
def _next_layer(self, remainder):
"""将其视为一个字符串,然后以DarkNet的分隔符来逐段处理.
在最近的分隔符之后,返回层参数和剩下的字符串
如文件中第一个Conv层 ...
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=32
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
... 会变成如下形式字典:
{'activation': 'leaky', 'stride': 1, 'pad': 1, 'filters': 32,
'batch_normalize': 1, 'type': 'convolutional', 'size': 3}.
'001_convolutional' 是层名layer_name, 后续所有字符以remainder表示的字符串返回
Keyword argument:
remainder -- 仍需要处理的字符串
"""
remainder = remainder.split('[', 1)
if len(remainder) == 2:
remainder = remainder[1]
else:
return None, None, None
remainder = remainder.split(']', 1)
if len(remainder) == 2:
layer_type, remainder = remainder
else:
return None, None, None
if remainder.replace(' ', '')[0] == '#':
remainder = remainder.split('\n', 1)[1]
layer_param_block, remainder = remainder.split('\n\n', 1)
layer_param_lines = layer_param_block.split('\n')[1:]
layer_name = str(self.layer_counter).zfill(3) + '_' + layer_type
layer_dict = dict(type=layer_type)
if layer_type in self.supported_layers:
for param_line in layer_param_lines:
if param_line[0] == '#':
continue
param_type, param_value = self._parse_params(param_line)
layer_dict[param_type] = param_value
self.layer_counter += 1
return layer_dict, layer_name, remainder
def _parse_params(self, param_line):
"""解析每一行参数,当遇到layers时,返回list,其余返回字符串,整数,浮点数类型.
Keyword argument:
param_line -- 块中的一行需要解析的参数行
"""
param_line = param_line.replace(' ', '')
param_type, param_value_raw = param_line.split('=')
param_value = None
if param_type == 'layers':
layer_indexes = list()
for index in param_value_raw.split(','):
layer_indexes.append(int(index))
param_value = layer_indexes
elif isinstance(param_value_raw, str) and not param_value_raw.isalpha():
condition_param_value_positive = param_value_raw.isdigit()
condition_param_value_negative = param_value_raw[0] == '-' and \
param_value_raw[1:].isdigit()
if condition_param_value_positive or condition_param_value_negative:
param_value = int(param_value_raw)
else:
param_value = float(param_value_raw)
else:
param_value = str(param_value_raw)
return param_type, param_value
‘’‘main第四步:被第三步类的_make_onnx_node方法调用 ‘’’
class MajorNodeSpecs(object):
“”“Helper class用于存储ONNX输出节点的信息,对应DarkNet 层的输出和该层输出通道,
一些DarkNet层并未被创建,因此没有对应的ONNX 节点,
不过仍然需要对其进行追踪以建立skip 连接
“””
def __init__(self, name, channels):
""" 初始化一个MajorNodeSpecs对象
Keyword arguments:
name -- ONNX节点的名称
channels -- 该节点的输出通道的数量
"""
self.name = name
self.channels = channels
self.created_onnx_node = False
if name is not None and isinstance(channels, int) and channels > 0:
self.created_onnx_node = True
‘’‘main第四步:被第三步类的_make_conv_node方法调用 ‘’’
class ConvParams(object):
“”"Helper class用于存储卷积层的超参数,包括在ONNX graph中的前置name和
为了卷积,偏置,BN等权重期望的维度
另外该类还扮演着为所有权重生成安全名称的封装,并检查合适的组合搭配
"""
def __init__(self, node_name, batch_normalize, conv_weight_dims):
"""基于base 节点名称 (e.g. 101_convolutional),BN设置,卷积权重shape的构造器
Keyword arguments:
node_name -- YOLO卷积层的base名称
batch_normalize -- bool值,表示是否使用BN
conv_weight_dims -- 该层的卷积权重的维度
"""
self.node_name = node_name
self.batch_normalize = batch_normalize
assert len(conv_weight_dims) == 4
self.conv_weight_dims = conv_weight_dims
def generate_param_name(self, param_category, suffix):
"""基于两个字符串输入生成一个名称,并检查组合搭配是否合理"""
assert suffix
assert param_category in ['bn', 'conv']
assert(suffix in ['scale', 'mean', 'var', 'weights', 'bias'])
if param_category == 'bn':
assert self.batch_normalize
assert suffix in ['scale', 'bias', 'mean', 'var']
elif param_category == 'conv':
assert suffix in ['weights', 'bias']
if suffix == 'bias':
assert not self.batch_normalize
param_name = self.node_name + '_' + param_category + '_' + suffix
return param_name
‘’‘man第四步:被第三步类的build_onnx_graph方法调用 ‘’’
class WeightLoader(object):
“”“Helper class用于载入序列化的权重,
“””
def __init__(self, weights_file_path):
"""读取YOLOv3权重文件
Keyword argument:
weights_file_path --权重文件的路径.
"""
self.weights_file = self._open_weights_file(weights_file_path)
def load_conv_weights(self, conv_params):
"""返回权重文件的初始化器和卷积层的输入tensor
Keyword argument:
conv_params -- a ConvParams object
"""
initializer = list()
inputs = list()
if conv_params.batch_normalize:
bias_init, bias_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'bn', 'bias')
bn_scale_init, bn_scale_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'bn', 'scale')
bn_mean_init, bn_mean_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'bn', 'mean')
bn_var_init, bn_var_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'bn', 'var')
initializer.extend(
[bn_scale_init, bias_init, bn_mean_init, bn_var_init])
inputs.extend([bn_scale_input, bias_input,
bn_mean_input, bn_var_input])
else:
bias_init, bias_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'conv', 'bias')
initializer.append(bias_init)
inputs.append(bias_input)
conv_init, conv_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'conv', 'weights')
initializer.append(conv_init)
inputs.append(conv_input)
return initializer, inputs
def _open_weights_file(self, weights_file_path):
"""打开Yolov3 DarkNet文件流,并跳过开头.
Keyword argument:
weights_file_path -- 权重文件路径
"""
weights_file = open(weights_file_path, 'rb')
length_header = 5
np.ndarray(
shape=(length_header, ), dtype='int32', buffer=weights_file.read(
length_header * 4))
return weights_file
def _create_param_tensors(self, conv_params, param_category, suffix):
"""用权重文件中,与输入tensors一起的权重去初始化一个初始化器.
Keyword arguments:
conv_params -- a ConvParams object
param_category -- the category of parameters to be created ('bn' or 'conv')
suffix -- a string determining the sub-type of above param_category (e.g.,
'weights' or 'bias')
"""
param_name, param_data, param_data_shape = self._load_one_param_type(
conv_params, param_category, suffix)
initializer_tensor = helper.make_tensor(
param_name, TensorProto.FLOAT, param_data_shape, param_data)
input_tensor = helper.make_tensor_value_info(
param_name, TensorProto.FLOAT, param_data_shape)
return initializer_tensor, input_tensor
def _load_one_param_type(self, conv_params, param_category, suffix):
"""基于DarkNet顺序进行文件流的反序列化.
Keyword arguments:
conv_params -- a ConvParams object
param_category -- the category of parameters to be created ('bn' or 'conv')
suffix -- a string determining the sub-type of above param_category (e.g.,
'weights' or 'bias')
"""
param_name = conv_params.generate_param_name(param_category, suffix)
channels_out, channels_in, filter_h, filter_w = conv_params.conv_weight_dims
if param_category == 'bn':
param_shape = [channels_out]
elif param_category == 'conv':
if suffix == 'weights':
param_shape = [channels_out, channels_in, filter_h, filter_w]
elif suffix == 'bias':
param_shape = [channels_out]
param_size = np.product(np.array(param_shape))
param_data = np.ndarray(
shape=param_shape,
dtype='float32',
buffer=self.weights_file.read(param_size * 4))
param_data = param_data.flatten().astype(float)
return param_name, param_data, param_shape
‘’‘main第三步 ‘’’
class GraphBuilderONNX(object):
“”“用于创建ONNX graph的类,基于之前从yolov3.cfg读取的网络结构。该类函数方法有:
build_onnx_graph : 构建
_make_onnx_node
_make_input_tensor
_get_previous_node_specs
_make_conv_node
_make_shortcut_node
_make_route_node
_make_upsample_node
“””
def __init__(self, output_tensors):
"""用所有DarkNet默认参数来初始化;
然后基于output_tensors指定输出维度;
以他们的name为key
Keyword argument:
output_tensors -- 一个 OrderedDict类型
"""
self.output_tensors = output_tensors
self._nodes = list()
self.graph_def = None
self.input_tensor = None
self.epsilon_bn = 1e-5
self.momentum_bn = 0.99
self.alpha_lrelu = 0.1
self.param_dict = OrderedDict()
self.major_node_specs = list()
self.batch_size = 1
def build_onnx_graph(
self,
layer_configs,
weights_file_path,
verbose=True):
"""基于所有的层配置进行迭代,创建一个ONNX graph,
然后用下载的yolov3 权重文件进行填充,最后返回该graph定义.
Keyword arguments:
layer_configs -- OrderedDict对象,包含所有解析的层的配置
weights_file_path -- 权重文件的位置
verbose -- 是否在创建之后显示该graph(default: True)
"""
for layer_name in layer_configs.keys():
layer_dict = layer_configs[layer_name]
major_node_specs = self._make_onnx_node(layer_name, layer_dict)
if major_node_specs.name:
self.major_node_specs.append(major_node_specs)
outputs = list()
for tensor_name in self.output_tensors.keys():
output_dims = [self.batch_size, ] + \
self.output_tensors[tensor_name]
output_tensor = helper.make_tensor_value_info(
tensor_name, TensorProto.FLOAT, output_dims)
outputs.append(output_tensor)
inputs = [self.input_tensor]
weight_loader = WeightLoader(weights_file_path)
initializer = list()
for layer_name in self.param_dict.keys():
_, layer_type = layer_name.split('_', 1)
conv_params = self.param_dict[layer_name]
assert layer_type == 'convolutional'
initializer_layer, inputs_layer = weight_loader.load_conv_weights(
conv_params)
initializer.extend(initializer_layer)
inputs.extend(inputs_layer)
del weight_loader
self.graph_def = helper.make_graph(
nodes=self._nodes,
name='YOLOv3-608',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=outputs,
initializer=initializer
)
if verbose:
print(helper.printable_graph(self.graph_def))
model_def = helper.make_model(self.graph_def,
producer_name='NVIDIA TensorRT sample')
return model_def
def _make_onnx_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""输入一个layer参数字典,选择对应的函数来创建ONNX节点,然后将为图创建的重要的信息存储为
MajorNodeSpec对象
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- layer的名称 (即layer_configs中的key)
layer_dict -- 一个layer参数字典 (layer_configs的value)
"""
layer_type = layer_dict['type']
if self.input_tensor is None:
if layer_type == 'net':
major_node_output_name, major_node_output_channels = self._make_input_tensor(
layer_name, layer_dict)
major_node_specs = MajorNodeSpecs(major_node_output_name,
major_node_output_channels)
else:
raise ValueError('The first node has to be of type "net".')
else:
node_creators = dict()
node_creators['convolutional'] = self._make_conv_node
node_creators['shortcut'] = self._make_shortcut_node
node_creators['route'] = self._make_route_node
node_creators['upsample'] = self._make_upsample_node
if layer_type in node_creators.keys():
major_node_output_name, major_node_output_channels = \
node_creators[layer_type](layer_name, layer_dict)
major_node_specs = MajorNodeSpecs(major_node_output_name,
major_node_output_channels)
else:
print(
'Layer of type %s not supported, skipping ONNX node generation.' %
layer_type)
major_node_specs = MajorNodeSpecs(layer_name,
None)
return major_node_specs
def _make_input_tensor(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""为net layer创建输入tensor,并存储对应batch size.可以看出,该函数只被调用一次
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- 层的名字 (如 layer_configs中key)
layer_dict -- 一个layer参数字典( layer_configs中的value)
"""
batch_size = layer_dict['batch']
channels = layer_dict['channels']
height = layer_dict['height']
width = layer_dict['width']
self.batch_size = batch_size
input_tensor = helper.make_tensor_value_info(
str(layer_name), TensorProto.FLOAT, [
batch_size, channels, height, width])
self.input_tensor = input_tensor
return layer_name, channels
def _get_previous_node_specs(self, target_index=-1):
"""获取之前创建好的onnx节点(跳过那些没生成的节点,比如yolo节点).
target_index可以能够直接跳到对应节点.
Keyword arguments:
target_index -- 可选的参数,帮助跳到具体索引(default: -1 表示跳到前一个元素)
"""
previous_node = None
for node in self.major_node_specs[target_index::-1]:
if node.created_onnx_node:
previous_node = node
break
assert previous_node is not None
return previous_node
def _make_conv_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""用可选的bn和激活函数nonde去创建一个onnx的卷积node
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- 层的名字 (如 layer_configs中key)
layer_dict -- 一个layer参数字典( layer_configs中的value)
"""
previous_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs()
''' i) 处理卷积层'''
inputs = [previous_node_specs.name]
previous_channels = previous_node_specs.channels
kernel_size = layer_dict['size']
stride = layer_dict['stride']
filters = layer_dict['filters']
batch_normalize = False
if 'batch_normalize' in layer_dict.keys(
) and layer_dict['batch_normalize'] == 1:
batch_normalize = True
kernel_shape = [kernel_size, kernel_size]
weights_shape = [filters, previous_channels] + kernel_shape
conv_params = ConvParams(layer_name, batch_normalize, weights_shape)
strides = [stride, stride]
dilations = [1, 1]
weights_name = conv_params.generate_param_name('conv', 'weights')
inputs.append(weights_name)
if not batch_normalize:
bias_name = conv_params.generate_param_name('conv', 'bias')
inputs.append(bias_name)
conv_node = helper.make_node(
'Conv',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name],
kernel_shape=kernel_shape,
strides=strides,
auto_pad='SAME_LOWER',
dilations=dilations,
name=layer_name
)
self._nodes.append(conv_node)
inputs = [layer_name]
layer_name_output = layer_name
''' ii) 处理BN层'''
if batch_normalize:
layer_name_bn = layer_name + '_bn'
bn_param_suffixes = ['scale', 'bias', 'mean', 'var']
for suffix in bn_param_suffixes:
bn_param_name = conv_params.generate_param_name('bn', suffix)
inputs.append(bn_param_name)
batchnorm_node = helper.make_node(
'BatchNormalization',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name_bn],
epsilon=self.epsilon_bn,
momentum=self.momentum_bn,
name=layer_name_bn
)
self._nodes.append(batchnorm_node)
inputs = [layer_name_bn]
layer_name_output = layer_name_bn
''' iii) 处理激活函数'''
if layer_dict['activation'] == 'leaky':
layer_name_lrelu = layer_name + '_lrelu'
lrelu_node = helper.make_node(
'LeakyRelu',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name_lrelu],
name=layer_name_lrelu,
alpha=self.alpha_lrelu
)
self._nodes.append(lrelu_node)
inputs = [layer_name_lrelu]
layer_name_output = layer_name_lrelu
elif layer_dict['activation'] == 'linear':
pass
else:
print('Activation not supported.')
self.param_dict[layer_name] = conv_params
return layer_name_output, filters
def _make_shortcut_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""从DarkNet graph中读取信息,基于onnx 的add 节点创建shortcut 节点.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- 层的名字 (如 layer_configs中key)
layer_dict -- 一个layer参数字典( layer_configs中的value)
"""
shortcut_index = layer_dict['from']
activation = layer_dict['activation']
assert activation == 'linear'
first_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs()
second_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs(
target_index=shortcut_index)
assert first_node_specs.channels == second_node_specs.channels
channels = first_node_specs.channels
inputs = [first_node_specs.name, second_node_specs.name]
shortcut_node = helper.make_node(
'Add',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name],
name=layer_name,
)
self._nodes.append(shortcut_node)
return layer_name, channels
def _make_route_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""如果来自DarkNet配置的layer参数只有一个所以,那么接着在指定(负)索引上创建节点
否则,创建一个onnx concat 节点来实现路由特性.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- 层的名字 (如 layer_configs中key)
layer_dict -- 一个layer参数字典( layer_configs中的value)
"""
route_node_indexes = layer_dict['layers']
if len(route_node_indexes) == 1:
split_index = route_node_indexes[0]
assert split_index < 0
split_index += 1
self.major_node_specs = self.major_node_specs[:split_index]
layer_name = None
channels = None
else:
inputs = list()
channels = 0
for index in route_node_indexes:
if index > 0:
index += 1
route_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs(
target_index=index)
inputs.append(route_node_specs.name)
channels += route_node_specs.channels
assert inputs
assert channels > 0
route_node = helper.make_node(
'Concat',
axis=1,
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name],
name=layer_name,
)
self._nodes.append(route_node)
return layer_name, channels
def _make_upsample_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""创建一个onnx的Upsample节点.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- 层的名字 (如 layer_configs中key)
layer_dict -- 一个layer参数字典( layer_configs中的value)
"""
upsample_factor = float(layer_dict['stride'])
previous_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs()
inputs = [previous_node_specs.name]
channels = previous_node_specs.channels
assert channels > 0
upsample_node = helper.make_node(
'Upsample',
mode='nearest',
scales=[1.0, 1.0, upsample_factor, upsample_factor],
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name],
name=layer_name,
)
self._nodes.append(upsample_node)
return layer_name, channels
def generate_md5_checksum(local_path):
“”"计算本地文件的md5
Keyword argument:
local_path -- 本地文件路径
"""
with open(local_path) as local_file:
data = local_file.read()
return hashlib.md5(data).hexdigest()
def download_file(local_path, link, checksum_reference=None):
“”"下载指定url到本地,并进行摘要校对.
Keyword arguments:
local_path -- 本地文件存储路径
link -- 需要下载的url
checksum_reference -- expected MD5 checksum of the file
"""
if not os.path.exists(local_path):
print('Downloading from %s, this may take a while...' % link)
wget.download(link, local_path)
print()
if checksum_reference is not None:
checksum = generate_md5_checksum(local_path)
if checksum != checksum_reference:
raise ValueError(
'The MD5 checksum of local file %s differs from %s, please manually remove \
the file and try again.' %
(local_path, checksum_reference))
return local_path
def main():
"""Run the DarkNet-to-ONNX conversion for YOLOv3-608."""
''' 1 - 下载yolov3的配置文件,并进行摘要验证'''
cfg_file_path = download_file(
'yolov3.cfg',
‘https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pjreddie/darknet/f86901f6177dfc6116360a13cc06ab680e0c86b0/cfg/yolov3.cfg’,
‘b969a43a848bbf26901643b833cfb96c’)
supported_layers = ['net', 'convolutional', 'shortcut',
'route', 'upsample']
''' 2 - 创建一个DarkNetParser对象,并生成一个OrderedDict,包含cfg文件读取的所有层配置'''
parser = DarkNetParser(supported_layers)
layer_configs = parser.parse_cfg_file(cfg_file_path)
del parser
''' 3 - 实例化一个GraphBuilderONNX类对象,用已知输出tensor维度进行初始化'''
output_tensor_dims = OrderedDict()
output_tensor_dims['082_convolutional'] = [255, 19, 19]
output_tensor_dims['094_convolutional'] = [255, 38, 38]
output_tensor_dims['106_convolutional'] = [255, 76, 76]
builder = GraphBuilderONNX(output_tensor_dims)
''' 4 - 调用GraphBuilderONNX的build_onnx_graph方法
用之前解析好的层配置信息和权重文件,生成ONNX graph'''
''' 从作者官网下载yolov3的权重文件,以此填充tensorrt的network '''
weights_file_path = download_file(
'yolov3.weights',
'https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights',
'c84e5b99d0e52cd466ae710cadf6d84c')
yolov3_model_def = builder.build_onnx_graph(
layer_configs=layer_configs,
weights_file_path=weights_file_path,
verbose=True)
del builder
''' 5 - 在ONNX模型定义上进行健全检查'''
onnx.checker.check_model(yolov3_model_def)
''' 6 - 序列化生成的ONNX graph到文件'''
output_file_path = 'yolov3.onnx'
onnx.save(yolov3_model_def, output_file_path)
if name == ‘main’:
main()
结果如下:
[root@30d4bceec4c4 yolov3_onnx]# python yolov3_to_onnx.py
Layer of type yolo not supported, skipping ONNX node generation.
Layer of type yolo not supported, skipping ONNX node generation.
Layer of type yolo not supported, skipping ONNX node generation.
graph YOLOv3-608 (
%000_net[FLOAT, 64x3x608x608]
) initializers (
%001_convolutional_bn_scale[FLOAT, 32]
%001_convolutional_bn_bias[FLOAT, 32]
%001_convolutional_bn_mean[FLOAT, 32]
%001_convolutional_bn_var[FLOAT, 32]
%001_convolutional_conv_weights[FLOAT, 32x3x3x3]
%002_convolutional_bn_scale[FLOAT, 64]
......
%105_convolutional_conv_weights[FLOAT, 256x128x3x3]
%106_convolutional_conv_bias[FLOAT, 255]
%106_convolutional_conv_weights[FLOAT, 255x256x1x1]
) {
%001_convolutional = Conv[auto_pad = 'SAME_LOWER', dilations = [1, 1], kernel_shape = [3, 3], strides = [1, 1]](%000_net, %001_convolutional_conv_weights)
%001_convolutional_bn = BatchNormalization[epsilon = 9.99999974737875e-06, momentum = 0.990000009536743](%001_convolutional,
......
%105_convolutional_bn = BatchNormalization[epsilon = 9.99999974737875e-06, momentum = 0.990000009536743](%105_convolutional, %105_convolutional_bn_scale, %105_convolutional_bn_bias, %105_convolutional_bn_mean, %105_convolutional_bn_var)
%105_convolutional_lrelu = LeakyRelu[alpha = 0.100000001490116](%105_convolutional_bn)
%106_convolutional = Conv[auto_pad = 'SAME_LOWER', dilations = [1, 1], kernel_shape = [1, 1], strides = [1, 1]](%105_convolutional_lrelu, %106_convolutional_conv_weights, %106_convolutional_conv_bias)
return %082_convolutional, %094_convolutional, %106_convolutional
}
ps:在该例子中onnx不要安装1.4.1版本,可以安装如1.2.1版本,否则会出现
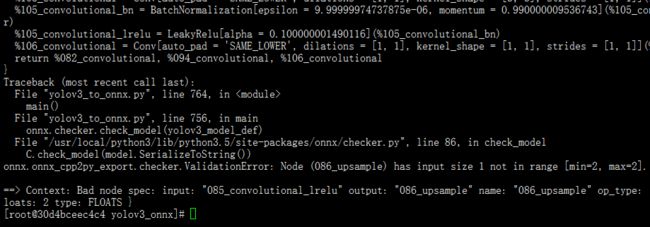
此时会生成文件yolov3.onnx。
3 onnx转trt并进行inference
接下来看onnx_to_tensorrt.py
from __future__ import print_function
import numpy as np
import tensorrt as trt
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import pycuda.autoinit
from PIL import ImageDraw
from yolov3_to_onnx import download_file
from data_processing import PreprocessYOLO, PostprocessYOLO, ALL_CATEGORIES
import sys, os
‘’‘main第3.2步 ‘’’
def allocate_buffers(engine):
inputs = []
outputs = []
bindings = []
stream = cuda.Stream()
for binding in engine:
size = trt.volume(engine.get_binding_shape(binding)) * engine.max_batch_size
dtype = trt.nptype(engine.get_binding_dtype(binding))
host_mem = cuda.pagelocked_empty(size, dtype)
device_mem = cuda.mem_alloc(host_mem.nbytes)
bindings.append(int(device_mem))
if engine.binding_is_input(binding):
inputs.append(HostDeviceMem(host_mem, device_mem))
else:
outputs.append(HostDeviceMem(host_mem, device_mem))
return inputs, outputs, bindings, stream
‘’‘main中第3.3步 ‘’’
def do_inference(context, bindings, inputs, outputs, stream, batch_size=1):
[cuda.memcpy_htod_async(inp.device, inp.host, stream) for inp in inputs]
context.execute_async(batch_size=batch_size, bindings=bindings, stream_handle=stream.handle)
[cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(out.host, out.device, stream) for out in outputs]
stream.synchronize()
return [out.host for out in outputs]
TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger()
def draw_bboxes(image_raw, bboxes, confidences, categories, all_categories, bbox_color=‘blue’):
“”"在原始输入图片上标记bounding box没然后返回结果.
Keyword arguments:
image_raw -- a raw PIL Image
bboxes -- NumPy array containing the bounding box coordinates of N objects, with shape (N,4).
categories -- NumPy array containing the corresponding category for each object,
with shape (N,)
confidences -- NumPy array containing the corresponding confidence for each object,
with shape (N,)
all_categories -- a list of all categories in the correct ordered (required for looking up
the category name)
bbox_color -- an optional string specifying the color of the bounding boxes (default: 'blue')
"""
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image_raw)
print(bboxes, confidences, categories)
for box, score, category in zip(bboxes, confidences, categories):
x_coord, y_coord, width, height = box
left = max(0, np.floor(x_coord + 0.5).astype(int))
top = max(0, np.floor(y_coord + 0.5).astype(int))
right = min(image_raw.width, np.floor(x_coord + width + 0.5).astype(int))
bottom = min(image_raw.height, np.floor(y_coord + height + 0.5).astype(int))
draw.rectangle(((left, top), (right, bottom)), outline=bbox_color)
draw.text((left, top - 12), '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(all_categories[category], score), fill=bbox_color)
return image_raw
def get_engine(onnx_file_path, engine_file_path=""):
“”“如果已经有序列化engine,则直接用,否则构建新的tensorrt engine然后保存.”""
def build_engine():
“”“Takes an ONNX file and creates a TensorRT engine to run inference with”""
with trt.Builder(TRT_LOGGER) as builder,
builder.create_network() as network,
trt.OnnxParser(network, TRT_LOGGER) as parser:
builder.max_workspace_size = 1 << 30
builder.max_batch_size = 1
if not os.path.exists(onnx_file_path):
print('ONNX file {} not found, please run yolov3_to_onnx.py first to generate it.'.format(onnx_file_path))
exit(0)
print('Loading ONNX file from path {}...'.format(onnx_file_path))
with open(onnx_file_path, 'rb') as model:
print('Beginning ONNX file parsing')
parser.parse(model.read())
print('Completed parsing of ONNX file')
print('Building an engine from file {}; this may take a while...'.format(onnx_file_path))
engine = builder.build_cuda_engine(network)
print("Completed creating Engine")
with open(engine_file_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(engine.serialize())
return engine
if os.path.exists(engine_file_path):
print("Reading engine from file {}".format(engine_file_path))
with open(engine_file_path, "rb") as f, \
trt.Runtime(TRT_LOGGER) as runtime:
return runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
else:
return build_engine()
def main():
“”“Create a TensorRT engine for ONNX-based YOLOv3-608 and run inference.”""
''' 1 - 装载之前转换好的onnx,准备测试图片'''
onnx_file_path = 'yolov3.onnx'
engine_file_path = "yolov3.trt"
input_image_path = download_file('dog.jpg',
'https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet/raw/f86901f6177dfc6116360a13cc06ab680e0c86b0/data/dog.jpg', checksum_reference=None)
''' 2 - 对图片进行预处理'''
input_resolution_yolov3_HW = (608, 608)
preprocessor = PreprocessYOLO(input_resolution_yolov3_HW)
image_raw, image = preprocessor.process(input_image_path)
shape_orig_WH = image_raw.size
''' 3 - 基于tensorrt进行yolov3模型的运行'''
output_shapes = [(1, 255, 19, 19), (1, 255, 38, 38), (1, 255, 76, 76)]
trt_outputs = []
‘’’ 3.1 - 基于get_engine生成engine’’’
with get_engine(onnx_file_path, engine_file_path) as engine,
engine.create_execution_context() as context:
''' 3.2 - 分配host,device端的buffer'''
inputs, outputs, bindings, stream = allocate_buffers(engine)
print('Running inference on image {}...'.format(input_image_path))
''' 3.3 - 进行inference'''
inputs[0].host = image
trt_outputs = do_inference(context, bindings=bindings, inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, stream=stream)
''' 4 - 对tensorrt在onnx结构的yolov3上得到的结果进行后处理'''
trt_outputs = [output.reshape(shape) for output, shape in zip(trt_outputs, output_shapes)]
postprocessor_args = {"yolo_masks": [(6, 7, 8), (3, 4, 5), (0, 1, 2)],
"yolo_anchors": [(10, 13), (16, 30), (33, 23), (30, 61), (62, 45),
(59, 119), (116, 90), (156, 198), (373, 326)],
"obj_threshold": 0.6,
"nms_threshold": 0.5,
"yolo_input_resolution": input_resolution_yolov3_HW}
postprocessor = PostprocessYOLO(**postprocessor_args)
boxes, classes, scores = postprocessor.process(trt_outputs, (shape_orig_WH))
''' 5 - 在原始输入图像上将检测框标记,并保存png文件 '''
obj_detected_img = draw_bboxes(image_raw, boxes, scores, classes, ALL_CATEGORIES)
output_image_path = 'dog_bboxes.png'
obj_detected_img.save(output_image_path, 'PNG')
print('Saved image with bounding boxes of detected objects to {}.'.format(output_image_path))
if name == ‘main’:
main()
运行程序及结果:
python onnx_to_tensorrt.py

此时文件目录为:
.
├── coco_labels.txt
├── data_processing.py
├── dog_bboxes.png
├── dog.jpg
├── onnx_to_tensorrt.py
├── __pycache__
│ ├── data_processing.cpython-35.pyc
│ └── yolov3_to_onnx.cpython-35.pyc
├── README.md
├── requirements.txt
├── yolov3.cfg
├── yolov3.onnx
├── yolov3_to_onnx.py
├── yolov3.trt
└── yolov3.weights
最后我们来看下data_processing.py
import math
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
def load_label_categories(label_file_path):
categories = [line.rstrip(’\n’) for line in open(label_file_path)]
return categories
LABEL_FILE_PATH = ‘coco_labels.txt’
ALL_CATEGORIES = load_label_categories(LABEL_FILE_PATH)
CATEGORY_NUM = len(ALL_CATEGORIES)
assert CATEGORY_NUM == 80
class PreprocessYOLO(object):
“”“装载图像,然后reshape成yolov3-608需要的分辨率.
“””
def __init__(self, yolo_input_resolution):
"""指定yolov3的输入分辨率.
Keyword arguments:
yolo_input_resolution -- two-dimensional tuple with the target network's (spatial)
input resolution in HW order
"""
self.yolo_input_resolution = yolo_input_resolution
def process(self, input_image_path):
"""载入图像,然后进行预处理,如resize,归一化等等
Keyword arguments:
input_image_path -- string path of the image to be loaded
"""
image_raw, image_resized = self._load_and_resize(input_image_path)
image_preprocessed = self._shuffle_and_normalize(image_resized)
return image_raw, image_preprocessed
def _load_and_resize(self, input_image_path):
"""对图像进行resize,然后返回numpy对象
Keyword arguments:
input_image_path -- string path of the image to be loaded
"""
image_raw = Image.open(input_image_path)
new_resolution = (
self.yolo_input_resolution[1],
self.yolo_input_resolution[0])
image_resized = image_raw.resize(
new_resolution, resample=Image.BICUBIC)
image_resized = np.array(image_resized, dtype=np.float32, order='C')
return image_raw, image_resized
def _shuffle_and_normalize(self, image):
"""将图像归一化到[0,1]之间,然后将HWC结构转换成NCHW结构
Keyword arguments:
image -- image as three-dimensional NumPy float array, in HWC format
"""
image /= 255.0
image = np.transpose(image, [2, 0, 1])
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=0)
image = np.array(image, dtype=np.float32, order='C')
return image
class PostprocessYOLO(object):
“”“后处理yolov3-608的三个输出tensor.”""
def __init__(self,
yolo_masks,
yolo_anchors,
obj_threshold,
nms_threshold,
yolo_input_resolution):
"""Initialize with all values that will be kept when processing several frames.
Assuming 3 outputs of the network in the case of (large) YOLOv3.
Keyword arguments:
yolo_masks -- a list of 3 three-dimensional tuples for the YOLO masks
yolo_anchors -- a list of 9 two-dimensional tuples for the YOLO anchors
object_threshold -- threshold for object coverage, float value between 0 and 1
nms_threshold -- threshold for non-max suppression algorithm,
float value between 0 and 1
input_resolution_yolo -- two-dimensional tuple with the target network's (spatial)
input resolution in HW order
"""
self.masks = yolo_masks
self.anchors = yolo_anchors
self.object_threshold = obj_threshold
self.nms_threshold = nms_threshold
self.input_resolution_yolo = yolo_input_resolution
def process(self, outputs, resolution_raw):
"""Take the YOLOv3 outputs generated from a TensorRT forward pass, post-process them
and return a list of bounding boxes for detected object together with their category
and their confidences in separate lists.
Keyword arguments:
outputs -- outputs from a TensorRT engine in NCHW format
resolution_raw -- the original spatial resolution from the input PIL image in WH order
"""
outputs_reshaped = list()
for output in outputs:
outputs_reshaped.append(self._reshape_output(output))
boxes, categories, confidences = self._process_yolo_output(
outputs_reshaped, resolution_raw)
return boxes, categories, confidences
def _reshape_output(self, output):
"""Reshape a TensorRT output from NCHW to NHWC format (with expected C=255),
and then return it in (height,width,3,85) dimensionality after further reshaping.
Keyword argument:
output -- an output from a TensorRT engine after inference
"""
output = np.transpose(output, [0, 2, 3, 1])
_, height, width, _ = output.shape
dim1, dim2 = height, width
dim3 = 3
dim4 = (4 + 1 + CATEGORY_NUM)
return np.reshape(output, (dim1, dim2, dim3, dim4))
def _process_yolo_output(self, outputs_reshaped, resolution_raw):
"""Take in a list of three reshaped YOLO outputs in (height,width,3,85) shape and return
return a list of bounding boxes for detected object together with their category and their
confidences in separate lists.
Keyword arguments:
outputs_reshaped -- list of three reshaped YOLO outputs as NumPy arrays
with shape (height,width,3,85)
resolution_raw -- the original spatial resolution from the input PIL image in WH order
"""
boxes, categories, confidences = list(), list(), list()
for output, mask in zip(outputs_reshaped, self.masks):
box, category, confidence = self._process_feats(output, mask)
box, category, confidence = self._filter_boxes(box, category, confidence)
boxes.append(box)
categories.append(category)
confidences.append(confidence)
boxes = np.concatenate(boxes)
categories = np.concatenate(categories)
confidences = np.concatenate(confidences)
width, height = resolution_raw
image_dims = [width, height, width, height]
boxes = boxes * image_dims
nms_boxes, nms_categories, nscores = list(), list(), list()
for category in set(categories):
idxs = np.where(categories == category)
box = boxes[idxs]
category = categories[idxs]
confidence = confidences[idxs]
keep = self._nms_boxes(box, confidence)
nms_boxes.append(box[keep])
nms_categories.append(category[keep])
nscores.append(confidence[keep])
if not nms_categories and not nscores:
return None, None, None
boxes = np.concatenate(nms_boxes)
categories = np.concatenate(nms_categories)
confidences = np.concatenate(nscores)
return boxes, categories, confidences
def _process_feats(self, output_reshaped, mask):
"""Take in a reshaped YOLO output in height,width,3,85 format together with its
corresponding YOLO mask and return the detected bounding boxes, the confidence,
and the class probability in each cell/pixel.
Keyword arguments:
output_reshaped -- reshaped YOLO output as NumPy arrays with shape (height,width,3,85)
mask -- 2-dimensional tuple with mask specification for this output
"""
def sigmoid(value):
"""Return the sigmoid of the input."""
return 1.0 / (1.0 + math.exp(-value))
def exponential(value):
"""Return the exponential of the input."""
return math.exp(value)
sigmoid_v = np.vectorize(sigmoid)
exponential_v = np.vectorize(exponential)
grid_h, grid_w, _, _ = output_reshaped.shape
anchors = [self.anchors[i] for i in mask]
anchors_tensor = np.reshape(anchors, [1, 1, len(anchors), 2])
box_xy = sigmoid_v(output_reshaped[..., :2])
box_wh = exponential_v(output_reshaped[..., 2:4]) * anchors_tensor
box_confidence = sigmoid_v(output_reshaped[..., 4])
box_confidence = np.expand_dims(box_confidence, axis=-1)
box_class_probs = sigmoid_v(output_reshaped[..., 5:])
col = np.tile(np.arange(0, grid_w), grid_w).reshape(-1, grid_w)
row = np.tile(np.arange(0, grid_h).reshape(-1, 1), grid_h)
col = col.reshape(grid_h, grid_w, 1, 1).repeat(3, axis=-2)
row = row.reshape(grid_h, grid_w, 1, 1).repeat(3, axis=-2)
grid = np.concatenate((col, row), axis=-1)
box_xy += grid
box_xy /= (grid_w, grid_h)
box_wh /= self.input_resolution_yolo
box_xy -= (box_wh / 2.)
boxes = np.concatenate((box_xy, box_wh), axis=-1)
return boxes, box_confidence, box_class_probs
def _filter_boxes(self, boxes, box_confidences, box_class_probs):
"""Take in the unfiltered bounding box descriptors and discard each cell
whose score is lower than the object threshold set during class initialization.
Keyword arguments:
boxes -- bounding box coordinates with shape (height,width,3,4); 4 for
x,y,height,width coordinates of the boxes
box_confidences -- bounding box confidences with shape (height,width,3,1); 1 for as
confidence scalar per element
box_class_probs -- class probabilities with shape (height,width,3,CATEGORY_NUM)
"""
box_scores = box_confidences * box_class_probs
box_classes = np.argmax(box_scores, axis=-1)
box_class_scores = np.max(box_scores, axis=-1)
pos = np.where(box_class_scores >= self.object_threshold)
boxes = boxes[pos]
classes = box_classes[pos]
scores = box_class_scores[pos]
return boxes, classes, scores
def _nms_boxes(self, boxes, box_confidences):
"""Apply the Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) algorithm on the bounding boxes with their
confidence scores and return an array with the indexes of the bounding boxes we want to
keep (and display later).
Keyword arguments:
boxes -- a NumPy array containing N bounding-box coordinates that survived filtering,
with shape (N,4); 4 for x,y,height,width coordinates of the boxes
box_confidences -- a Numpy array containing the corresponding confidences with shape N
"""
x_coord = boxes[:, 0]
y_coord = boxes[:, 1]
width = boxes[:, 2]
height = boxes[:, 3]
areas = width * height
ordered = box_confidences.argsort()[::-1]
keep = list()
while ordered.size > 0:
i = ordered[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x_coord[i], x_coord[ordered[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y_coord[i], y_coord[ordered[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x_coord[i] + width[i], x_coord[ordered[1:]] + width[ordered[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y_coord[i] + height[i], y_coord[ordered[1:]] + height[ordered[1:]])
width1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
height1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
intersection = width1 * height1
union = (areas[i] + areas[ordered[1:]] - intersection)
iou = intersection / union
indexes = np.where(iou <= self.nms_threshold)[0]
ordered = ordered[indexes + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep

